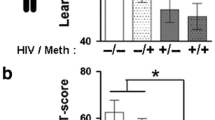
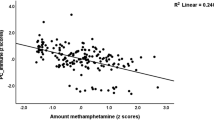
Methamphetamine (MA) dependence and HIV infection are independently associated with cerebral dysfunction, especially within frontal-basal ganglia circuits. Recent evidence indicates that MA dependence has an additive effect on neuropsychological (NP) deficits associated with HIV infection. This study extends prior findings by examining the combined effects of MA dependence (MA+) and immunosuppression (i.e., CD4 lymphocyte count <200) on NP functioning in 284 HIV+ individuals. Prevalence of NP impairment was examined in four demographically comparable groups: (1) MA+/CD4 < 200; (2) MA+/CD4 ≥ 200; (3) MA−/CD4 < 200; and (4) MA−/CD4 ≥ 200. Results revealed that both MA dependence and immunosuppression were significant predictors of NP impairment. More importantly, additive effects were evident whereby the MA+/CD4 < 200 group exhibited the highest rate of NP impairment. Findings indicate that MA dependence conveys an additive deleterious impact on NP status in immunosuppressed persons with HIV infection, perhaps reflecting the combined effects of neuropathophysiological mechanisms in fronto-striatal circuits.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, D.C.: Author.
Ammassari, A., Trotta, M. P., Murri, R., Castelli, F., Narciso, P., Noto, P., Vecchiet, J., D'Arminio Monforte, A., Wu, A. W., Antinori, A., and The AdICoNA Study Group. (2002). Correlates and predictors of adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy: Overview of published literature. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 31, S123–S127.
Basso, M. R., and Bornstein, R. A. (2000). Effects of immunosuppression and disease severity upon neuropsychological function in HIV infection. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 22, 104–114.
Beck, A. T. (1987). The Beck Depression Inventory. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
Chang, L., Ernst, T., Witt, M. D., Ames, N., Gaiefsky, M., and Miller, E. (2002). Relationships among brain metabolites, cognitive function, and viral loads in antiretroviral-naïve HIV patients. NeuroImage, 17, 1638–1648.
Cherner, M., Masliah, E., Ellis, R. J., Marcotte, T. D., Moore, D. J., Grant, I., Heaton, R. K., and The HNRC Group. (2002). Neurocognitive dysfunction during life predicts postmortem findings of HIV encephalitis. Neurology, 59, 1563–1567.
De Ronchi, D., Faranca, I., Berardi, D., Scudellari, P., Borderi, M., Manfredi, R., and Fratiglioni, L. (2002). Risk factors for cognitive impairment in HIV-1-infected persons with different risk behaviors. Archives of Neurology, 59, 812–818.
Ellis, R. J., Childers, M. E., Cherner, M., Lazzaretto, D., Letendre, S., Grant, I., and The HNRC Group (2003). Increased human immunodeficiency virus loads in active methamphetamine users are explained by reduced effectiveness of antiretroviral therapy. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 188, 1820–1826.
Fals-Stewart, W. (1993). Neurocognitive defects and their impact on substance abuse treatment. Journal of Addictions and Offender Counseling, 13, 46–57.
First, M. B., Spitzer, R. L., Gibbon, M., and Williams, J. B. (1996). Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders. New York: Biometrics Research Department.
Grant, I., Atkinson, J. H., Hesselink, J. R., Kennedy, C. J., Richman, D. D., Spector, S. A., and McCutchan, J. A. (1987). Evidence for early central nervous system involvement in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and other human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections. Annals of Internal Medicine, 107, 828–836.
Heaton, R. K., Kirson, D., Velin, R. A., Grant, I., and The HNRC Group. (1994). The utility of clinical ratings for detecting cognitive change in HIV infection. In I. Grant and A. Martin (Eds.), Neuropsychology of HIV infection (pp. 188–206). New York: Oxford University Press.
Heaton, R. K., Grant, I., Butters, N., White, D. A., Kirson, D., Atkinson, J. H., McCutchan, J. A., Taylor, M. J., Kelly, M. D., Ellis, R. J., Wolfson, T., Velin, R., Marcotte, T. D., Hesselink, J. R., Jernigan, T. L., Chandler, J., Wallace, M., Abramson, I., and The HNRC Group. (1995). The HNRC 500—Neuropsychology of HIV infection at different disease stages. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 1, 231–251.
Langford, D., Adame, A., Grigorian, A., Grant, I., McCutchan, J. A., Ellis, R. J., Marcotte, T. D., Masliah, E., and The HNRC Group (2003). Selective damage of calbindin immunoreactive neurons in methamphetamine-user HIVE patients. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 15, 467–474.
Loughlin, A., Metsch, L., Gardner, L., Anderson-Mahoney, P., Barrigan, M., and Strathdee, S. (2004). Provider barriers to prescribing HAART to medically-eligible HIV-infected drug users. AIDS Care, 16, 485–500.
Martín-García, J., Kolson, D. L., and González-Scarano, F. (2002). Chemokine receptors in the brain: Their role in HIV infection and pathogenesis. AIDS, 16, 1709–1730.
McArthur, J. C., Hoover, D. R., Bacellar, M. A., Miller, E. N., Cohen, B. A., Becker, J. T., Graham, N. M. H., McArthur, J. H., Selnes, O. A., Jacobsen, L. P., Visscher, B. R., Concha, M., Saah, A., and The Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. (1993). Dementia in AIDS patients: Incidence and risk factors. Neurology, 43, 2245–2252.
Nath, A., Hauser, K. F., Wojna, V., Booze, R. M., Maragos, W., Prendergast, M., Cass, W., and Turchan, J. T. (2002). Molecular basis for interactions of HIV and drugs of abuse. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 31, S62–S69.
Nordahl, T. E., Salo, R., and Leamon, M. (2003). Neuropsychological effects of chronic methamphetamine use on neurotransmitters and cognition: A review. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 15, 317–325.
Reger, M., Welsh, R., Razani, J., Martin, D. J., and Boone, K. B. (2002). A meta-analysis of the neuropsychological sequelae of HIV infection. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 8, 410–424.
Rippeth, J. D., Heaton, R. K., Carey, C. L., Marcotte, T. D., Moore, D. J., Gonzalez, R., Wolfson, T., Grant, I., and The HNRC Group. (2004). Methamphetamine dependence increases risk of neuropsychological impairment in HIV-infected persons. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 10, 1–14.
Simon, S. L., Domier, C. P., Carnell, J., Brethen, P., Rawson, R. A., and Ling, W. (2000). Cognitive impairment in individuals currently using methamphetamine. The American Journal on Addictions, 9, 222–231.
Taylor, M. J., Alhassoon, O. M., Schweinsburg, B. C., Videen, J. S., Grant, I., and The HNRC Group. (2000). MR spectroscopy in HIV and stimulant dependence. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 6, 83–85.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) research report series. (2002). Methamphetamine abuse and addiction. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health.
Wilkinson, G. S. (1993). The Wide Range Achievement Test—Revision 3. Wilmington, DE: Wide Range, Inc.
Woods, S. P., Rippeth, J. D., Frol, A. B., Hinkin, C. H., Levy, J. K., Ryan, E., Soukup, V. M., Lazzaretto, D., Cherner, M., Marcotte, T. D., Gelman, B. B., Morgello, S., Singer, E. J., Grant, I., and Heaton, R. K. (2004). Interrater reliability of clinical ratings and neurocognitive diagnoses in HIV. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 26, 759–778.
Woody, G. E., Donnell, D., Seage, G. R., Metzger, D., Marmor, M., Koblin, B. A., Buchbinder, S., Gross, M., Stone, B., and Judson, F. N. (1999). Non-injection substance use correlates with risky sex among men having sex with men. Data from HIVNET. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 53, 197–205.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Catherine L. Carey is now at the Department of Psychiatry at the University of California, San Francisco. Julie D. Rippeth is now at the Department of Psychology at Walter Reed Army Medical Center. Raul Gonzalez is now at the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
The research described herein was supported by center award CSPAR P30MH62512-02 from the National Institute of Mental Health, as well as Program Project P01DA12065 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, nor the United States Government.
The San Diego HIV Neurobehavioral Research Center [HNRC] group is affiliated with the University of California, San Diego, the Naval Hospital, San Diego, and the San Diego Veterans Affairs Healthcare System, and includes: Director: Igor Grant, M.D.; Co-Directors: J. Hampton Atkinson, M.D. and J. Allen McCutchan, M.D.; Center Manager: Thomas D. Marcotte, Ph.D.; Naval Hospital San Diego: Mark R. Wallace, M.D. (P.I.); Neuromedical Component: J. Allen McCutchan, M.D. (P.I.), Ronald J. Ellis, M.D., Ph.D., Scott Letendre, M.D., Rachel Schrier, Ph.D.; Neurobehavioral Component: Robert K. Heaton, Ph.D. (P.I.), Mariana Cherner, Ph.D., Julie Rippeth, Ph.D., Joseph Sadek, Ph.D., Steven Paul Woods, Psy.D., Corinna Young, Ph.D.; Imaging Component: Terry Jernigan, Ph.D. (P.I.), John Hesselink, M.D., Michael J. Taylor, Ph.D.; Neuropathology Component: Eliezer Masliah, M.D. (P.I.), Dianne Langford, Ph.D.; Clinical Trials Component: J. Allen McCutchan, M.D., J. Hampton Atkinson, M.D., Ronald J. Ellis, M.D., Ph.D., Scott Letendre, M.D.; Data Management Unit: Daniel R. Masys, M.D. (P.I.), Michelle Frybarger, B.A. (Data Systems Manager); Statistics Unit: Ian Abramson, Ph.D. (P.I.), Reena Deutsch, Ph.D., Deborah Lazzaretto, M.S. The authors are especially appreciative of Ms. Lazzaretto's assistance with the data analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carey, C.L., Woods, S.P., Rippeth, J.D. et al. Additive Deleterious Effects of Methamphetamine Dependence and Immunosuppression on Neuropsychological Functioning in HIV Infection. AIDS Behav 10, 185–190 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-005-9056-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-005-9056-4