Abstract
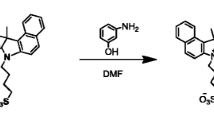
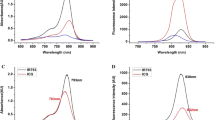
IR-789, a novel near-infrared fluorescent probe, was designed, synthesized, and applied to living cells. The probe exhibited better response fluorescence characteristics than the only FDA-approved agent, indocyanine green. Cell experiments showed that the probe had high affinity and without apparent cytotoxicity. Fluorescent image experiments in living MCF-7 cells (human breast adenocarcinoma cell line) further demonstrated the potential applications of the probe in biological systems. The probe effectively prevented the influence of autofluorescence and native cellular species in biological systems. It also exhibited high sensitivity, good photostability, and excellent cell membrane permeability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson RC, Kues HA (1978) Fluorescence properties of indocyanine green as related to angiography. Phys Med Biol 23:159–163
Brancato R, Trabucchi G (1998) Fluorescein and indocyanine green angiography in vascular chorioretinal diseases. Semin Ophthalmol 13:189–198
Caesar J, Shaldon S, Chiandussi L, Guevara L, Sherlock S (1961) The use of indocyanine green in the measurement of hepatic blood flow and as a test of hepatic function. Clin Sci 21:43–57
Czarnik AW (1993) Fluorescent chemosensors for ion and molecule recognition. ACS, Washington DC 538
Czarnik AW (1994) Chemical communication in water using fluorescent chemosensors. Acc Chem Res 27:302–308
Demas JN, Crosby GA (1971) Measurement of photoluminescence quantum yields. J Phys Chem 75:991–1023
Formica M, Fusi V, Giorgi L, Micheloni M (2012) New fluorescent chemosensors for metal ions in solution. Coord Chem Rev 256:170–192
Haglund MM, Berger MS, Hochman DW (1996) Enhanced optical imaging of human gliomas and tumor margins. Neurosurgery 38:308–317
Hilderbrand SA, Weissleder R (2010) Near-infrared fluorescence: application to in vivo molecular imaging. Curr Opin Chem Biol 14:71e9
Huber W, Koella JC (1993) A comparison of three methods of estimating EC50 in studies of drug resistance of malaria parasites. Acta Trop 55:257–261
Klohs J, Wunder A, Licha K (2008) Near-infrared fluorescent probes for imaging vascular pathophysiology. Basic Res Cardiol 103:144–151
Landsman ML, Kwant G, Mook GA, Zijlstra WG (1976) Light-absorbing properties, stability, and spectral stabilization of indocyanine green. J Appl Physiol 40:575–583
Ntziachristos V, Yodh AG, Schnall M, Chance B (2000) Concurrent MRI and diffuse optical tomography of breast following indocyanine green enhancement. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2767–2772
Padhani AR (2005) Where are we with imaging oxygenation in human tumours? Cancer Imag 5:128–130
Reynolds JS, Troy TL, Mayer RH, Thompson AB, Waters DJ, Cornell KK, Snydera PW, Sevick-Muraca EM (1999) Imaging of spontaneous canine mammary tumors using fluorescent contrast agents. Photochem Photobiol 70:87–94
Seidl K, Zinkernagel AS (2013) The MTT assay is a rapid and reliable quantitative method to assess Staphylococcus aureus induced endothelial cell damage. J Microbiol Meth 92:307–309
Silva AP, Gunaratne HQN, Gunnlaugsson T, Huxley AJM, McCoy CP, Rademacher J, Rice TE (1997) Signaling recognition events with fluorescent sensors and switches. Chem Rev 97:1515–1566
Tang B, Liu X, Xu K, Huang H, Yang G, An L (2007) A dual near-infrared pH fluorescent probe and its application in imaging of HepG2 cells. Chem Commun 36:3726–3728
Tromberg BJ, Shah N, Lanning R, Cerussi A, Espinoza J, Pham T, Svaasand L, Butler J (2000) Non-invasive in vivo characterization of breast tumors using photon migration spectroscopy. Neoplasia 2:26–40
Zhao S, O’Leary MA, Nioka S, Chance B (1995) Breast tumor detection using continuous wave light source. Proc SPIE 2389:789–798
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Basic Research Program of P. R. China (No. 2011CB933503) and Technology Supporting Program of Jiangsu province (BE2012657).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Wu, Y., Cai, J. et al. Synthesis of a near-infrared fluorescent probe and its application in imaging of MCF-7 cells. Biotechnol Lett 36, 1203–1207 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1478-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1478-5