Abstract
Background
Creatinine clearance (Ccr) overestimates glomerular filtration rate (GFR) due to the tubular secretion of creatinine. It is known that fractional excretion of creatinine (FE-Cr) increases with decreasing GFR. Association of serum albumin level with the tubular secretion of creatinine was also reported previously. Alteration of FE-Cr may affect the performance of GFR estimating equations based on serum creatinine. Therefore, we analyzed the factors influencing FE-Cr and compared the performance of GFR equations in subjects stratified by serum albumin levels.
Methods
Seven hundred and fifty-seven Japanese subjects were included. GFR was measured by inulin renal clearance. GFR and Ccr were measured simultaneously. FE-Cr was calculated as the ratio of Ccr to GFR. Multivariate analysis was performed to evaluate the factors influencing FE-Cr. Age, gender, GFR, body mass index (BMI), body weight, height and serum albumin level were analyzed as the parameters. Estimated GFR was calculated by Japanese GFR equations based on serum creatinine (Eq-cr), serum cystatin C (Eq-cys) and 5 variables including serum albumin (Eq-5var).
Results
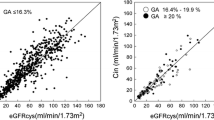
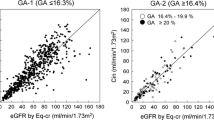
FE-Cr in subjects with serum albumin <3.0, 3.0–3.9 and ≥4.0 g/dl were 1.63 ± 0.48, 1.53 ± 0.55, and 1.40 ± 0.36, respectively. FE-Cr in subjects with serum albumin <3.0 or 3.0–3.9 g/dl were significantly higher than the value in subjects with serum albumin ≥4.0 g/dl. Multivariate analysis showed that GFR (p < 0.0001) and serum albumin level (p = 0.004) were independent parameters affecting FE-Cr. Biases of Eq-cr, Eq-cys and Eq-5var in subjects with serum albumin <3.0 g/dl were −9.5 ± 17.5, −0.7 ± 17.1 and −0.6 ± 14.8 ml/min/1.73 m2, respectively. Eq-cr significantly overestimated GFR compared with Eq-cys or Eq-5var. Biases in subjects with serum albumin ≥4.0 g/dl were 6.4 ± 18.8, 2.0 ± 18.1 and 3.0 ± 18.3 ml/min/1.73 m2, respectively. Eq-cr significantly underestimated GFR compared with Eq-cys or Eq-5var.
Conclusion
GFR and serum albumin level were independent parameters affecting FE-Cr. Alteration of FE-Cr according to the serum albumin levels may be one of the reasons of the bias of GFR equation based on serum creatinine.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walser M. Assessing renal function from creatinine measurements in adults with chronic renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998;32:23–31.
Branten AJ, Vervoort G, Wetzels JF. Serum creatinine is a poor marker of GFR in nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2005;20:707–11.
Sinkeler SJ, Visser FW, Krikken JA, Stegeman CA, Homan van der Heide JJ, Navis G. Higher body mass index is associated with higher fractional creatinine excretion in healthy subjects. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2011;26:3181–8.
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, et al. Revised equations for estimating glomerular filtration rate (GFR) from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:982–92.
Horio M, Imai E, Yasuda Y, Watanabe T, Matsuo S. GFR estimation using standardized serum cystatin C in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;61:197–203.
Eisner C, Faulhaber-Walter R, Wang Y, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PS, Mizel D, et al. Major contribution of tubular secretion to creatinine clearance in mice. Kidney Int. 2010;77:519–26.
Ciarimboli G, Lancaster CS, Schlatter E, Franke RM, Sprowl JA, Pavenstädt H, et al. Proximal tubular secretion of creatinine by organic cation transporter OCT2 in cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:1101–8.
Urakami Y, Kimura N, Okuda M, Inui K. Creatinine transport by basolateral organic cation transporter hOCT2 in the human kidney. Pharm Res. 2004;21:976–81.
Baumgartner RN, Koehler KM, Romero L, Garry PJ. Serum albumin is associated with skeletal muscle in elderly men and women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996;64:552–8.
Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Greene T, Li L, Beck GJ, Joffe MM, et al. Factors other than glomerular filtration rate affect serum cystatin C levels. Kidney Int. 2009;75:652–60.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the grant from the Japanese Society of Nephrology and Health and Labor Sciences Research Grant from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan.
Conflict of interest
All the authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Horio, M., Imai, E., Yasuda, Y. et al. Lower serum albumin level is associated with higher fractional excretion of creatinine. Clin Exp Nephrol 18, 469–474 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-013-0841-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-013-0841-5