Abstract
Objectives
We used optical imaging of live animals and transgenic technology to develop a pulmonary fibrosis model in mice that can non-invasively and in real-time trace the pulmonary fibrosis process.
Results
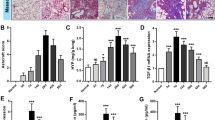
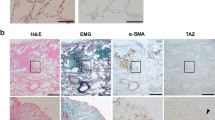
Fibroblast activation protein-α (FAPα) is selectively expressed in fibrotic foci of human pulmonary fibrosis. It is not expressed in normal tissue. We confirmed that FAPα is upregulated in fibroblasts of murine pulmonary fibrosis. Moreover, TGF-β1, a central pathological mediator of fibrotic diseases, could promote FAPα expression in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Luciferase reporter assays showed that 5.4 kb FAPα promoter response activities to TGF-β1 was stronger than of the 2.1 kb promoter. We generated a transgenic mouse line expressing firefly luciferase under the control of the 5.4 kb FAPα gene promoter (FAPα-p-luc). After experimentally inducing murine pulmonary fibrosis, there luminescence appeared in the chests and excised lungs of FAPα-p-luc mice. The intensity of luminescence became stronger with the exacerbation of pulmonary fibrosis.
Conclusion
Fluorescence intensity reflects the degree of pulmonary fibrosis in FAPα-p-luc mice. and this mouse model may be used to investigate molecular mechanisms and drug screening of pulmonary fibrosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BLI:
-
Bioluminescence imaging
- BLM:
-
Bleomycin
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EGR1:
-
Early growth response 1
- FAPα:
-
Fibroblast activation protein-α
- IPF:
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Luc:
-
Luciferase
- MEFs:
-
Mouse embryonic fibroblasts
- IPF:
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- TGF-β1:
-
Transforming growth factor-β1
- Tg:
-
Transgenic
References
Acharya PS, Zukas A, Chandan V, Katzenstein AL, Pure E (2006) Fibroblast activation protein: a serine protease expressed at the remodeling interface in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Hum Pathol 37:352–360
Badr CE (2014) Bioluminescence imaging: basics and practical limitations. Methods Mol Biol 1098:1–18
Desmouliere A, Geinoz A, Gabbiani F, Gabbiani G (1993) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 122:103–111
Jacob M, Chang L, Pure E (2012) Fibroblast activation protein in remodeling tissues. Curr Mol Med 12:1220–1243
Leilei Y, Bing L, Yang L, Shaoxia W, Yuan X, Dongping W, Huahu Y, Shichen S, Guangzhou Z, Ruiyun P, Lin Z, Wenlong L (2014) iRhom2 mutation leads to aberrant hair follicle differentiation in mice. PLoS ONE 9:e115114
Levy MT, McCaughan GW, Marinos G, Gorrell MD (2002) Intrahepatic expression of the hepatic stellate cell marker fibroblast activation protein correlates with the degree of fibrosis in hepatitis C virus infection. Liver 22:93–101
Liu B, Xu Y, Li WL, Zeng L (2015) Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed skin proteins in iRhom2(Uncv) mice. BMB Rep 48:19–24
Martinez FJ, Safrin S, Weycker D, Starko KM, Bradford WZ, King TE Jr, Flaherty KR, Schwartz DA, Noble PW, Raghu G, Brown KK (2005) The clinical course of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ann Intern Med 142:963–967
Moeller A, Ask K, Warburton D, Gauldie J, Kolb M (2008) The bleomycin animal model: a useful tool to investigate treatment options for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:362–382
Mouratis MA, Aidinis V (2011) Modeling pulmonary fibrosis with bleomycin. Curr Opin Pulm Med 17:355–361
Noble PW, Homer RJ (2005) Back to the future: historical perspective on the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 33:113–120
Rettig WJ, Su SL, Fortunato SR, Scanlan MJ, Raj BK, Garin-Chesa P, Healey JH, Old LJ (1994) Fibroblast activation protein: purification, epitope mapping and induction by growth factors. Int J Cancer 58:385–392
Scanlan MJ, Raj BK, Calvo B, Garin-Chesa P, Sanz-Moncasi MP, Healey JH, Old LJ, Rettig WJ (1994) Molecular cloning of fibroblast activation protein alpha, a member of the serine protease family selectively expressed in stromal fibroblasts of epithelial cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5657–5661
Wang Y, Sun Z, Peng J, Zhan L (2007) Bioluminescent imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma in live mice. Biotechnol Lett 29:1665–1670
Wolters PJ, Collard HR, Jones KD (2014) Pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol 9:157–179
Yang L, Wang L, Yang X (2009) Disruption of Smad4 in mouse epidermis leads to depletion of follicle stem cells. Mol Biol Cell 20:882–890
Zhang J, Valianou M, Cheng JD (2010) Identification and characterization of the promoter of fibroblast activation protein. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 2:1154–1163
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Tao Zhou, Ms Weili Gong for performing in vivo BLI, Dr. Xing Huang for careful review of the manuscript. We would like to thank staff of the Institute of JingFeng Medical Laboratory Animal for animal husbandry. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31101679).
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Li Wenlong and Yang Leilei have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wenlong, L., Leilei, Y., Wei, F. et al. Luciferase expression is driven by the promoter of fibroblast activation protein-α in murine pulmonary fibrosis. Biotechnol Lett 37, 1757–1763 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1855-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1855-8