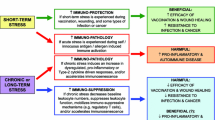
Abstract
Systems theory has long been used in psychology, biology, and sociology. This paper applies newer methods of control systems modeling for assessing system stability in health and disease. Control systems can be characterized as open or closed systems with feedback loops. Feedback produces oscillatory activity, and the complexity of naturally occurring oscillatory patterns reflects the multiplicity of feedback mechanisms, such that many mechanisms operate simultaneously to control the system. Unstable systems, often associated with poor health, are characterized by absence of oscillation, random noise, or a very simple pattern of oscillation. This modeling approach can be applied to a diverse range of phenomena, including cardiovascular and brain activity, mood and thermal regulation, and social system stability. External system stressors such as disease, psychological stress, injury, or interpersonal conflict may perturb a system, yet simultaneously stimulate oscillatory processes and exercise control mechanisms. Resonance can occur in systems with negative feedback loops, causing high-amplitude oscillations at a single frequency. Resonance effects can be used to strengthen modulatory oscillations, but may obscure other information and control mechanisms, and weaken system stability. Positive as well as negative feedback loops are important for system function and stability. Examples are presented of oscillatory processes in heart rate variability, and regulation of autonomic, thermal, pancreatic and central nervous system processes, as well as in social/organizational systems such as marriages and business organizations. Resonance in negative feedback loops can help stimulate oscillations and exercise control reflexes, but also can deprive the system of important information. Empirical hypotheses derived from this approach are presented, including that moderate stress may enhance health and functioning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Angelakis, E., Stathopoulou, S., Frymiare, J. L., Green, D. L., Lubar, J. F., & Kounios, J. (2007). EEG neurofeedback: A brief overview and an example of peak alpha frequency training for cognitive enhancement in the elderly. Clinical Neuropsychologist, 21, 110–129.
Arzeno, N. M., Kearney, M. T., Eckberg, D. L., Nolan, J., & Poon, C.-S. (2007). Heart rate chaos as a mortality predictor in mild to moderate heart failure. Conference Proceedings: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society, 2007, 5051–5054.
Attneave, F. (1959). Applications of information theory to psychology: A summary of basic concepts, methods, and results. New York: Holt.
Basar, E. (1999). Brain function and oscillation. New York: Springer.
Basar, E. (2006). The theory of the whole-brain-work. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 60, 133–138.
Basar, E., Gönder, A., & Ungan, P. (1976). Important relation between EEG and brain evoked potential. Biological Cybernetics, 25, 27–40.
Bayram, A., Bayraktrogly, Z., Karahan, E., Erdogan, B., Bilgic, B., Özker, M., et al. (2011). Simultaneous EEG/fMRI analysis of the resonance phenomena in steady-state evoked responses. Clinical EEG and Neuroscience, 42, 98–106.
Beckham, A. J., Greene, T. B., & Meltzer-Brody, S. (2013). A pilot study of heart rate variability biofeedback therapy in the treatment of perinatal depression on a specialized perinatal psychiatry inpatient unit. Archives of Women’s Mental Health, 16, 59–65.
Bernard-Weil, E. (1986). A general model for the simulation of balance, imbalance and control by agonistic antagonistic biological couples. Mathematical Modelling, 7(9–12), 1587–1600.
Berntson, G. G., Bigger, J. T., Jr, Eckberg, D. L., Grossman, P., Kaufmann, P. G., Malik, M., et al. (1997). Heart rate variability: Origins, methods, and interpretive caveats. Psychophysiology, 34, 623–648.
Berthoud, H.-R. (2006). Homeostatic and non-homeostatic pathways involved in the control of food intake and energy balance. Obesity, 14(Suppl 5), 197S–200S.
Berthouze, Luc., James, L. M., & Farmer, S. F. (2010). Human EEG shows long-range temporal correlations of oscillation amplitude in theta, alpha and beta bands across a wide age range. Clinical Neurophysiology, 121, 1187–1197.
Bertram, R., Sherman, A., & Satin, L. S. (2010). Electrical bursting, calcium oscillations, and synchronization of pancreatic islets. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 654, 261–279.
Bob, P. (2007). Chaos, brain and divided consciousness. Acta Universitatis Carolinae—Medica—Monographia, 153, 9–80.
Bosl, W., Tierney, A., Tager-Flusberg, H., & Nelson, C. (2011). EEG complexity as a biomarker for autism spectrum disorder risk. BMC Medicine, 9, 18.
Brown, C. M., Hecht, M. J., Weih, A., Neundorfer, B., & Hilz, M. J. (2003). Effects of age on the cardiac and vascular limbs of the arterial baroreflex. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 33, 10–16.
Buzsaki, G. (2006). Rhythms of the brain. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Cancian, F. M., & Gordon, S. L. (1988). Changing emotion norms in marriage: Love and anger in U.S. women’s magazines since 1900. Gender & Society, 2, 308–342.
Chemtob, C. M., Roitblat, H., Hamada, R. S., Carlson, J. G., & Twentyman, C. T. (1988). A cognitive action theory of post-traumatic stress disorder. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 2, 253–275.
Chen, J.-L., Yeh, D.-P., Lee, J.-P., Chen, C.-Y., Huang, C.-Y., Lee, S.-D., et al. (2011). Parasympathetic nervous activity mirrors recovery status in weightlifting performance after training. Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research, 25, 1546–1552.
Cinquin, O., & Demongeot, J. (2002). Roles of positive and negative feedback in biological systems. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 325, 1085–1095.
Crunelli, V., & Hughes, S. W. (2010). The slow (<1 Hz) rhythm of non-REM sleep: A dialogue between three cardinal oscillators. Nature Neuroscience, 13, 9–17.
Cugini, P., Ferrari, P., De Rosa, R., Caliumi, C., Delfini, E., Colotto, M., et al. (2003). Severity of human hypertension in relation to the age in which high blood pressure makes its presumptive appearance. Clinica Terapeutica, 154, 21–26.
Dworkin, B. R. (1993). Learning and physiological regulation. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Elbert, T., Ray, W. J., Kowalik, Z. J., Skinner, J. E., Graf, K. E., & Birbaumer, N. (1994). Chaos and physiology: Deterministic chaos in excitable cell assemblies. Physiological Reviews, 74, 1–47.
Fedotchev, A. I., Bondar, A. T., & Konovalov, V. F. (1990). Stability of resonance EEG reactions to flickering light in humans. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 9, 189–193.
Feigl, E. O. (1998). Neural control of coronary blood flow. Journal of Vascular Research, 35, 85–92.
Fogel, S. M., & Smith, C. T. (2011). The function of the sleep spindle: A physiological index of intelligence and a mechanism for sleep-dependent memory consolidation. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35, 1154–1165.
Fry, S. N., Rohrseitz, N., Straw, A. D., & Dickinson, M. H. (2008). TrackFly: Virtual reality for a behavioral system analysis in free-flying fruit flies. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 171, 110–117.
Garau, C., Aparicio, S., Rial, R. V., Nicolau, M. C., & Esteban, S. (2006). Age related changes in the activity-rest circadian rhythms and c-fos expression of ring doves with aging. Effects of tryptophan intake. Experimental Gerontology, 41, 430–438.
Gellhorn, E. (1969). Further studies on the physiology and pathophysiology of the tuning of the central nervous system. Psychosomatics: Journal of Consultation Liaison Psychiatry, 10, 94–104.
Gellhorn, E. (1970). The emotions and the ergotropic and trophotriopic systems. Psychologische Forschung, 34, 48–94.
Gengerelli, J. A. (1978). Wave coherence in the human EEG. Journal of Psychology, 99(2d Half), 203–223.
Gleik, J. (1987). Chaos: Making a new science. New York: Penguin Books.
Goldberger, A. L., Peng, C. K., & Lipsitz, L. A. (2002). What is physiologic complexity and how does it change with aging and disease? Neurobiology of Aging, 23, 23–26.
Gottesmann, C. (1999). Neurophysiological support of consciousness during waking and sleep. Progress in Neurobiology, 59, 469–508.
Gottman, J. M., Murray, J. D., Swanson, C. C., Tyson, R., & Swanson, K. R. (2002). The mathematics of marriage: Dynamic nonlinear models. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
Gottschalk, A., Bauer, M. S., & Whybrow, P. C. (1995). Evidence of chaotic mood variation in bipolar disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 52, 947.
Grodins, F. S. (1963). Control theory and biological systems. New York: Columbia University Press.
Gruzelier, J., Egner, T., & Vernon, D. (2006). Validating the efficacy of neurofeedback for optimising performance. Progress in Brain Research, 159, 421–431.
Guastello, S. J., Koopmans, M., & Pincus, D. (Eds.). (2009). Chaos and complexity in psychology. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Haffen, E., & Sechter, D. (2006). Disruption of biological rhythms and mood disorders. Encephale, 32(5 Pt 2), S795–S801.
Hallman, D. M., Olsson, E. M., von Scheele, B., Melin, L., & Lyskov, E. (2011). Effects of heart rate variability biofeedback in subjects with stress-related chronic neck pain: A pilot study. Applied Psychophysiology & Biofeedback, 36, 71–80.
Henriques, G., Keffer, S., Abrahamson, C., & Horst, S. J. (2011). Exploring the effectiveness of a computer-based heart rate variability biofeedback program in reducing anxiety in college students. Applied Psychophysiology & Biofeedback, 36, 101–112.
Herrmann, C. S. (2001). Human EEG responses to 1–100 Hz flicker: Resonance phenomena in visual cortex and their potential correlation to cognitive phenomena. Experimental Brain Research, 137(3–4), 346–353.
Ho, Y.-L., Lin, C., Lin, Y.-H., & Lo, M.-T. (2011). The prognostic value of non-linear analysis of heart rate variability in patients with congestive heart failure—A pilot study of multiscale entropy. PLoS ONE, 6, e18699.
Hyndman, B. W. (1974). The role of rhythms in homeostasis. Biological Cybernetics, 15, 227–236.
Isler, Y., & Kuntalp, M. (2007). Combining classical HRV indices with wavelet entropy measures improves to performance in diagnosing congestive heart failure. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 37, 1502–1510.
Jacobs, G. D. (2001). The physiology of mind-body interactions: The stress response and the relaxation response. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 7(Suppl 1), S83–S92.
Juster, R. P., McEwen, B. S., & Lupien, S. J. (2010). Allostatic load biomarkers of chronic stress and impact on health and cognition. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35, 2–16.
Kaneko, W., Phillips, E., Riley, E., & Ehlers, C. (1996). EEG findings in fetal alcohol syndrome and Down syndrome children. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 98, 20–28.
Karavidas, M. K., Lehrer, P. M., Vaschillo, E., Vaschillo, B., Marin, H., Buyske, S., et al. (2007). Preliminary results of an open label study of heart rate variability biofeedback for the treatment of major depression. Applied Psychophysiology & Biofeedback, 32, 19–30.
Kasevich, R. S., & LaBerge, D. (2011). Theory of electric resonance in the neocortical apical dendrite. PLoS ONE, 6, e23412.
Kellert, S. H. (1993). In the wake of Chaos: Unpredictable order in dynamical systems. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Klapp, O. E. (1975). Opening and closing in open systems. Behavioral Science, 20, 251–257.
Klevecz, R. R., Li, C. M., Marcus, I., & Frankel, P. H. (2008). Collective behavior in gene regulation: The cell is an oscillator, the cell cycle a developmental process. FEBS Journal, 275, 2372–2384.
Klimesch, W. (1996). Memory processes, brain oscillations and EEG synchronization. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 24(1–2), 61–100.
Klimesch, W., Schack, B., & Sauseng, P. (2005). The functional significance of theta and upper alpha oscillations. Experimental Psychology, 52, 99–108.
Knyazev, G. G. (2007). Motivation, emotion, and their inhibitory control mirrored in brain oscillations. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 31, 37–395.
Krantz, D. S., Contrada, R. J., LaRiccia, P. J., Anderson, J. R., Durel, L. A., Dembroski, T. M., et al. (1987). Effects of beta-adrenergic stimulation and blockade on cardiovascular reactivity, affect, and type A behavior. Psychosomatic Medicine, 49, 146–158.
Kurbel, S. (2012). A phase plane graph based model of the ovulatory cycle lacking the “positive feedback” phenomenon. Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling, 9, 35.
Lehrer, P. M. (2007). Biofeedback training to increase heart rate variability. Principles and practice of stress management (3rd ed., pp. 227–248). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Lehrer, P. M., Karavidas, M. K., Lu, S.-E., Coyle, S. M., Oikawa, L. O., Macor, M., et al. (2010). Voluntarily produced increases in heart rate variability modulate autonomic effects of endotoxin induced systemic inflammation: An exploratory study. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 35, 303–315.
Lehrer, P. M., Vaschillo, E. G., Vaschillo, B., Lu, S.-E., Eckberg, D. L., Edelberg, R., et al. (2003). Heart rate variability biofeedback increases baroreflex gain and peak expiratory flow. Psychosomatic Medicine, 65, 796–805.
Lehrer, P. M., Vaschillo, E. G., Vaschillo, B., Lu, S.-E., Scardella, A., Siddique, M., et al. (2004). Biofeedback treatment for asthma. Chest, 126, 352–361.
Lempel, A., & Ziv, J. (1976). On the complexity of finite sequences. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 22, 75–81.
Lin, G., Xiang, Q., Fu, X., Wang, S., Wang, S., Chen, S., et al. (2012). Heart rate variability biofeedback decreases blood pressure in prehypertensive subjects by improving autonomic function and baroreflex. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 18, 143–152.
Liu, C., Liu, C., Shao, P., Li, L., Sun, X., Wang, X., et al. (2011). Comparison of different threshold values r for approximate entropy: Application to investigate the heart rate variability between heart failure and healthy control groups. Physiological Measurement, 32, 167–180.
Mandelbrot, B. B. (1983). The fractal geometry of nature. New York: Macmillan.
Martinez, L., Perez, T., Mirasso, C. R., & Manjarrez, E. (2007). Stochastic resonance in the motor system: Effects of noise on the monosynaptic reflex pathway of the cat spinal cord. Journal of Neurophysiology, 97, 4007–4016.
Mason, O. J., & Brady, F. (2009). The psychotomimetic effects of short-term sensory deprivation. Journal of Nervous & Mental Disease, 197, 783–785.
Maurer, C., Mergner, T., & Peterka, R. J. (2004). Abnormal resonance behavior of the postural control loop in Parkinson’s disease. Experimental Brain Research, 157, 369–376.
Mayhew, D. R. (2002). Electoral realignments: A critique of an American genre new haven. CT: Yale University Press.
McEwen, B. S. (2004). Protection and damage from acute and chronic stress: Allostasis and allostatic overload and relevance to the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1032, 1–7.
Mindell, D., Segal, J., & Gerovitch, S. (2003). Cybernetics and information theory in the United States, France and the Soviet Union. In M. Walker (Ed.), Science and ideology: A comparative history (pp. 66–95). London: Routledge.
Montano, N., Porta, A., Cogliati, C., Costantino, G., Tobaldini, E., Casali, K. R., et al. (2009). Heart rate variability explored in the frequency domain: A tool to investigate the link between heart and behavior. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 33, 71–80.
Moore, N. C. (2000). A review of EEG biofeedback treatment of anxiety disorders. Clinical Electroencephalography, 31, 1–6.
Nandrino, J. L., Pezard, L., Martinerie, J., el Massioui, F., Renault, B., Jouvent, R., et al. (1994). Decrease of complexity in EEG as a symptom of depression. NeuroReport, 5, 528–530.
Nishi, A., Bibb, J. A., Snyder, G. L., Higashi, H., Nairn, A. C., & Greengard, P. (2000). Amplification of dopaminergic signaling by a positive feedback loop. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 12840–12845.
Nolan, R. P., Floras, J. S., Harvey, P. J., Kamath, M. V., Picton, P. E., Chessex, C., et al. (2010). Behavioral neurocardiac training in hypertension: A randomized, controlled trial. Hypertension, 55, 1033–1039.
Norris, P. R., Anderson, S. M., Jenkins, J. M., Williams, A. E., & Morris, J. A., Jr. (2008a). Heart rate multiscale entropy at three hours predicts hospital mortality in 3,154 trauma patients. Shock, 30, 17–22.
Norris, P. R., Stein, P. K., & Morris, J. A., Jr. (2008b). Reduced heart rate multiscale entropy predicts death in critical illness: A study of physiologic complexity in 285 trauma patients. Journal of Critical Care, 23, 399–405.
Onton, J., Westerfield, M., Townsend, J., & Makeig, S. (2006). Imaging human EEG dynamics using independent component analysis. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 30, 808–822.
Orme-Johnson, D. W., & Haynes, C. T. (1981). EEG phase coherence, pure consciousness, creativity, and TM–Sidhi experiences. International Journal of Neuroscience, 13, 211–217.
Panzeri, S., Brunel, N., Logothetis, N. K., & Kayser, C. (2010). Sensory neural codes using multiplexed temporal scales. Trends in Neurosciences, 33, 111–120.
Patron, E., Benvenuti, S. M., Favretto, G., Valfre, C., Bonfa, C., Gasparotto, R., et al. (2013). Biofeedback assisted control of respiratory sinus arrhythmia as a biobehavioral intervention for depressive symptoms in patients after cardiac surgery: A preliminary study. Applied Psychophysiology & Biofeedback, 38, 1–9.
Paul, M., & Garg, K. (2012). The effect of heart rate variability biofeedback on performance psychology of basketball players. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 37, 131–144. doi:10.1007/s10484-012-9185-2.
Paulus, M. P., & Braff, D. L. (2003). Chaos and schizophrenia: Does the method fit the madness? Biological Psychiatry, 53, 3–11.
Paulus, M. P., Geyer, M. A., & Braff, D. L. (1996). Use of methods from chaos theory to quantify a fundamental dysfunction in the behavioral organization of schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry, 153, 714–717.
Pezard, L., Nandrino, J. L., Renault, B., el Massioui, F., Allilaire, J. F., Muller, J., et al. (1996). Depression as a dynamical disease. Biological Psychiatry, 39, 991–999.
Pfurtscheller, G., & Lopes da Silva, F. H. (1999). Event-related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization: Basic principles. Clinical Neurophysiology, 110, 1842–1857.
Pigolott, I. S., Krishna, S., & Jensen, M. H. (2007). Oscillation patterns in negative feedback loops. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 6533–6537.
Pincus, S. M. (1991). Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 88, 2297–2301.
Pincus, S. M. (1998). Approximate entropy (ApEn) as a regularity measure (pp. 243–268)., Applications of nonlinear dynamics to developmental process modeling Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Plahte, E., Mestl, T., & Omholt, S. W. (1995). Feedback loops, stability, and multistationarity in dynamical systems. Journal of Biological Systems, 3, 409–413.
Polonsky, K. S., Sturis, J., & Van Cauter, E. (2000). Temporal profiles and clinical significance of pulsatile insulin secretion. Hormone Research in Paediatrics, 49, 178–184.
Pomerening, J. R., Kim, S. Y., & Ferrell, J. E., Jr. (2005). Systems-level dissection of the cell-cycle oscillator: Bypassing positive feedback produces damped oscillations. Cell, 122, 565–578.
Prochazka, A., Gillard, D., & Bennett, D. J. (1997). Implications of positive feedback in the control of movement. Journal of Neurophysiology, 77, 3237–3251.
Putman, P., van Peer, J., Maimari, I., & van der Werff, S. (2010). EEG theta/beta ratio in relation to fear-modulated response-inhibition, attentional control, and affective traits. Biological Psychology, 83, 73–78.
Rahman, F., Pechnik, S., Gross, D., Sewell, L., & Goldstein, D. S. (2011). Low frequency power of heart rate variability reflects baroreflex function, not cardiac sympathetic innervation. Clinical Autonomic Research, 21, 133–141.
Ramirez, P. M., Desantis, D., & Opler, L. A. (2001). EEG biofeedback treatment of ADD. A viable alternative to traditional medical intervention? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 931, 342–358.
Reineke, A. (2008). The effects of heart rate variability biofeedback in reducing blood pressure for the treatment of essential hypertension. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering, 68(7-B), 4880.
Roschke, J., Fell, J., & Beckmann, P. (1995). Nonlinear analysis of sleep EEG data in schizophrenia: Calculation of the principal Lyapunov exponent. Psychiatry Research, 56, 257–269.
Rossiter, T. (2004). The effectiveness of neurofeedback and stimulant drugs in treating AD/HD: Part I. Review of methodological issues. Applied Psychophysiology & Biofeedback, 29, 95–112.
Rossler, O. E., & Rossler, R. (1994). Chaos in physiology. Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science, 29, 328–333.
Schwartz, G. E. (1981). A systems analysis of psychobiology and behavior therapy. Implications for behavioral medicine. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 36(3–4), 159–184.
Schwartz, G. E., Shapiro, A. P., Redmond, D. P., Ferguson, D. C., Ragland, D. R., & Weiss, S. M. (1979). Behavioral medicine approaches to hypertension: An integrative analysis of theory and research. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 2, 311–363.
Shannon, C. E. (1948). A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Systems Technology Journal, 27, 379–423.
Shannon, C. E., & Weaver, W. (1949). The mathematical theory of communication. Champaign, IL: Univ of Illinois.
Shenefelt, P. D. (2010). Relaxation strategies for patients during dermatologic surgery. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology: JDD, 9, 795–799.
Siebert, W. M. C. (1986). Circuits, signals, and systems. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Siepmann, M., Aykac, V., Unterdorfer, J., Petrowski, K., & Mueck-Weymann, M. (2008). A pilot study on the effects of heart rate variability biofeedback in patients with depression and in healthy subjects. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 33, 195–201.
Sohn, H., Kim, I., Lee, W., Peterson, B. S., Hong, H., Chae, J.-H., et al. (2010). Linear and non-linear EEG analysis of adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder during a cognitive task. Clinical Neurophysiology, 121, 1863–1870.
Sowder, E., Gevirtz, R., Shapiro, W., & Ebert, C. (2010). Restoration of vagal tone: A possible mechanism for functional abdominal pain. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 35, 199–206.
Spiegler, A., Knösche, T. R., Schwab, K., Haueisen, J., & Atay, F. M. (2011). Modeling brain resonance phenomena using a neural mass model. PLOS Computational Biology, 7, e1002298.
Strine, G. N. (2004). Self-reports of pain reduction through paced respiration and heart rate variability biofeedback with nursing home residents. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering, 65(5-B), 2685.
Thayer, J. F., & Lane, R. D. (2000). A model of neurovisceral integration in emotion regulation and dysregulation. Journal of Affective Disorders, 61, 201–216.
Thurner, S., Mittermaier, C., & Ehrenberger, K. (2002). Change of complexity patterns in human posture during aging. Audiology & Neuro-Otology, 7, 240–248.
Timofeev, I., & Chauvette, S. (2011). Thalamocortical oscillations: local control of EEG slow waves. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 11, 2457–2471.
Tognoli, E., & Kelso, J. A. (2009). Brain coordination dynamics: true and false faces of phase synchrony and metastability. Progress in Neurobiology, 87, 31–40.
Tolic, I., Mosekilde, E., & Sturis, J. (2000). Modeling the insulin-glucose feedback system: The significance of pulsatile insulin secretion. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 207, 361–375.
Tsai, T. Y.-C., Choi, Y. S., Ma, W., Pomerening, J. R., Tang, C., & Ferrell, J. E., Jr. (2008). Robust, tunable biological oscillations from interlinked positive and negative feedback loops. Science, 321(5885), 126–129.
Tschacher, W., Scheier, C., & Hashimoto, Y. (1997). Dynamical analysis of schizophrenia courses. Biological Psychiatry, 41, 428–437.
Vaschillo, E. G., Lehrer, P. M., Rishe, N., & Konstantinov, M. (2002). Heart rate variability biofeedback as a method for assessing baroreflex function: A preliminary study of resonance in the cardiovascular system. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 27, 1–27.
Vaschillo, E. G., Vaschillo, B., Buckman, J. F., Pandina, R. J., & Bates, M. E. (2012). Measurement of vascular tone and stroke volume baroreflex gain. Psychophysiology, 49, 193–197.
Vaschillo, E. G., Vaschillo, B., & Lehrer, P. M. (2006). Characteristics of resonance in heart rate variability stimulated by biofeedback. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 31, 129–142.
Vaschillo, E. G., Vaschillo, B., Pandina, R. J., & Bates, M. E. (2011). Resonances in the cardiovascular system caused by rhythmical muscle tension. Psychophysiology, 48, 927–936.
Ward, L. M., MacLean, S. E., & Kirschner, A. (2010). Stochastic resonance modulates neural synchronization within and between cortical sources. PLoS ONE, 5, e14371.
Weaver, R. L., & Lobkis, O. I. (2006). On the linewidth of the ultrasonic Larsen effect in a reverberant body. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 120, 102–109.
Weick, K. E. (2009). Making sense of the organization: the impermanent organization. Chichester, Sussex, UK: Wiley.
Weinert, D., & Waterhouse, J. (2007). The circadian rhythm of core temperature: Effects of physical activity and aging. Physiology & Behavior, 90(2–3), 246–256.
Weiss, J. N., Garfinkel, A., Speno, M. L., & Ditto, W. L. (1994). Chaos and chaos. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 93, 1355–1360.
Wiener, N. (1948). Cybernetics; or control and communication in the animal and the machine. Oxford: Wiley.
Wiener, N. (1961). Cybernetics: Or control and communication in the animal and the machine. Cambridge, MA: The MIT press.
Wiesenfeld, K., & Moss, F. (1995). Stochastic resonance and the benefits of noise: From ice ages to crayfish and squids. Nature, 373(6509), 33–36.
Winterer, G., Ziller, M., Dorn, H., Frick, K., Mulert, C., Dahhan, N., et al. (1999). Cortical activation, signal-to-noise ratio and stochastic resonance during information processing in man. Clinical Neurophysiology, 110, 1193–1203.
Yerkes, R. M., & Dodson, J. D. (1908). The relation of strength of stimulus to rapidity of habit-formation. Journal of Comparative Neurology and Psychology, 18, 459–482.
Yetwin, A. K. (2012). Heart rate variability biofeedback therapy for children and adolescents with chronic pain. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering, 72(12-B), 7704.
Yockey, H. P. (2005). Information theory, evolution, and the origin of life. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Zarjam, P., Epps, J., & Chen, F. (2011, August 30–September 3, 2011). Spectral EEG features for evaluating cognitive load. Paper presented at the 334d Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Boston, MA.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grant # 5R01HL089495-02 from the National Institutes of Health. For helpful comments in preparing this manuscript, the authors are indebted to Dr. Jaye Derrick of the State University of Buffalo and to the patient and thorough editorial reviewers for Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehrer, P., Eddie, D. Dynamic Processes in Regulation and Some Implications for Biofeedback and Biobehavioral Interventions. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 38, 143–155 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-013-9217-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-013-9217-6