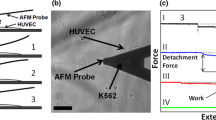
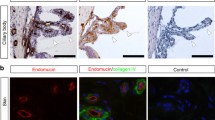
Abstract
The endothelial cell (EC) surface is coated with a layer of polysaccharides linked to membrane-bound and trans-membrane proteoglycans that comprise the glycocalyx, which is augmented by adsorbed proteins derived from the blood stream. This surface layer has been shown to affect hemodynamics in small blood vessels of the microcirculation, the resistance to flow, and leukocyte (WBC) to EC adhesion. Parallel studies of WBC–EC adhesion in response to chemoattractants and cytokines, and shedding of constituents of the glycocalyx, have suggested a role for activation of extracellular proteases in mediating the dynamics of WBC adhesion in response to inflammatory and ischemic stimuli. Likely candidates among the many proteases present are the matrix metalloproteases (MMPs). Inhibition of MMP activation with sub-antimicrobial doses of doxycycline, or zinc chelators, has also inhibited WBC adhesion and shedding of glycans from the EC surface in response to the chemoattractant fMLP. Taken together, these studies suggest that shedding of the EC glycocalyx exposes adhesion receptors and thus enhances WBC–EC adhesion. Future therapeutic strategies for treating pathologies such as the low flow state and inflammation may benefit by further exploration of the mechanics of the glycocalyx in light of protease activation and shear-dependent effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson, R. H., and G. Clough. Plasma proteins modify the endothelial cell glycocalyx of frog mesenteric microvessels. J. Physiol. 445:473–486, 1992.
Alon, R., D. A. Hammer, and T. A. Springer. Lifetime of the P-selectin–carbohydrate bond and its response to tensile force in hydrodynamic flow. Nature 374:539–542, 1995.
Arfors, K. E., C. Lundberg, L. Lindbom, K. Lundberg, P. G. Beatty, and J. M. Harlan. A monoclonal antibody to the membrane glycoprotein complex CD18 inhibits polymorphonuclear leukocyte accumulation and plasma leakage in vivo. Blood 69:338–340, 1987.
Arisaka, T., M. Mitsumata, M. Kawasumi, T. Tohjima, S. Hirose, and Y. Yoshida. Effects of shear stress on glycosaminoglycan synthesis in vascular endothelial cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 748:543–554, 1995.
Barabino, G. A., M. O. Platt, and D. K. Kaul. Sickle cell biomechanics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 12:345–367, 2010.
Bennett, H. S., J. H. Luft, and J. C. Hampton. Morphological classifications of vertebrate blood capillaries. Am. J. Physiol. 196:381–390, 1959.
Bruegger, D., M. Jacob, M. Rehm, M. Loetsch, U. Welsch, P. Conzen, and B. F. Becker. Atrial natriuretic peptide induces shedding of endothelial glycocalyx in coronary vascular bed of guinea pig hearts. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 289:H1993–H1999, 2005.
Brule, S., N. Charnaux, A. Sutton, D. Ledoux, T. Chaigneau, L. Saffar, and L. Gattegno. The shedding of syndecan-4 and syndecan-1 from HeLa cells and human primary macrophages is accelerated by SDF-1/CXCL12 and mediated by the matrix metalloproteinase-9. Glycobiology 16:488–501, 2006.
Cabrales, P., B. Y. Vazquez, A. G. Tsai, and M. Intaglietta. Microvascular and capillary perfusion following glycocalyx degradation. J. Appl. Physiol. 102:2251–2259, 2007.
Chappell, D., K. Hofmann-Kiefer, M. Jacob, M. Rehm, J. Briegel, U. Welsch, P. Conzen, and B. F. Becker. TNF-alpha induced shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx is prevented by hydrocortisone and antithrombin. Basic Res. Cardiol. 104:78–89, 2009.
Chappell, D., M. Jacob, O. Paul, M. Rehm, U. Welsch, M. Stoeckelhuber, P. Conzen, and B. F. Becker. The glycocalyx of the human umbilical vein endothelial cell: an impressive structure ex vivo but not in culture. Circ. Res. 104:1313–1317, 2009.
Colburn, P., E. Kobayashi, and V. Buonassisi. Depleted level of heparan sulfate proteoglycan in the extracellular matrix of endothelial cell cultures exposed to endotoxin. J. Cell. Physiol. 159:121–130, 1994.
Constantinescu, A. A., H. Vink, and J. A. Spaan. Elevated capillary tube hematocrit reflects degradation of endothelial cell glycocalyx by oxidized LDL. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 280:H1051–H1057, 2001.
Constantinescu, A. A., H. Vink, and J. A. Spaan. Endothelial cell glycocalyx modulates immobilization of leukocytes at the endothelial surface. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23:1541–1547, 2003.
Danielli, J. F. Capillary permeability and oedema in the perfused frog. J. Physiol. 98:109–129, 1940.
DeLano, F. A., and G. W. Schmid-Schonbein. Proteinase activity and receptor cleavage: mechanism for insulin resistance in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension 52:415–423, 2008.
Desjardins, C., and B. R. Duling. Heparinase treatment suggests a role for the endothelial cell glycocalyx in regulation of capillary hematocrit. Am. J. Physiol. 258:H647–H654, 1990.
Ding, K., M. Lopez-Burks, J. A. Sanchez-Duran, M. Korc, and A. D. Lander. Growth factor-induced shedding of syndecan-1 confers glypican-1 dependence on mitogenic responses of cancer cells. J. Cell Biol. 171:729–738, 2005.
Endo, K., T. Takino, H. Miyamori, H. Kinsen, T. Yoshizaki, M. Furukawa, and H. Sato. Cleavage of syndecan-1 by membrane type matrix metalloproteinase-1 stimulates cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 278:40764–40770, 2003.
Fahraeus, R. The suspension stability of blood. Physiol. Rev. 9:241–274, 1929.
Fitzgerald, M. L., Z. Wang, P. W. Park, G. Murphy, and M. Bernfield. Shedding of syndecan-1 and -4 ectodomains is regulated by multiple signaling pathways and mediated by a TIMP-3-sensitive metalloproteinase. J. Cell Biol. 148:811–824, 2000.
Fux, L., N. Ilan, R. D. Sanderson, and I. Vlodavsky. Heparanase: busy at the cell surface. Trends Biochem. Sci. 34:511–519, 2009.
Gao, L., and H. H. Lipowsky. Composition of the endothelial glycocalyx and its relation to its thickness and diffusion of small solutes. Microvasc. Res. 80:394–401, 2010.
Golub, L. M., H. M. Lee, M. E. Ryan, W. V. Giannobile, J. Payne, and T. Sorsa. Tetracyclines inhibit connective tissue breakdown by multiple non-antimicrobial mechanisms. Adv. Dent. Res. 12:12–26, 1998.
Gotte, M. Syndecans in inflammation. FASEB J. 17:575–591, 2003.
Gouverneur, M., J. A. Spaan, H. Pannekoek, R. D. Fontijn, and H. Vink. Fluid shear stress stimulates incorporation of hyaluronan into endothelial cell glycocalyx. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 290:H458–H462, 2006.
Grimm, J., R. Keller, and P. G. de Groot. Laminar flow induces cell polarity and leads to rearrangement of proteoglycan metabolism in endothelial cells. Thromb. Haemost. 60:437–441, 1988.
Gronski, Jr., T. J., R. L. Martin, D. K. Kobayashi, B. C. Walsh, M. C. Holman, M. Huber, H. E. Van Wart, and S. D. Shapiro. Hydrolysis of a broad spectrum of extracellular matrix proteins by human macrophage elastase. J. Biol. Chem. 272:12189–12194, 1997.
Haas, T. L., M. Milkiewicz, S. J. Davis, A. L. Zhou, S. Egginton, M. D. Brown, J. A. Madri, and O. Hudlicka. Matrix metalloproteinase activity is required for activity-induced angiogenesis in rat skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 279:1540–1547, 2000.
Hafezi-Moghadam, A., K. L. Thomas, A. J. Prorock, Y. Huo, and K. Ley. l-Selectin shedding regulates leukocyte recruitment. J. Exp. Med. 193:863–872, 2001.
Haldenby, K. A., D. C. Chappell, C. P. Winlove, K. H. Parker, and J. A. Firth. Focal and regional variations in the composition of the glycocalyx of large vessel endothelium. J. Vasc. Res. 31:2–9, 1994.
Hayward, R., R. Scalia, B. Hopper, J. Z. Appel, III, and A. M. Lefer. Cellular mechanisms of heparinase III protection in rat traumatic shock. Am. J. Physiol. 275:H23–H30, 1998.
Henry, C. B., and B. R. Duling. TNF-alpha increases entry of macromolecules into luminal endothelial cell glycocalyx. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 279:H2815–H2823, 2000.
Hofmann-Kiefer, K. F., G. I. Kemming, D. Chappell, M. Flondor, H. Kisch-Wedel, A. Hauser, S. Pallivathukal, P. Conzen, and M. Rehm. Serum heparan sulfate levels are elevated in endotoxemia. Eur. J. Med. Res. 14:526–531, 2009.
Hoover, R. L., R. Folger, W. A. Haering, B. R. Ware, and M. J. Karnovsky. Adhesion of leukocytes to endothelium: roles of divalent cations, surface charge, chemotactic agents and substrate. J. Cell Sci. 45:73–86, 1980.
House, S. D., and H. H. Lipowsky. Leukocyte–endothelium adhesion: microhemodynamics in mesentery of the cat. Microvasc. Res. 34:363–379, 1987.
House, S. D., and H. H. Lipowsky. Microvascular hematocrit and red cell flux in rat cremaster muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 252:H211–H222, 1987.
Huxley, V. H., and F. E. Curry. Differential actions of albumin and plasma on capillary solute permeability. Am. J. Physiol. 260:H1645–H1654, 1991.
Ihrcke, N. S., and J. L. Platt. Shedding of heparan sulfate proteoglycan by stimulated endothelial cells: evidence for proteolysis of cell-surface molecules. J. Cell. Physiol. 168:625–637, 1996.
Ihrcke, N. S., L. E. Wrenshall, B. J. Lindman, and J. L. Platt. Role of heparan sulfate in immune system–blood vessel interactions. Immunol. Today 14:500–505, 1993.
Iigo, Y., M. Suematsu, T. Higashida, J. Oheda, K. Matsumoto, Y. Wakabayashi, Y. Ishimura, M. Miyasaka, and T. Takashi. Constitutive expression of ICAM-1 in rat microvascular systems analyzed by laser confocal microscopy. Am. J. Physiol. 273:H138–H147, 1997.
Jung, U., K. E. Norman, K. Scharffetter-Kochanek, A. L. Beaudet, and K. Ley. Transit time of leukocytes rolling through venules controls cytokine-induced inflammatory cell recruitment in vivo. J. Clin. Invest. 102:1526–1533, 1998.
Kinashi, T., and K. Katagiri. Regulation of lymphocyte adhesion and migration by the small GTPase Rap1 and its effector molecule, RAPL. Immunol. Lett. 93:1–5, 2004.
Klitzman, B., and B. R. Duling. Microvascular hematocrit and red cell flow in resting and contracting striated muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 237:H481–H490, 1979.
Laudanna, C., J. Y. Kim, G. Constantin, and E. Butcher. Rapid leukocyte integrin activation by chemokines. Immunol. Rev. 186:37–46, 2002.
Laurent, T. C., and J. R. Fraser. Hyaluronan. FASEB J. 6:2397–2404, 1992.
Lawrence, M. B., L. V. McIntire, and S. G. Eskin. Effect of flow on polymorphonuclear leukocyte/endothelial cell adhesion. Blood 70:1284–1290, 1987.
Lawrence, M. B., and T. A. Springer. Leukocytes roll on a selectin at physiologic flow rates: distinction from and prerequisite for adhesion through integrins. Cell 65:859–873, 1991.
Lawrence, M. B., and T. A. Springer. Neutrophils roll on E-selectin. J. Immunol. 151:6338–6346, 1993.
Ley, K., D. C. Bullard, M. L. Arbones, R. Bosse, D. Vestweber, T. F. Tedder, and A. L. Beaudet. Sequential contribution of L- and P-selectin to leukocyte rolling in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 181:669–675, 1995.
Li, Z., L. Li, H. R. Zielke, L. Cheng, R. Xiao, M. T. Crow, W. G. Stetler-Stevenson, J. Froehlich, and E. G. Lakatta. Increased expression of 72-kd type IV collagenase (MMP-2) in human aortic atherosclerotic lesions. Am. J. Pathol. 148:121–128, 1996.
Li, Q., P. W. Park, C. L. Wilson, and W. C. Parks. Matrilysin shedding of syndecan-1 regulates chemokine mobilization and transepithelial efflux of neutrophils in acute lung injury. Cell 111:635–646, 2002.
Lipowsky, H. H., R. Sah, and A. Lescanic. Relative roles of doxycycline and cation chelation in endothelial glycan shedding and adhesion of leukocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 300:H415–H422, 2011.
Luft, J. H. Fine structures of capillary and endocapillary layer as revealed by ruthenium red. Fed. Proc. 25:1773–1783, 1966.
Luo, B. H., C. V. Carman, and T. A. Springer. Structural basis of integrin regulation and signaling. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25:619–647, 2007.
Mulivor, A. W., and H. H. Lipowsky. Role of glycocalyx in leukocyte–endothelial cell adhesion. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 283:H1282–H1291, 2002.
Mulivor, A. W., and H. H. Lipowsky. Inflammation- and ischemia-induced shedding of venular glycocalyx. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 286:H1672–H1680, 2004.
Mulivor, A. W., and H. H. Lipowsky. Inhibition of glycan shedding and leukocyte–endothelial adhesion in postcapillary venules by suppression of matrixmetalloprotease activity with doxycycline. Microcirculation 16:657–666, 2009.
Park, P. W., O. Reizes, and M. Bernfield. Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans: selective regulators of ligand–receptor encounters. J. Biol. Chem. 275:29923–29926, 2000.
Platt, J. L., A. P. Dalmasso, B. J. Lindman, N. S. Ihrcke, and F. H. Bach. The role of C5a and antibody in the release of heparan sulfate from endothelial cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 21:2887–2890, 1991.
Platt, J. L., G. M. Vercellotti, B. J. Lindman, T. R. Oegema, Jr., F. H. Bach, and A. P. Dalmasso. Release of heparan sulfate from endothelial cells. Implications for pathogenesis of hyperacute rejection. J. Exp. Med. 171:1363–1368, 1990.
Platts, S. H., and B. R. Duling. Adenosine A3 receptor activation modulates the capillary endothelial glycocalyx. Circ. Res. 94:77–82, 2004.
Platts, S. H., J. Linden, and B. R. Duling. Rapid modification of the glycocalyx caused by ischemia-reperfusion is inhibited by adenosine A2A receptor activation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 284:H2360–H2367, 2003.
Poiseuille, J. L. M. Recherches sur les causes du mouvement du sang dans les vaisseaux capillaries. C. R. Acad. Sci. 6:554–560, 1835.
Potter, D. R., and E. R. Damiano. The hydrodynamically relevant endothelial cell glycocalyx observed in vivo is absent in vitro. Circ. Res. 102:770–776, 2008.
Pries, A. R., T. W. Secomb, and P. Gaehtgens. The endothelial surface layer. Pflugers Arch. 440:653–666, 2000.
Pries, A. R., T. W. Secomb, P. Gaehtgens, and J. F. Gross. Blood flow in microvascular networks. Experiments and simulation. Circ. Res. 67:826–834, 1990.
Pries, A. R., T. W. Secomb, H. Jacobs, M. Sperandio, K. Osterloh, and P. Gaehtgens. Microvascular blood flow resistance: role of endothelial surface layer. Am. J. Physiol. 273:H2272–H2279, 1997.
Purushothaman, A., T. Uyama, F. Kobayashi, S. Yamada, K. Sugahara, A. C. Rapraeger, and R. D. Sanderson. Heparanase-enhanced shedding of syndecan-1 by myeloma cells promotes endothelial invasion and angiogenesis. Blood 115:2449–2457, 2010.
Rapraeger, A. Transforming growth factor (type beta) promotes the addition of chondroitin sulfate chains to the cell surface proteoglycan (syndecan) of mouse mammary epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 109:2509–2518, 1989.
Rehm, M., D. Bruegger, F. Christ, P. Conzen, M. Thiel, M. Jacob, D. Chappell, M. Stoeckelhuber, U. Welsch, B. Reichart, K. Peter, and B. F. Becker. Shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx in patients undergoing major vascular surgery with global and regional ischemia. Circulation 116:1896–1906, 2007.
Reitsma, S., D. W. Slaaf, H. Vink, M. A. van Zandvoort, and M. G. oude Egbrink. The endothelial glycocalyx: composition, functions, and visualization. Pflugers Arch. 454:345–359, 2007.
Smith, M. L., D. S. Long, E. R. Damiano, and K. Ley. Near-wall micro-PIV reveals a hydrodynamically relevant endothelial surface layer in venules in vivo. Biophys. J. 85:637–645, 2003.
Spinale, F. G. Myocardial matrix remodeling and the matrix metalloproteinases: influence on cardiac form and function. Physiol. Rev. 87:1285–1342, 2007.
Springer, T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature 346:425–434, 1990.
Squire, J. M., M. Chew, G. Nneji, C. Neal, J. Barry, and C. Michel. Quasi-periodic substructure in the microvessel endothelial glycocalyx: a possible explanation for molecular filtering? J. Struct. Biol. 136:239–255, 2001.
Subramanian, S. V., M. L. Fitzgerald, and M. Bernfield. Regulated shedding of syndecan-1 and -4 ectodomains by thrombin and growth factor receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 272:14713–14720, 1997.
Sutera, S. P., V. Seshadri, P. A. Croce, and R. M. Hochmuth. Capillary blood flow. II. Deformable model cells in tube flow. Microvasc. Res. 2:420–433, 1970.
Svennevig, K., T. Hoel, A. Thiara, S. Kolset, A. Castelheim, T. Mollnes, F. Brosstad, E. Fosse, and J. Svennevig. Syndecan-1 plasma levels during coronary artery bypass surgery with and without cardiopulmonary bypass. Perfusion 23:165–171, 2008.
Taraboletti, G., S. D’Ascenzo, P. Borsotti, R. Giavazzi, A. Pavan, and V. Dolo. Shedding of the matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2, MMP-9, and MT1-MMP as membrane vesicle-associated components by endothelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 160:673–680, 2002.
Vink, H., and B. R. Duling. Identification of distinct luminal domains for macromolecules, erythrocytes, and leukocytes within mammalian capillaries. Circ. Res. 79:581–589, 1996.
Vogl-Willis, C. A., and I. J. Edwards. High-glucose-induced structural changes in the heparan sulfate proteoglycan, perlecan, of cultured human aortic endothelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1672:36–45, 2004.
Weinbaum, S., J. M. Tarbell, and E. R. Damiano. The structure and function of the endothelial glycocalyx layer. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 9:121–167, 2007.
Xu, J., D. Qu, N. L. Esmon, and C. T. Esmon. Metalloproteolytic release of endothelial cell protein C receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 275:6038–6044, 2000.
Yaras, N., M. Sariahmetoglu, A. Bilginoglu, A. Aydemir-Koksoy, A. Onay-Besikci, B. Turan, and R. Schulz. Protective action of doxycycline against diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 155:1174–1184, 2008.
Yu, W. H., and J. F. Woessner, Jr. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans as extracellular docking molecules for matrilysin (matrix metalloproteinase 7). J. Biol. Chem. 275:4183–4191, 2000.
Zarbock, A., and K. Ley. Neutrophil adhesion and activation under flow. Microcirculation 16:31–42, 2009.
Zcharia, E., J. Jia, X. Zhang, L. Baraz, U. Lindahl, T. Peretz, I. Vlodavsky, and J. P. Li. Newly generated heparanase knock-out mice unravel co-regulation of heparanase and matrix metalloproteinases. PLoS One 4:e5181, 2009.
Zuurbier, C. J., C. Demirci, A. Koeman, H. Vink, and C. Ince. Short-term hyperglycemia increases endothelial glycocalyx permeability and acutely decreases lineal density of capillaries with flowing red blood cells. J. Appl. Physiol. 99:1471–1476, 2005.
Zweifach, B. W. Structural makeup of capillary wall. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 61:670–677, 1955.
Acknowledgment
This research was supported in part by NIH R01-HL39286-20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Konstantinos Konstantopoulos oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lipowsky, H.H. The Endothelial Glycocalyx as a Barrier to Leukocyte Adhesion and Its Mediation by Extracellular Proteases. Ann Biomed Eng 40, 840–848 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0427-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0427-x