Abstract
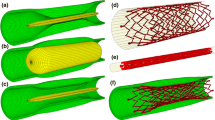
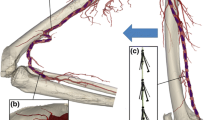
Nitinol stent oversizing is frequently performed in peripheral arteries to ensure a desirable lumen gain. However, the clinical effect of mis-sizing remains controversial. The goal of this study was to provide a better understanding of the structural and hemodynamic effects of Nitinol stent oversizing. Five patient-specific numerical models of non-calcified popliteal arteries were developed to simulate the deployment of Nitinol stents with oversizing ratios ranging from 1.1 to 1.8. In addition to arterial biomechanics, computational fluid dynamics methods were adopted to simulate the physiological blood flow inside the stented arteries. Results showed that stent oversizing led to a limited increase in the acute lumen gain, albeit at the cost of a significant increase in arterial wall stresses. Furthermore, localized areas affected by low Wall Shear Stress increased with higher oversizing ratios. Stents were also negatively impacted by the procedure as their fatigue safety factors gradually decreased with oversizing. These adverse effects to both the artery walls and stents may create circumstances for restenosis. Although the ideal oversizing ratio is stent-specific, this study showed that Nitinol stent oversizing has a very small impact on the immediate lumen gain, which contradicts the clinical motivations of the procedure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cha, S.-H., M. H. Han, Y. H. Choi, C. J. Yoon, S. K. Baik, S. J. Kim, and K. H. Chang. Vascular responses in normal canine carotid arteries. Invest. Radiol. 38:95–101, 2003.
Chatzizisis, Y. S., A. U. Coskun, M. Jonas, E. R. Edelman, C. L. Feldman, and P. H. Stone. Role of endothelial shear stress in the natural history of coronary atherosclerosis and vascular remodeling. molecular, cellular, and vascular behavior. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 49:2379–2393, 2007.
Chen, H. Y., A. K. Sinha, J. S. Choy, H. Zheng, M. Sturek, B. Bigelow, D. L. Bhatt, and G. S. Kassab. Mis-sizing of stent promotes intimal hyperplasia: impact of endothelial shear and intramural stress. AJP Heart Circ. Physiol. 301:H2254–H2263, 2011.
Chiastra, C., S. Morlacchi, D. Gallo, U. Morbiducci, R. Cárdenes, I. Larrabide, and F. Migliavacca. Computational fluid dynamic simulations of image-based stented coronary bifurcation models. J. R. Soc. Interface 10:20130193, 2013.
Conway, C., J. P. McGarry, and P. E. McHugh. Modelling of atherosclerotic plaque for use in a computational test-bed for stent angioplasty. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 42:2425–2439, 2014.
Early, M., C. Lally, P. J. Prendergast, and D. J. Kelly. Stresses in peripheral arteries following stent placement: a finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 12:25–33, 2009.
Elsheikh, A., C. Whitford, R. Hamarashid, W. Kassem, A. Joda, and P. Büchler. Stress free configuration of the human eye. Med. Eng. Phys. 35:211–216, 2013.
Gasser, T. C., R. W. Ogden, and G. A. Holzapfel. Hyperelastic modelling of arterial layers with distributed collagen fibre orientations. J. R. Soc. Interface 3:15–35, 2006.
Gökgöl, C., N. Diehm, and P. Büchler. Quantification of deformation of the femoro-popliteal arterial tract during leg flexion in subjects with peripheral arterial disease. J. Endovasc. Ther. 20:825–835, 2013.
Gornik, H. L., and J. A. Beckman. Cardiology patient page. Peripheral arterial disease. Circulation 111:e169–e172, 2005.
Hoffmann, R., G. S. Mintz, J. J. Popma, L. F. Satler, A. D. Pichard, K. M. Kent, C. Walsh, P. Mackell, and M. B. Leon. Chronic arterial responses to stent implantation: a serial intravascular ultrasound analysis of Palmaz–Schatz stents in native coronary arteries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 28:1134–1139, 1996.
Holzapfel, G. A. Mechanics of Angioplasty: wall, balloon and stent. In: Mechanics in Biology, AMD-Vol. 242/BED-Vol. 46, edited by J. Casey, and G. Bao. New York: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2000, pp. 141–156.
Holzapfel, G. A., G. Sommer, and P. Regitnig. Anisotropic mechanical properties of tissue components in human atherosclerotic plaques. J. Biomech. Eng. 126:657–665, 2004.
Huo, Y., T. Wischgoll, and G. S. Kassab. Flow patterns in three-dimensional porcine epicardial coronary arterial tree. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 293:H2959–H2970, 2007.
Katritsis, D. G., A. Theodorakakos, I. Pantos, M. Gavaises, N. Karcanias, and E. P. Efstathopoulos. Flow patterns at stented coronary bifurcations: computational fluid dynamics analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 5:530–539, 2012.
Kirsch, E. C., M. S. Khangure, P. Morling, T. J. York, and W. McAuliffe. Oversizing of self-expanding stents : influence on the development of neointimal hyperplasia of the carotid artery in a canine model. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 23:121–127, 2002.
Kröger, K., F. Santosa, and M. Goyen. Biomechanical incompatibility of popliteal stent placement. J. Endovasc. Ther. 11:686–694, 2004.
LaDisa, J. F., L. E. Olson, I. Guler, D. A. Hettrick, J. R. Kersten, D. C. Warltier, and P. S. Pagel. Circumferential vascular deformation after stent implantation alters wall shear stress evaluated with time-dependent 3D computational fluid dynamics models. J. Appl. Physiol. 98:947–957, 2005.
Milnor, W. R. Hemodynamics. Baltimore: Willliams & Wilkins, 1989.
Mortier, P., G. A. Holzapfel, M. De Beule, D. Van Loo, Y. Taeymans, P. Segers, P. Verdonck, and B. Verhegghe. A novel simulation strategy for stent insertion and deployment in curved coronary bifurcations: comparison of three drug-eluting stents. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:88–99, 2010.
Pelton, A. R., V. Schroeder, M. R. Mitchell, X.-Y. Gong, M. Barney, and S. W. Robertson. Fatigue and durability of Nitinol stents. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 1:153–164, 2008.
Piamsomboon, C., G. S. Roubin, M. W. Liu, S. S. Iyer, A. Mathur, L. S. Dean, C. R. Gomez, J. J. Vitek, N. Chattipakorn, and G. Yates. Relationship between oversizing of self-expanding stents and late loss index in carotid stenting. Cathet. Cardiovasc. Diagn. 143:139–143, 1998.
Poon, E. K. W., P. Barlis, S. Moore, W.-H. Pan, Y. Liu, Y. Ye, Y. Xue, S. J. Zhu, and A. S. H. Ooi. Numerical investigations of the haemodynamic changes associated with stent malapposition in an idealised coronary artery. J. Biomech. 47:2843–2851, 2014.
Rebelo, N., R. Fu, and M. Lawrenchuk. Study of a nitinol stent deployed into anatomically accurate artery geometry and subjected to realistic service loading. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 18:655–663, 2009.
Rikhtegar, F., J. A. Knight, U. Olgac, S. C. Saur, D. Poulikakos, W. Marshall, P. C. Cattin, H. Alkadhi, and V. Kurtcuoglu. Choosing the optimal wall shear parameter for the prediction of plaque location-A patient-specific computational study in human left coronary arteries. Atherosclerosis 221:432–437, 2012.
Rikhtegar, F., F. Pacheco, C. Wyss, K. S. Stok, H. Ge, R. J. Choo, A. Ferrari, D. Poulikakos, R. Müller, and V. Kurtcuoglu. Compound ex vivo and in silico method for hemodynamic analysis of stented arteries. PLoS ONE 8:e58147, 2013.
Safar, M. E., P. Priollet, F. Luizy, J.-J. Mourad, P. Cacoub, H. Levesque, J. Benelbaz, P. Michon, M. Herrmann, and J. Blacher. Peripheral arterial disease and isolated systolic hypertension: the ATTEST study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 23:182–187, 2009.
Saguner, A. M., T. Traupe, L. Räber, N. Hess, Y. Banz, A. R. Saguner, N. Diehm, and O. M. Hess. Oversizing and restenosis with self-expanding stents in iliofemoral arteries. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 35:906–913, 2012.
Scheinert, D., S. Scheinert, J. Sax, C. Piorkowski, S. Bräunlich, M. Ulrich, G. Biamino, and A. Schmidt. Prevalence and clinical impact of stent fractures after femoropopliteal stenting. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 45:312–315, 2005.
Schillinger, M., S. Sabeti, P. Dick, J. Amighi, W. Mlekusch, O. Schlager, C. Loewe, M. Cejna, J. Lammer, and E. Minar. Sustained benefit at 2 years of primary femoropopliteal stenting compared with balloon angioplasty with optional stenting. Circulation 115:2745–2749, 2007.
Schillinger, M., S. Sabeti, C. Loewe, P. Dick, J. Amighi, W. Mlekusch, O. Schlager, M. Cejna, J. Lammer, and E. Minar. Balloon angioplasty versus implantation of nitinol stents in the superficial femoral artery. N. Engl. J. Med. 354:1879–1888, 2006.
Schulze-bauer, C. A. J., P. Regitnig, and G. A. Holzapfel. Mechanics of the human femoral adventitia including the high-pressure response. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 282:2427–2440, 2002.
Seo, T., L. G. Schachter, and A. I. Barakat. Computational study of fluid mechanical disturbance induced by endovascular stents. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33:444–456, 2005.
Stiegler, H., and R. Brandl. Importance of ultrasound for diagnosing periphereal arterial disease. Ultraschall Med. 30:334–374, 2009.
Tai, N. R., A. Giudiceandrea, H. J. Salacinski, A. M. Seifalian, and G. Hamilton. In vivo femoropopliteal arterial wall compliance in subjects with and without lower limb vascular disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 30:936–945, 1999.
Thompson, R. B., and E. R. Mcveigh. Real-time volumetric flow measurements with complex-difference MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 50:1248–1255, 2008.
Timmins, L. H., C. A. Meyer, M. R. Moreno, and J. E. Moore. Effects of stent design and atherosclerotic plaque composition on arterial wall biomechanics. J. Endovasc. Ther. 15:643–654, 2008.
Timmins, L. H., M. W. Miller, F. J. Clubb, and J. E. Moore. Increased artery wall stress post-stenting leads to greater intimal thickening. Lab. Invest. 91:955–967, 2011.
Wu, W., W.-Q. Wang, D.-Z. Yang, and M. Qi. Stent expansion in curved vessel and their interactions: a finite element analysis. J. Biomech. 40:2580–2585, 2007.
Zhao, S., L. Gu, and S. R. Froemming. Finite element analysis of the implantation of a self-expanding stent: impact of lesion calcification. J. Med. Device. 6:021001, 2012.
Zhao, H. Q., A. Nikanorov, R. Virmani, R. Jones, E. Pacheco, and L. B. Schwartz. Late stent expansion and neointimal proliferation of oversized Nitinol stents in peripheral arteries. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 32:720–726, 2009.
Acknowledgments
This investigation was supported by the Research Council of the Kantonsspital Aarau, the Swiss Heart Foundation, the Gotthard Schettler Foundation and the Swiss National Science Foundation. The authors have no commercial, proprietary, or financial interest in any products or companies described in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Estefanía Peña oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gökgöl, C., Diehm, N., Nezami, F.R. et al. Nitinol Stent Oversizing in Patients Undergoing Popliteal Artery Revascularization: A Finite Element Study. Ann Biomed Eng 43, 2868–2880 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1358-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1358-8