Abstract
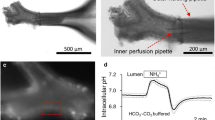
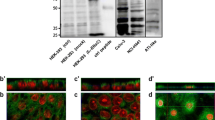
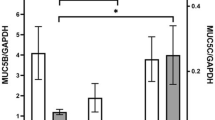
Airway epithelial cells prevent damaging effects of extracellular iron by taking up the metal and sequestering it within intracellular ferritin. Epithelial iron transport is associated with transcellular movement of other cations including changes in the expression or activity of Na, K-ATPase and epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC). Given this relationship between iron and Na+, we hypothesized that iron uptake by airway epithelial cells requires concurrent Na+ transport. In preliminary studies, we found that Na+-free buffer blocked iron uptake by human airway epithelial cell. Na+ channels inhibitors, including furosemide, bumetanide, and ethylisopropyl amiloride (EIPA) significantly decreased epithelial cell concentrations of non-heme iron suggesting that Na+-dependent iron accumulation involves generalized Na+ flux into the cells rather than participation of one or more specific Na+ channels. In addition, efflux of K+ was detected during iron uptake, as was the influx of phosphate to balance the inward movement of cations. Together, these data demonstrate that intracellular iron accumulation by airway epithelium requires concurrent Na+/K+exchange.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aisen P, Listowsky I (1980) Iron transport and storage proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 49:357–393
Aisen P, Leibman A, Zweier J (1978) Stoichiometric and site characteristics of the binding of iron to human transferrin. J Biol Chem 253:1930–1937
Assaf SY, Chung SH (1984) Release of endogenous Zn2+ from brain tissue during activity. Nature 308:734–736
Balla G, Jacob HS, Balla J, Rosenberg M, Nath K, Apple F, Eaton JW, Vercellotti GM (1992) Ferritin: a cytoprotective antioxidant strategem of endothelium. J Biol Chem 267:18148–18153
Biasio W, Chang T, McIntosh CJ, McDonald FJ (2004) Identification of Murr1 as a regulator of the human delta epithelial sodium channel. J Biol Chem 279:5429–5434
Ge SY, Ruan DY, Yu K, Chen JT, Wang M, Zhong GS (2001) Effects of Fe(2+) on ion channels: Na(+) channel, delayed rectified and transient outward K(+) channels. Food Chem Toxicol 39:1271–1278
Gorman AL, Hermann A (1979) Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurones. J Physiol 296:393–410
Gunshin H, Mackenzie B, Berger UV, Gunshin Y, Romero MF, Boron WF, Nussberger S, Gollan JL, Hediger MA (1997) Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature 388:482–488
Handy RD, Eddy FB, Baines H (2002) Sodium-dependent copper uptake across epithelia: a review of rationale with experimental evidence from gill and intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta 1566:104–115
Leinders T, van Kleef RG, Vijverberg HP (1992) Distinct metal ion binding sites on Ca(2+)-activated K + channels in inside-out patches of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1112:75–82
Mateos F, Brock JH, Perez-Arellano JL (1998) Iron metabolism in the lower respiratory tract. Thorax 53:594–600
Olakanmi O, McGowan SE, Hayek MB, Britigan BE (1993) Iron sequestration by macrophages decreases the potential for extracellular hydroxyl radical formation. J Clin Invest 91:889–899
Oudit GY, Sun H, Trivieri MG, Koch SE, Dawood F, Ackerley C, Yazdanpanah M, Wilson GJ, Schwartz A, Liu PP, Backx PH (2003) L-type Ca2+ channels provide a major pathway for iron entry into cardiomyocytes in iron-overload cardiomyopathy. Nat Med 9:1187–1194
Oudit GY, Trivieri MG, Khaper N, Liu PP, Backx PH (2006) Role of L-type Ca2+ channels in iron transport and iron-overload cardiomyopathy. J Mol Med 84:349–364
Pressley TA, Haber RS, Loeb JN, Edelman IS, Ismail-Beigi F (1986) Stimulation of Na, K-activated adenosine triphosphatase and active transport by low external K+ in a rat liver cell line. J Gen Physiol 87:591–606
Rafii B, Coutinho C, Otulakowski G, O’Brodovich H (2000) Oxygen induction of epithelial Na(+) transport requires heme proteins. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 278:L399–L406
Schroeder WH, Dobson M, Kane DM, Johnson ND (1987) Toxic trace elements associated with airborne particulate matter: a review. Japca 37:1267–1285
Thorstensen K, Romslo I (1990) The role of transferrin in the mechanism of cellular iron uptake. Biochem J 271:1–9
Tsushima RG, Wickenden AD, Bouchard RA, Oudit GY, Liu PP, Backx PH (1999) Modulation of iron uptake in heart by L-type Ca2+ channel modifiers: possible implications in iron overload. Circ Res 84:1302–1309
Turi JL, Yang F, Garrick MD, Piantadosi CA, Ghio AJ (2004) The iron cycle and oxidative stress in the lung. Free Radic Biol Med 36:850–857
van De Sluis B, Rothuizen J, Pearson PL, van Oost BA, Wijmenga C (2002) Identification of a new copper metabolism gene by positional cloning in a purebred dog population. Hum Mol Genet 11:165–173
Vijverberg HP, Leinders-Zufall T, van Kleef RG (1994) Differential effects of heavy metal ions on Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels. Cell Mol Neurobiol 14:841–857
Wang X, Ghio AJ, Yang F, Dolan KG, Garrick MD, Piantadosi CA (2002) Iron uptake and Nramp2/DMT1/DCT1 in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282:L987–L995
Winegar BD, Kelly R, Lansman JB (1991) Block of current through single calcium channels by Fe, Co, and Ni. Location of the transition metal binding site in the pore. J Gen Physiol 97:351–367
Yin W, Jiang G, Takeyasu K, Zhou X (2003) Stimulation of Na, K-ATPase by low potassium is dependent on transferrin. J Membr Biol 193:177–184
Zhou X, Yin W, Doi SQ, Robinson SW, Takeyasu K, Fan X (2003) Stimulation of Na, K-ATPase by low potassium requires reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285:C319–C326
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant 5K08HL081269–02 (J. L. Turi).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turi, J.L., Piantadosi, C.A., Stonehuerner, J.D. et al. Iron accumulation in bronchial epithelial cells is dependent on concurrent sodium transport. Biometals 21, 571–580 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9143-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9143-x