Abstract
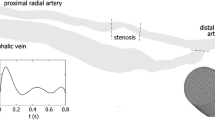
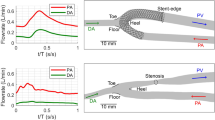
Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is the first choice for providing vascular access for hemodialysis patients, but maintaining its patency is challenging. AVF failure is primarily due to development of neointimal hyperplasia (NH) and subsequent stenosis. Using idealized models of AVF we previously suggested that reciprocating hemodynamic wall shear is implicated in vessel stenosis. The aim of the present study was to investigate local hemodynamics in patient-specific side-to-end AVF. We reconstructed realistic geometrical models of four AVFs from magnetic resonance images acquired in a previous clinical study. High-resolution computational fluid dynamics simulations using patient-specific blood rheology and flow boundary conditions were performed. We then characterized the flow field and categorized disturbed flow areas by means of established hemodynamic wall parameters. In all AVF, either in upper or lower arm location, we consistently observed transitional laminar to turbulent-like flow developing in the juxta-anastomotic vein and damping towards the venous outflow, but not in the proximal artery. High-frequency fluctuations of the velocity vectors in these areas result in eddies that induce similar oscillations of wall shear stress vector. This condition may importantly impair the physiological response of endothelial cells to blood flow and be responsible for NH formation in newly created AVF.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Jaishi, A. A., M. J. Oliver, S. M. Thomas, C. E. Lok, J. C. Zhang, A. X. Garg, S. D. Kosa, R. R. Quinn, and L. M. Moist. Patency rates of the arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 63:464–478, 2014.
Antiga, L., M. Piccinelli, L. Botti, B. Ene-Iordache, A. Remuzzi, and D. A. Steinman. An image-based modeling framework for patient-specific computational hemodynamics. Med Biol Eng Comput 46:1097–1112, 2008.
Badero, O. J., M. O. Salifu, H. Wasse, and J. Work. Frequency of swing-segment stenosis in referred dialysis patients with angiographically documented lesions. Am J Kidney Dis 51:93–98, 2008.
Bennett, S., M. S. Hammes, T. Blicharski, S. Watson, and B. Funaki. Characterization of the cephalic arch and location of stenosis. J Vasc Access 16:13–18, 2015.
Bode, A., A. Caroli, W. Huberts, N. Planken, L. Antiga, M. Bosboom, A. Remuzzi, and J. Tordoir. Clinical study protocol for the ARCH project—computational modeling for improvement of outcome after vascular access creation. J Vasc Access 12:369–376, 2011.
Bode, A. S., R. N. Planken, M. A. Merkx, F. M. van der Sande, L. Geerts, J. H. Tordoir, and T. Leiner. Feasibility of non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography for imaging upper extremity vasculature prior to vascular access creation. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 43:88–94, 2012.
Browne, L. D., M. T. Walsh, and P. Griffin. Experimental and numerical analysis of the bulk flow parameters within an arteriovenous fistula. Cardiovasc Eng Technol 6:450–462, 2015.
Caroli, A., S. Manini, L. Antiga, K. Passera, B. Ene-Iordache, S. Rota, G. Remuzzi, A. Bode, J. Leermakers, F. N. van de Vosse, R. Vanholder, M. Malovrh, J. Tordoir, and A. Remuzzi. Validation of a patient-specific hemodynamic computational model for surgical planning of vascular access in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 84:1237–1245, 2013.
Celik, I. B., U. Ghia, P. J. Roache, C. J. Freitas, H. Coleman, and P. E. Raad. Procedure for estimation and reporting of uncertainty due to discretization in CFD applications. J Fluids Eng 130:1–4, 2008.
Chiu, J. J., and S. Chien. Effects of disturbed flow on vascular endothelium: pathophysiological basis and clinical perspectives. Physiol Rev 91:327–387, 2011.
Davies, P. F. Hemodynamic shear stress and the endothelium in cardiovascular pathophysiology. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 6:16–26, 2009.
Davies, P. F., A. Remuzzi, E. J. Gordon, C. F. Dewey, Jr, and M. A. Gimbrone, Jr. Turbulent fluid shear stress induces vascular endothelial cell turnover in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2114–2117, 1986.
Decorato, I., Z. Kharboutly, T. Vassallo, J. Penrose, C. Legallais, and A. V. Salsac. Numerical simulation of the fluid structure interactions in a compliant patient-specific arteriovenous fistula. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 30:143–159, 2014.
Ene-Iordache, B., L. Mosconi, L. Antiga, S. Bruno, A. Anghileri, G. Remuzzi, and A. Remuzzi. Radial artery remodeling in response to shear stress increase within arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis access. Endothelium 10:95–102, 2003.
Ene-Iordache, B., and A. Remuzzi. Disturbed flow in radial-cephalic arteriovenous fistulae for haemodialysis: low and oscillating shear stress locates the sites of stenosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:358–368, 2012.
Ene-Iordache, B., C. Semperboni, G. Dubini, and A. Remuzzi. Disturbed flow in a patient-specific arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis: multidirectional and reciprocating near-wall flow patterns. J Biomech 48:2195–2200, 2015.
Fan, L., and T. Karino. Effect of a disturbed flow on proliferation of the cells of a hybrid vascular graft. Biorheology 47:31–38, 2010.
Fillinger, M. F., E. R. Reinitz, R. A. Schwartz, D. E. Resetarits, A. M. Paskanik, and C. E. Bredenberg. Beneficial effects of banding on venous intimal-medial hyperplasia in arteriovenous loop grafts. Am J Surg 158:87–94, 1989.
Gallo, D., D. A. Steinman, P. B. Bijari, and U. Morbiducci. Helical flow in carotid bifurcation as surrogate marker of exposure to disturbed shear. J Biomech 45:2398–2404, 2012.
Gimbrone, Jr., M. A., and G. Garcia-Cardena. Vascular endothelium, hemodynamics, and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Pathol 22:9–15, 2013.
He, X., and D. N. Ku. Pulsatile flow in the human left coronary artery bifurcation: average conditions. J Biomech Eng 118:74–82, 1996.
He, Y., C. M. Terry, C. Nguyen, S. A. Berceli, Y. T. Shiu, and A. K. Cheung. Serial analysis of lumen geometry and hemodynamics in human arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis using magnetic resonance imaging and computational fluid dynamics. J Biomech 46:165–169, 2013.
Himburg, H. A., and M. H. Friedman. Correspondence of low mean shear and high harmonic content in the porcine iliac arteries. J Biomech Eng 128:852–856, 2006.
Jha, V., G. Garcia-Garcia, K. Iseki, Z. Li, S. Naicker, B. Plattner, R. Saran, A. Y. Wang, and C. W. Yang. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 382:260–272, 2013.
Jia, L., L. Wang, F. Wei, H. Yu, H. Dong, B. Wang, Z. Lu, G. Sun, H. Chen, J. Meng, B. Li, R. Zhang, X. Bi, Z. Wang, H. Pang, and A. Jiang. Effects of wall shear stress in venous neointimal hyperplasia of arteriovenous fistulae. Nephrology (Carlton) 20:335–342, 2015.
Khan, M. O., K. Valen-Sendstad, and D. A. Steinman. Narrowing the expertise gap for predicting intracranial aneurysm hemodynamics: impact of solver numerics versus mesh and time-step resolution. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 36:1310–1316, 2015.
Lee, T., V. Chauhan, M. Krishnamoorthy, Y. Wang, L. Arend, M. J. Mistry, M. El-Khatib, R. Banerjee, R. Munda, and P. Roy-Chaudhury. Severe venous neointimal hyperplasia prior to dialysis access surgery. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:2264–2270, 2011.
Lee, S. W., D. S. Smith, F. Loth, P. F. Fischer, and H. S. Bassiouny. Importance of flow division on transition to turbulence within an arteriovenous graft. J Biomech 40:981–992, 2007.
Leschziner, M. Statistical turbulence modelling for fluid dynamics—demystified: an introductory text for graduate engineering students. London: Imperial College Press, 2015.
Lorensen, W. E., and H. E. Cline. Marching cubes: a high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. Computer Graphics 21:163–169, 1987.
Loth, F., P. F. Fischer, N. Arslan, C. D. Bertram, S. E. Lee, T. J. Royston, W. E. Shaalan, and H. S. Bassiouny. Transitional flow at the venous anastomosis of an arteriovenous graft: potential activation of the ERK1/2 mechanotransduction pathway. J Biomech Eng 125:49–61, 2003.
Malek, A. M., S. L. Alper, and S. Izumo. Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis. JAMA 282:2035–2042, 1999.
Marie, Y., A. Guy, K. Tullett, H. Krishnan, R. G. Jones, and N. G. Inston. Patterns of blood flow as a predictor of maturation of arteriovenous fistula for haemodialysis. J Vasc Access 15:169–174, 2014.
McGah, P. M., D. F. Leotta, K. W. Beach, and A. Aliseda. Effects of wall distensibility in hemodynamic simulations of an arteriovenous fistula. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 13:679–695, 2014.
McGah, P. M., D. F. Leotta, K. W. Beach, R. Eugene Zierler, and A. Aliseda. Incomplete restoration of homeostatic shear stress within arteriovenous fistulae. J Biomech Eng 135:011005, 2013.
Mitra, A. K., D. M. Gangahar, and D. K. Agrawal. Cellular, molecular and immunological mechanisms in the pathophysiology of vein graft intimal hyperplasia. Immunol Cell Biol 84:115–124, 2006.
Moffatt, H. K., and A. Tsinober. Helicity in laminar and turbulent flow. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 24:281–312, 1992.
Mohamied, Y., E. M. Rowland, E. L. Bailey, S. J. Sherwin, M. A. Schwartz, and P. D. Weinberg. Change of direction in the biomechanics of atherosclerosis. Ann Biomed Eng 43:16–25, 2015.
Morbiducci, U., R. Ponzini, D. Gallo, C. Bignardi, and G. Rizzo. Inflow boundary conditions for image-based computational hemodynamics: impact of idealized versus measured velocity profiles in the human aorta. J Biomech 46:102–109, 2013.
Morbiducci, U., R. Ponzini, M. Grigioni, and A. Redaelli. Helical flow as fluid dynamic signature for atherogenesis risk in aortocoronary bypass. A numeric study. J Biomech 40:519–534, 2007.
NKF, KDOQI. Clinical practice guidelines for vascular access. Am J Kidney Dis 48:S248–S273, 2006.
Noris, M., M. Morigi, R. Donadelli, S. Aiello, M. Foppolo, M. Todeschini, S. Orisio, G. Remuzzi, and A. Remuzzi. Nitric oxide synthesis by cultured endothelial cells is modulated by flow conditions. Circ Res 76:536–543, 1995.
OpenFoam. The OpenFOAM Foundation. http://www.openfoam.org, 2014.
Peiffer, V., S. J. Sherwin, and P. D. Weinberg. Computation in the rabbit aorta of a new metric—the transverse wall shear stress—to quantify the multidirectional character of disturbed blood flow. J Biomech 46:2651–2658, 2013.
Potter, C. M., M. H. Lundberg, L. S. Harrington, C. M. Warboys, T. D. Warner, R. E. Berson, A. V. Moshkov, J. Gorelik, P. D. Weinberg, and J. A. Mitchell. Role of shear stress in endothelial cell morphology and expression of cyclooxygenase isoforms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:384–391, 2011.
Remuzzi, A., and B. Ene-Iordache. Novel paradigms for dialysis vascular access: upstream hemodynamics and vascular remodeling in dialysis access stenosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:2186–2193, 2013.
Remuzzi, A., B. Ene-Iordache, L. Mosconi, S. Bruno, A. Anghileri, L. Antiga, and G. Remuzzi. Radial artery wall shear stress evaluation in patients with arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis access. Biorheology 40:423–430, 2003.
Roy-Chaudhury, P., Y. Wang, M. Krishnamoorthy, J. Zhang, R. Banerjee, R. Munda, S. Heffelfinger, and L. Arend. Cellular phenotypes in human stenotic lesions from haemodialysis vascular access. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:2786–2791, 2009.
Sethian, J. A. Level set methods and marching cubes methods: evolving interfaces in computational geometry, fluid mechanics, computer vision and materials science, Vol. 3. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1999.
Sigovan, M., V. Rayz, W. Gasper, H. F. Alley, C. D. Owens, and D. Saloner. Vascular remodeling in autogenous arterio-venous fistulas by MRI and CFD. Ann Biomed Eng 41:657–668, 2013.
Valen-Sendstad, K., M. Piccinelli, and D. A. Steinman. High-resolution computational fluid dynamics detects flow instabilities in the carotid siphon: implications for aneurysm initiation and rupture? J Biomech 47:3210–3216, 2014.
Van Canneyt, K., U. Morbiducci, S. Eloot, G. De Santis, P. Segers, and P. Verdonck. A computational exploration of helical arterio-venous graft designs. J Biomech 46:345–353, 2013.
Wang, C., B. M. Baker, C. S. Chen, and M. A. Schwartz. Endothelial cell sensing of flow direction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33:2130–2136, 2013.
Yamamoto, K., C. D. Protack, G. Kuwahara, M. Tsuneki, T. Hashimoto, M. R. Hall, R. Assi, K. E. Brownson, T. R. Foster, H. Bai, M. Wang, J. A. Madri, and A. Dardik. Disturbed shear stress reduces Klf2 expression in arterial-venous fistulae in vivo. Physiol Rep 3:e12348, 2015.
Yang, N., S. Deutsch, E. G. Paterson, and K. B. Manning. Numerical study of blood flow at the end-to-side anastomosis of a left ventricular assist device for adult patients. J Biomech Eng 131:111005, 2009.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Gabriele Dubini from Politecnico di Milano for helpful discussion. We acknowledge the ARCH Consortium colleagues for gaining the CE-MRA data during the clinical study (ARCH Project No. FP7-ICT-224390). Part of this study was presented at the 41st Annual ESAO Congress in Rome, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Ender Finol oversaw the review of this article.
Michela Bozzetto and Bogdan Ene-Iordache contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bozzetto, M., Ene-Iordache, B. & Remuzzi, A. Transitional Flow in the Venous Side of Patient-Specific Arteriovenous Fistulae for Hemodialysis. Ann Biomed Eng 44, 2388–2401 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1525-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1525-y