Abstract
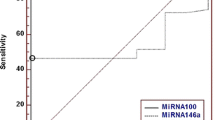
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a heterogeneous cancer commonly affecting children due to dysregulation of miRNA expression. In the current study, authors investigated the expression profile for miRNA-125b-1 and miRNA-203 among childhood ALL. Blood samples were collected from newly diagnosed childhood ALL and healthy control children. The expression profile for candidate miRNAs was detected using quantitative RT-PCR analysis. Statistical analysis were performed using receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) to examine the diagnostic efficacy of the two miRNA and their levels among ALL clinicopathological factors and phenotypes. The median expression level for miRNA-125b-1 was significantly high in childhood ALL; while miRNA-203 level was significantly low in childhood ALL as compared to control ones. MiRNA-125-1 reported significant increase in T-ALL as compared to other ALL phenotypes. Median miRNA-203 level was high in T-ALL followed by pre-B-ALL although no significant difference was reported. Clinicopathological factors did not emphasize significance with either detected miRNAs. Using ROC curve the diagnostic efficacy was significant with an area under the curve 0.858 for miRNA-125b-1 (83.72, 100%) and 0.878 for miRNA-203 (97.67, 86.96%). The combination of the two key miRNAs revealed absolute sensitivity (100%). MiRNA-125b-1 and miRNA-203 can be useful molecular markers for diagnosis of ALL. Further studies with large cohort are warranted to validate these results.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Cancer Society (2013) Cancer facts and figures 2013. American Cancer Society, Atlanta
Banzhaf-Strathmann J, Edbauer D (2014) Good guy or bad guy: the opposing roles of microRNA-125b in cancer. Cell Commun Signal 12:30–43
Boldrup L, Coates PJ, Wahlgren M, Laurell G, Nylander K (2012) Subsite-based alterations in miR-21, miR-125b, and miR-203 in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and correlation to important target proteins. J Carcinog 11:18
Bousqueta M, Harrisb MH, Zhoua B, Lodisha HF (2010) MicroRNA miR-125b causes leukemia. PNAS 107:21558–21563
Bueno MJ, de Castrode IP, de Cedron MG, Santos J, Calin GA, Cigudosa JC, Croce CM, Piqueras JF, Malumbres M (2003) Genetic and epigenetic silencing of MicroRNA-203 enhances ABL1 and BCR-ABL1 oncogene expression. Cancer Cell 13:496–506
Carroll WL, Raetz EA (2012) Clinical and laboratory biology of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Pediateric 160:10–18
Duyu M, Durmaz B, Gunduz C, Yergin C, Karapinar Y, Aksoylar S, kavaki K, Cetingul N, Yaman Y, Ozkiany F, Cogulu O (2014) Prospective evaluation of whole genome MicroRNA expression profiling in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/967585
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs—microRNAs with arole in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Fatica A, Fazi F (2013) MicroRNA-regulated pathways in hematological malignancies: how to avoid cells playing out of tune. Int J Mol Sci 14:20930–20953
Garzon R, Marcucci G, Croce CM (2010) Targeting microRNAsin cancer: rationale, strategies and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(10):775–789
Grasedieck S, Sorrentino A, Langer C, Buske C, Döhner H, Mertens D, Kuchenbaue F (2013) Circulating microRNAs in hematological diseases: principles, challenges, and perspectives. Blood 121(25):4977–4984
Hobert O (2008) Gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Science 319:1785–1786
Ibrahim AS, Khaled HM, Mikhail NN, Baraka H, Kamel H (2014) Cancer incidence in Egypt: results of the National Population-Based Cancer Registry Program. J Cancer Epidemiol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/437971
Imaoka H, Toiyama Y, Okigami M, Yasuda H, Saigusa S, Ohi M, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, Mohri Y, Kusunoki M (2016) Circulating microRNA-203 predicts metastases, early recurrence, and poor prognosis in human gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 19:744–753
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (2001) World Health Organisation classification of tumors, pathology and genetics: tumors of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. IARC Press, Lyon
Li J, Wan Y, Ji Q, Wu Y (2013) The role of microRNAs in B-cell development and function. Cell Mol Immunol 10:107–112
Li Q, Liu L, Li W (2014a) Identification of circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in diagnosis of hematologic cancers: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol 35(10):10467–10478
Li WY, Chen XM, Xiong W, Guo DM, Lu L, Li HY (2014b) Detection of microvesicle miRNA expression in ALL subtypes and analysis of their functional roles. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 34(5):640–645
Luan C, Yang Z, Chen B (2015) The functional role of microRNA in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: relevance for diagnosis, differential diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Oncotargets Ther 8:2903–2914
Pui CH, Robison LL, Look AT (2008) Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 371(3):1030–1043
Ramani R, Megason G, Schalheim J, Karlson C, Vijayakumar V, Vijayakumar S, Hicks C (2017) Integrative analysis of miRNA-mediated gene signatures and pathways modulating white blood cell count in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biomarkers Insight 17:1–12
Randolph TR (2004) Advances in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin Lab Sci 17(4):235–245
Redshaw N, Wilkes N, Whale A, Cowen S, Huggett J, Foy CA (2013) A comparison of miRNA: isolation and RT-qPCR technologies and their effects on quantification accuracy and repeatability. Bio Tech 54:155–164
Saki N, Abroun S, Hajizamani S, Rahim F, Shahjahani M (2014) Association of chromosomal translocation and MiRNA expression with the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Cell J (Yakhteh) 16(2):99–110
Schotte D, Pieters R, Den Boer ML (2012) MicroRNAs in acute leukemia: from biological players to clinical contributors. Leukemia 26:1–12
Shaham L, Binder V, Gefen N, Borkhardt A, Izraeli S (2012) MiR-125 in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Leukemia 26:2011–2018
Stumpe DJPM, Schotte D, Lange-Turenhout EAM, Schneider P, Seslija L, de Menezes RX, Pieters R, den Boer ML, Stam RW (2011) Hypermethylation of specific microRNA genes in MLL-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia: major matters at a micro scale. Leukemia 25:429–439
Tang R, Zhong T, Dang Y, Zhang X, Li P, Chen G (2016) Association between downexpression of MiR-203 and poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Transl Oncol 18:360–368
Wallaert A, Loocke WV, Hernandez L, Taghon T, Speleman F, Vlierberghe PV (2017) Comprehensive miRNA expression profiling in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia by small RNA-sequencing. Sci Rep 7:7901. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08148-x
Wang S, Zhao X, Wang J, Wen Y, Zhang L, Wang D, Chen H, Chen Q, Xiang W (2013) Upregulation of microRNA-203 is associated with advanced tumor progression and poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Med Oncol 30:681–687
Wang N, Liang H, Zhou Y, Wang C, Zhang S, Pan Y, Wang Y, Yan X, Zhang J, Zhang C-Y, Zen K, Li D, Chen X (2014) MiR-203 suppresses the proliferation and migration and promotes the apoptosis of lung cancer cells by targeting SRC. PLoS ONE 9(8):e105570
Zhang Y, Yan LX, Wu QN, Du ZM, Chen J, Liao DZ, Huang MY, Hou JH, Wu QL, Zeng MS, Huang WL, Zeng YX, Shao YJ (2011) MiR-125b is methylated and functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating the ETS1 protooncogene in human invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res 71(10):1–11
Zhao S, Yao D, Chen J, Ding N (2013) Aberrant expression of miR-20a and miR-203 in cervical cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14(4):2289–2293
Zhu T, Gao W, Chen X, Zhang Y, Wu M, Zhang P, Wang S (2016) A pilot study of circulating MicroRNA-125b as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1097/IGC.0000000000000846
Acknowledgement
This work was partially funded through National Research Centre, Giza, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swellam, M., Hashim, M., Mahmoud, M.S. et al. Aberrant Expression of Some Circulating miRNAs in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Biochem Genet 56, 283–294 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-018-9844-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-018-9844-y