Abstract
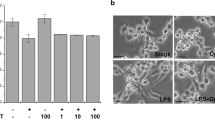
Antimicrobial peptide P18 markedly inhibited the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophage cells, whereas magainin 2 did not inhibit these activities. P18 dose-dependently reduced nitric oxide (NO) production by LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells, with complete inhibition at 20 μg P18 ml−1. In contrast, P18 had no effect on NO production and the expression of iNOS mRNA and iNOS protein by interferon-gamma (IFN-γ)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, suggesting P18 selectively inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory responses in macrophages. An LAL assay showed that P18 has strong LPS-neutralizing activity, indicating that P18 inhibits the inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated macrophages by direct binding to LPS. Collectively, our results indicate that P18 has promising therapeutic potential as a novel anti-inflammatory as well as antimicrobial agent.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogdan C, Rollinghoff M, Diefenbach A (2000) The role of nitric oxide in innate immunity. Immunol Rev 173:17–26
Boman HG (1995) Peptide antibiotics, their role in innate immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 13:61–92
Bowdish DM, Davidson DJ, Hancock RE (2005) A re-evaluation of the role of host defence peptides in mammalian immunity. Curr Protein Pept Sci 6:35–51
Ciornei CD, Egesten A, Engstrom M, Tornebrandt K, Bodelsson M (2002) Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein inhibits endotoxin-induced vascular nitric oxide synthesis. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 46:1111–1118
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok S, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Korhonen R, Lahti A, Kankaanranta H, Moilanen E (2005) Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4:471–479
Raetz CR, Whitfield C (2002) Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem 71:635–700
Rimbach G, Park YC, Guo Q, Moini H, Qureshi N, Saliou C, Takayama K, Virgili F, Packer L (2000) Nitric oxide synthesis and TNF-alpha secretion in RAW 264.7 macrophages: mode of action of a fermented papaya preparation. Life Sci 67:679–694
Scott MG, Davidson DJ, Gold MR, Bowdish D, Hancock RE (2002) The human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 is a multifunctional modulator of innate immune responses. J Immunol 169:3883–3891
Shin SY, Yang ST, Park EJ, Eom SH, Song WK, Kim Y, Hahm KS, Kim JI (2002) Salt resistance and synergistic effect with vancomycin of α-helical antimicrobial peptide P18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:558–562
Turner J, Cho T, Dinh NN, Waring AJ, Lehrer RI (1998) Activities of LL-37, a cathelin-associated antimicrobial peptide of human neutrophils. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42:2206–2214
Xaus J, Comalada M, Valledor AF, Lloberas J, Lopez-Soriano F, Argiles JM (2000) LPS induces apoptosis in macrophages mostly through the autocrine production of TNF-α. Blood 95:3823–3831
Yang D, Biragyn A, Hoover DM, Lubkowski J, Oppenheim JJ (2004) Multiple roles of antimicrobial defensins, cathelicidins, and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in host defense. Annu Rev Immunol 22:181–215
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nan, Y.H., Jeon, Y.J., Park, IS. et al. Antimicrobial peptide P18 inhibits inflammatory responses by LPS- but not by IFN-γ-stimulated macrophages. Biotechnol Lett 30, 1183–1187 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9682-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9682-9