Abstract
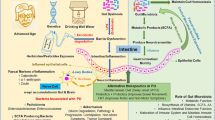
Alterations in the composition of the intestinal flora are associated with the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease (PD). More importantly, the possible cause-effect links between gut flora and PD pathogenesis have been identified using PD animal models. Recent studies have found that probiotics improve the symptoms associated with constipation in PD patients. In addition, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) was recently shown to provide a protective effect against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)–induced neurotoxicity in mice. Effective microbial therapy for PD includes probiotics and FMT. Therefore, microbial therapy may be a useful and novel approach for treatment of PD. In this review, I discuss the use of microbial treatment in PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Disease GBD, Injury I, Prevalence C (2016) Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388(10053):1545–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6
Knudsen K, Haase AM, Fedorova TD, Bekker AC, Ostergaard K, Krogh K, Borghammer P (2017) Gastrointestinal transit time in Parkinson’s disease using a magnetic tracking system. J Parkinsons Dis 7(3):471–479. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-171131
Sveinbjornsdottir S (2016) The clinical symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 139 Suppl 1:318–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13691
Abbott RD, Petrovitch H, White LR, Masaki KH, Tanner CM, Curb JD, Grandinetti A, Blanchette PL, Popper JS, Ross GW (2001) Frequency of bowel movements and the future risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 57(3):456–462
Georgescu D, Ancusa OE, Georgescu LA, Ionita I, Reisz D (2016) Nonmotor gastrointestinal disorders in older patients with Parkinson’s disease: is there hope? Clin Interv Aging 11:1601–1608. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S106284
Cassani E, Privitera G, Pezzoli G, Pusani C, Madio C, Iorio L, Barichella M (2011) Use of probiotics for the treatment of constipation in Parkinson’s disease patients. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 57(2):117–121
Barichella M, Pacchetti C, Bolliri C, Cassani E, Iorio L, Pusani C, Pinelli G, Privitera G, Cesari I, Faierman SA, Caccialanza R, Pezzoli G, Cereda E (2016) Probiotics and prebiotic fiber for constipation associated with Parkinson disease: an RCT. Neurology 87(12):1274–1280. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003127
Carlucci C, Petrof EO, Allen-Vercoe E (2016) Fecal microbiota-based therapeutics for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, ulcerative colitis and obesity. EBioMedicine 13:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.09.029
Sun MF, Zhu YL, Zhou ZL, Jia XB, Xu YD, Yang Q, Cui C, Shen YQ (2018) Neuroprotective effects of fecal microbiota transplantation on MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease mice: gut microbiota, glial reaction and TLR4/TNF-alpha signaling pathway. Brain Behav Immun 70:48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2018.02.005
Tamtaji OR, Taghizadeh M, Daneshvar Kakhaki R, Kouchaki E, Bahmani F, Borzabadi S, Oryan S, Mafi A, Asemi Z (2018) Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic administration in people with Parkinson’s disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.05.018
Cersosimo MG, Benarroch EE (2008) Neural control of the gastrointestinal tract: implications for Parkinson disease. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society 23(8):1065–1075. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22051
Svensson E, Henderson VW, Borghammer P, Horvath-Puho E, Sorensen HT (2016) Constipation and risk of Parkinson’s disease: a Danish population-based cohort study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 28:18–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.05.016
Gao X, Chen H, Schwarzschild MA, Ascherio A (2011) A prospective study of bowel movement frequency and risk of Parkinson’s disease. Am J Epidemiol 174(5):546–551. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwr119
Yu QJ, Yu SY, Zuo LJ, Lian TH, Hu Y, Wang RD, Piao YS, Guo P, Liu L, Jin Z, Li LX, Chan P, Chen SD, Wang XM, Zhang W (2018) Parkinson disease with constipation: clinical features and relevant factors. Sci Rep 8(1):567. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16790-8
Chen H, O'Reilly E, McCullough ML, Rodriguez C, Schwarzschild MA, Calle EE, Thun MJ, Ascherio A (2007) Consumption of dairy products and risk of Parkinson’s disease. Am J Epidemiol 165(9):998–1006. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwk089
Hughes KC, Gao X, Kim IY, Wang M, Weisskopf MG, Schwarzschild MA, Ascherio A (2017) Intake of dairy foods and risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 89(1):46–52. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004057
Knudsen K, Krogh K, Ostergaard K, Borghammer P (2017) Constipation in Parkinson’s disease: subjective symptoms, objective markers, and new perspectives. Mov Disord 32(1):94–105. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26866
Waller PA, Gopal PK, Leyer GJ, Ouwehand AC, Reifer C, Stewart ME, Miller LE (2011) Dose-response effect of Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 on whole gut transit time and functional gastrointestinal symptoms in adults. Scand J Gastroenterol 46(9):1057–1064. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2011.584895
Bar F, Von Koschitzky H, Roblick U, Bruch HP, Schulze L, Sonnenborn U, Bottner M, Wedel T (2009) Cell-free supernatants of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 modulate human colonic motility: evidence from an in vitro organ bath study. Neurogastroenterol Motil 21 (5):559–566, e516-557. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2008.01258.x
Mertsalmi TH, Aho VTE, Pereira PAB, Paulin L, Pekkonen E, Auvinen P, Scheperjans F (2017) More than constipation - bowel symptoms in Parkinson’s disease and their connection to gut microbiota. Eur J Neurol 24(11):1375–1383. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13398
Minato T, Maeda T, Fujisawa Y, Tsuji H, Nomoto K, Ohno K, Hirayama M (2017) Progression of Parkinson’s disease is associated with gut dysbiosis: two-year follow-up study. PLoS One 12(11):e0187307. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187307
Vandeputte D, Falony G, Vieira-Silva S, Tito RY, Joossens M, Raes J (2016) Stool consistency is strongly associated with gut microbiota richness and composition, enterotypes and bacterial growth rates. Gut 65(1):57–62. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309618
Dimidi E, Christodoulides S, Scott SM, Whelan K (2017) Mechanisms of action of probiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota on gut motility and constipation. Adv Nutr 8(3):484–494. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.116.014407
Gilbert JA, Blaser MJ, Caporaso JG, Jansson JK, Lynch SV, Knight R (2018) Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nat Med 24(4):392–400. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4517
Krygowska-Wajs A, Cheshire WP Jr, Wszolek ZK, Hubalewska-Dydejczyk A, Jasinska-Myga B, Farrer MJ, Moskala M, Sowa-Staszczak A (2009) Evaluation of gastric emptying in familial and sporadic Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15(9):692–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2009.04.003
Hardoff R, Sula M, Tamir A, Soil A, Front A, Badarna S, Honigman S, Giladi N (2001) Gastric emptying time and gastric motility in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 16(6):1041–1047
Djaldetti R, Baron J, Ziv I, Melamed E (1996) Gastric emptying in Parkinson’s disease: patients with and without response fluctuations. Neurology 46(4):1051–1054
Doi H, Sakakibara R, Sato M, Masaka T, Kishi M, Tateno A, Tateno F, Tsuyusaki Y, Takahashi O (2012) Plasma levodopa peak delay and impaired gastric emptying in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 319(1–2):86–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2012.05.010
Indrio F, Riezzo G, Raimondi F, Bisceglia M, Filannino A, Cavallo L, Francavilla R (2011) Lactobacillus reuteri accelerates gastric emptying and improves regurgitation in infants. Eur J Clin Investig 41(4):417–422. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2010.02425.x
Pierantozzi M, Pietroiusti A, Sancesario G, Lunardi G, Fedele E, Giacomini P, Frasca S, Galante A, Marciani MG, Stanzione P (2001) Reduced L-dopa absorption and increased clinical fluctuations in Helicobacter pylori-infected Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurol Sci 22(1):89–91
Hashim H, Azmin S, Razlan H, Yahya NW, Tan HJ, Manaf MR, Ibrahim NM (2014) Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection improves levodopa action, clinical symptoms and quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 9(11):e112330. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112330
Pierantozzi M, Pietroiusti A, Brusa L, Galati S, Stefani A, Lunardi G, Fedele E, Sancesario G, Bernardi G, Bergamaschi A, Magrini A, Stanzione P, Galante A (2006) Helicobacter pylori eradication and L-dopa absorption in patients with PD and motor fluctuations. Neurology 66(12):1824–1829. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000221672.01272.ba
Chenoll E, Casinos B, Bataller E, Astals P, Echevarria J, Iglesias JR, Balbarie P, Ramon D, Genoves S (2011) Novel probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum CECT 7366 strain active against the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(4):1335–1343. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01820-10
Ojetti V, Bruno G, Ainora ME, Gigante G, Rizzo G, Roccarina D, Gasbarrini A (2012) Impact of Lactobacillus reuteri supplementation on anti-Helicobacter pylori levofloxacin-based second-line therapy. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2012:740381:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/740381
Augustin AD, Charlett A, Weller C, Dobbs SM, Taylor D, Bjarnason I, Dobbs RJ (2016) Quantifying rigidity of Parkinson’s disease in relation to laxative treatment: a service evaluation. Br J Clin Pharmacol 82(2):441–450. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12967
Pfeiffer HC, Lokkegaard A, Zoetmulder M, Friberg L, Werdelin L (2014) Cognitive impairment in early-stage non-demented Parkinson’s disease patients. Acta Neurol Scand 129(5):307–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12189
Garcia-Ptacek S, Kramberger MG (2016) Parkinson disease and dementia. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 29(5):261–270. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891988716654985
Kobayashi Y, Sugahara H, Shimada K, Mitsuyama E, Kuhara T, Yasuoka A, Kondo T, Abe K, Xiao JZ (2017) Therapeutic potential of Bifidobacterium breve strain A1 for preventing cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 7(1):13510. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13368-2
Akbari E, Asemi Z, Daneshvar Kakhaki R, Bahmani F, Kouchaki E, Tamtaji OR, Hamidi GA, Salami M (2016) Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function and metabolic status in Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized, double-blind and controlled trial. Front Aging Neurosci 8:256. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2016.00256
Bonfili L, Cecarini V, Berardi S, Scarpona S, Suchodolski JS, Nasuti C, Fiorini D, Boarelli MC, Rossi G, Eleuteri AM (2017) Microbiota modulation counteracts Alzheimer’s disease progression influencing neuronal proteolysis and gut hormones plasma levels. Sci Rep 7(1):2426. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02587-2
Bonfili L, Cecarini V, Cuccioloni M, Angeletti M, Berardi S, Scarpona S, Rossi G, Eleuteri AM (2018) SLAB51 probiotic formulation activates SIRT1 pathway promoting antioxidant and neuroprotective effects in an AD mouse model. Mol Neurobiol 55:7987–8000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0973-4
Aarsland D, Bronnick K, Ehrt U, De Deyn PP, Tekin S, Emre M, Cummings JL (2007) Neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease and dementia: frequency, profile and associated care giver stress. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(1):36–42. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2005.083113
Liu WH, Chuang HL, Huang YT, Wu CC, Chou GT, Wang S, Tsai YC (2016) Alteration of behavior and monoamine levels attributable to Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 in germ-free mice. Behav Brain Res 298(Pt B):202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.10.046
Pinto-Sanchez MI, Hall GB, Ghajar K, Nardelli A, Bolino C, Lau JT, Martin FP, Cominetti O, Welsh C, Rieder A, Traynor J, Gregory C, De Palma G, Pigrau M, Ford AC, Macri J, Berger B, Bergonzelli G, Surette MG, Collins SM, Moayyedi P, Bercik P (2017) Probiotic Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 reduces depression scores and alters brain activity: a pilot study in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 153(2):448–459. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.003
Kazemi A, Noorbala AA, Azam K, Eskandari MH, Djafarian K (2018) Effect of probiotic and prebiotic vs placebo on psychological outcomes in patients with major depressive disorder: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.04.010
Brochard V, Combadiere B, Prigent A, Laouar Y, Perrin A, Beray-Berthat V, Bonduelle O, Alvarez-Fischer D, Callebert J, Launay JM, Duyckaerts C, Flavell RA, Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Infiltration of CD4+ lymphocytes into the brain contributes to neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. J Clin Invest 119(1):182–192. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI36470
Harms AS, Thome AD, Yan Z, Schonhoff AM, Williams GP, Li X, Liu Y, Qin H, Benveniste EN, Standaert DG (2018) Peripheral monocyte entry is required for alpha-synuclein induced inflammation and neurodegeneration in a model of Parkinson disease. Exp Neurol 300:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.11.010
Takata K, Kinoshita M, Okuno T, Moriya M, Kohda T, Honorat JA, Sugimoto T, Kumanogoh A, Kayama H, Takeda K, Sakoda S, Nakatsuji Y (2011) The lactic acid bacterium Pediococcus acidilactici suppresses autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inducing IL-10-producing regulatory T cells. PLoS One 6(11):e27644. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027644
Salehipour Z, Haghmorad D, Sankian M, Rastin M, Nosratabadi R, Soltan Dallal MM, Tabasi N, Khazaee M, Nasiraii LR, Mahmoudi M (2017) Bifidobacterium animalis in combination with human origin of Lactobacillus plantarum ameliorate neuroinflammation in experimental model of multiple sclerosis by altering CD4+ T cell subset balance. Biomed Pharmacother 95:1535–1548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.117
Kwon HK, Kim GC, Kim Y, Hwang W, Jash A, Sahoo A, Kim JE, Nam JH, Im SH (2013) Amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by probiotic mixture is mediated by a shift in T helper cell immune response. Clin Immunol 146(3):217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2013.01.001
Tankou SK, Regev K, Healy BC, Tjon E, Laghi L, Cox LM, Kivisakk P, Pierre IV, Lokhande H, Gandhi R, Cook S, Glanz B, Stankiewicz J, Weiner HL (2018) A probiotic modulates the microbiome and immunity in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 83:1147–1161. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25244
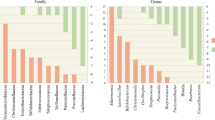
Scheperjans F, Aho V, Pereira PA, Koskinen K, Paulin L, Pekkonen E, Haapaniemi E, Kaakkola S, Eerola-Rautio J, Pohja M, Kinnunen E, Murros K, Auvinen P (2015) Gut microbiota are related to Parkinson’s disease and clinical phenotype. Mov Disord 30(3):350–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26069
Yang X, Qian Y, Xu S, Song Y, Xiao Q (2017) Longitudinal analysis of fecal microbiome and pathologic processes in a rotenone induced mice model of Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 9:441. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00441
Li W, Wu X, Hu X, Wang T, Liang S, Duan Y, Jin F, Qin B (2017) Structural changes of gut microbiota in Parkinson’s disease and its correlation with clinical features. Sci China Life Sci 60(11):1223–1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-9001-4
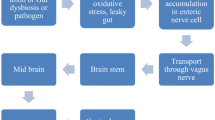
Sampson TR, Debelius JW, Thron T, Janssen S, Shastri GG, Ilhan ZE, Challis C, Schretter CE, Rocha S, Gradinaru V, Chesselet MF, Keshavarzian A, Shannon KM, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Wittung-Stafshede P, Knight R, Mazmanian SK (2016) Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 167(6):1469–1480 e1412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.018
Erny D, Hrabe de Angelis AL, Jaitin D, Wieghofer P, Staszewski O, David E, Keren-Shaul H, Mahlakoiv T, Jakobshagen K, Buch T, Schwierzeck V, Utermohlen O, Chun E, Garrett WS, McCoy KD, Diefenbach A, Staeheli P, Stecher B, Amit I, Prinz M (2015) Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat Neurosci 18(7):965–977. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4030
Hemarajata P, Versalovic J (2013) Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota: mechanisms of intestinal immunomodulation and neuromodulation. Ther Adv Gastroenterol 6(1):39–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756283X12459294
Kim HK, Rutten NB, Besseling-van der Vaart I, Niers LE, Choi YH, Rijkers GT, van Hemert S (2015) Probiotic supplementation influences faecal short chain fatty acids in infants at high risk for eczema. Benefic Microbes 6(6):783–790. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2015.0056
Hemalatha R, Ouwehand AC, Saarinen MT, Prasad UV, Swetha K, Bhaskar V (2017) Effect of probiotic supplementation on total lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and short chain fatty acids in 2-5-year-old children. Microb Ecol Health Dis 28(1):1298340. https://doi.org/10.1080/16512235.2017.1298340
Choi JG, Kim N, Ju IG, Eo H, Lim SM, Jang SE, Kim DH, Oh MS (2018) Oral administration of Proteus mirabilis damages dopaminergic neurons and motor functions in mice. Sci Rep 8(1):1275. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19646-x
Calabrese V, Santoro A, Monti D, Crupi R, Di Paola R, Latteri S, Cuzzocrea S, Zappia M, Giordano J, Calabrese EJ, Franceschi C (2018) Aging and Parkinson’s disease: inflammaging, neuroinflammation and biological remodeling as key factors in pathogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med 115:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.10.379
Forsyth CB, Shannon KM, Kordower JH, Voigt RM, Shaikh M, Jaglin JA, Estes JD, Dodiya HB, Keshavarzian A (2011) Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 6(12):e28032. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028032
Castano A, Herrera AJ, Cano J, Machado A (1998) Lipopolysaccharide intranigral injection induces inflammatory reaction and damage in nigrostriatal dopaminergic system. J Neurochem 70(4):1584–1592
Rodes L, Khan A, Paul A, Coussa-Charley M, Marinescu D, Tomaro-Duchesneau C, Shao W, Kahouli I, Prakash S (2013) Effect of probiotics Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium on gut-derived lipopolysaccharides and inflammatory cytokines: an in vitro study using a human colonic microbiota model. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(4):518–526
Musa NH, Mani V, Lim SM, Vidyadaran S, Abdul Majeed AB, Ramasamy K (2017) Lactobacilli-fermented cow’s milk attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and memory impairment in vitro and in vivo. J Dairy Res 84(4):488–495. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022029917000620
Subramaniam SR, Chesselet MF (2013) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 106-107:17–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.04.004
Chunchai T, Thunapong W, Yasom S, Wanchai K, Eaimworawuthikul S, Metzler G, Lungkaphin A, Pongchaidecha A, Sirilun S, Chaiyasut C, Pratchayasakul W, Thiennimitr P, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2018) Decreased microglial activation through gut-brain axis by prebiotics, probiotics, or synbiotics effectively restored cognitive function in obese-insulin resistant rats. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1055-2
Zhang F, Cui B, He X, Nie Y, Wu K, Fan D, Group FM-sS (2018) Microbiota transplantation: concept, methodology and strategy for its modernization. Protein & cell. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-018-0541-8
Rothschild D, Weissbrod O, Barkan E, Kurilshikov A, Korem T, Zeevi D, Costea PI, Godneva A, Kalka IN, Bar N, Shilo S, Lador D, Vila AV, Zmora N, Pevsner-Fischer M, Israeli D, Kosower N, Malka G, Wolf BC, Avnit-Sagi T, Lotan-Pompan M, Weinberger A, Halpern Z, Carmi S, Fu J, Wijmenga C, Zhernakova A, Elinav E, Segal E (2018) Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 555(7695):210–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25973
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Varma Y, Fischbach MA, Biddinger SB, Dutton RJ, Turnbaugh PJ (2014) Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 505(7484):559–563. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12820
Ericsson AC, Gagliardi J, Bouhan D, Spollen WG, Givan SA, Franklin CL (2018) The influence of caging, bedding, and diet on the composition of the microbiota in different regions of the mouse gut. Sci Rep 8(1):4065. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21986-7
Tian H, Ge X, Nie Y, Yang L, Ding C, McFarland LV, Zhang X, Chen Q, Gong J, Li N (2017) Fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with slow-transit constipation: a randomized, clinical trial. PLoS One 12(2):e0171308. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171308
Tian H, Ding C, Gong J, Ge X, McFarland LV, Gu L, Wei Y, Chen Q, Zhu W, Li J, Li N (2016) Treatment of slow transit constipation with fecal microbiota transplantation: a pilot study. J Clin Gastroenterol 50(10):865–870. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0000000000000472
Ge X, Tian H, Ding C, Gu L, Wei Y, Gong J, Zhu W, Li N, Li J (2016) Fecal microbiota transplantation in combination with soluble dietary fiber for treatment of slow transit constipation: a pilot study. Arch Med Res 47(3):236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2016.06.005
Zhang X, Tian H, Gu L, Nie Y, Ding C, Ge X, Yang B, Gong J, Li N (2018) Long-term follow-up of the effects of fecal microbiota transplantation in combination with soluble dietary fiber as a therapeutic regimen in slow transit constipation. Sci China Life Sci 61:779–786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-017-9229-1
Ge X, Zhao W, Ding C, Tian H, Xu L, Wang H, Ni L, Jiang J, Gong J, Zhu W, Zhu M, Li N (2017) Potential role of fecal microbiota from patients with slow transit constipation in the regulation of gastrointestinal motility. Sci Rep 7(1):441. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00612-y
Cao H, Liu X, An Y, Zhou G, Liu Y, Xu M, Dong W, Wang S, Yan F, Jiang K, Wang B (2017) Dysbiosis contributes to chronic constipation development via regulation of serotonin transporter in the intestine. Sci Rep 7(1):10322. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10835-8
Pamer EG (2014) Fecal microbiota transplantation: effectiveness, complexities, and lingering concerns. Mucosal Immunol 7(2):210–214. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2013.117
Ma Y, Liu J, Rhodes C, Nie Y, Zhang F (2017) Ethical issues in fecal microbiota transplantation in practice. Am J Bioeth 17(5):34–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/15265161.2017.1299240
Ma Y, Chen H, Lan C, Ren J (2018) Help, hope and hype: ethical considerations of human microbiome research and applications. Protein Cell 9:404–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-018-0537-4
Acknowledgments
I particularly appreciate the support of Ying Liu.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81660203) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20142BAB205092 and 20181BAB205030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not applicable to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, X. Microbial treatment: the potential application for Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci 40, 51–58 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3641-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3641-6