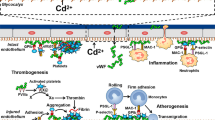
Abstract
Today cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the killer number one world wide. In 2004 an estimated 17.1 million people died due to CVDs and this number will further increase to an estimated 23.6 million by 2030. Importantly, currently known risk factors, like hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia, can only be made responsible for about 50–75% of all CVDs, highlighting the urgent need to search for and define new CVD risk factors. Cadmium (Cd) was shown to have the potential to serve as one such novel risk factor, as it was demonstrated—in vitro, in animal studies, and in human studies—that Cd causes atherosclerosis (the basis of most CVDs). Herein, we discuss the molecular and cellular biological effects of Cd in the cardiovascular system; we present concepts on the pathophysiology of Cd-caused atherosclerosis, and provide data that indicate an epidemiological relevance of Cd as a risk factor for CVDs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abouhamed M, Wolff NA, Lee WK et al (2007) Knockdown of endosomal/lysosomal divalent metal transporter 1 by RNA interference prevents cadmium-metallothionein-1 cytotoxicity in renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F705–F712
Abu-Hayyeh S, Sian M, Jones KG et al (2001) Cadmium accumulation in aortas of smokers. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:863–867
Agrawal A, Bhattacharya S (1989) Appearance of C-reactive protein (CRP) in serum and liver cytosol of cadmium-treated rats. Indian J Exp Biol 27:1024–1027
Alsberg C, Schwartze S (1919) Pharmacological action of cadmium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther
Bernhard D, Rossmann A, Wick G (2005) Metals in cigarette smoke. IUBMB Life 57:805–809
Bernhard D, Rossmann A, Henderson B et al (2006) Increased serum cadmium and strontium levels in young smokers: effects on arterial endothelial cell gene transcription. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:833–838
Bhatnagar A (2006) Environmental cardiology: studying mechanistic links between pollution and heart disease. Circ Res 99:692–705
Carraway MS, Suliman HB, Madden MC et al (2006) Metabolic capacity regulates iron homeostasis in endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 41:1662–1669
Crowther MA (2005) Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Prog 436–441
DiFrancesco D, Ferroni A, Visentin S et al (1985) Cadmium-induced blockade of the cardiac fast Na channels in calf Purkinje fibres. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 223:475–484
Dong Z, Wang L, Xu J et al (2009) Promotion of autophagy and inhibition of apoptosis by low concentrations of cadmium in vascular endothelial cells. Toxicol In Vitro 23:105–110
Erfurt C, Roussa E, Thevenod F (2003) Apoptosis by Cd2+ or CdMT in proximal tubule cells: different uptake routes and permissive role of endo/lysosomal CdMT uptake. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285:C1367–C1376
Eum KD, Lee MS, Paek D (2008) Cadmium in blood and hypertension. Sci Total Environ 407:147–153
Follmer CH, Lodge NJ, Cullinan CA et al (1992) Modulation of the delayed rectifier, IK, by cadmium in cat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol 262:C75–C83
Fujiwara Y, Watanabe S, Kaji T (1998) Promotion of cultured vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by low levels of cadmium. Toxicol Lett 94:175–180
Fujiwara Y, Kitagawa T, Shinkai Y et al (2009) Cilostazol induces metallothionein expression in vascular cells. Yakugaku Zasshi 129:1415–1422
Garlanda C, Dejana E (1997) Heterogeneity of endothelial cells. Specific markers. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17:1193–1202
Gosselet F, Candela P, Sevin E et al (2009) Transcriptional profiles of receptors and transporters involved in brain cholesterol homeostasis at the blood-brain barrier: use of an in vitro model. Brain Res 1249:34–42
Hanke H, Lenz C, Finking G (2001) The discovery of the pathophysiological aspects of atherosclerosis—a review. Acta Chir Belg 101:162–169
He L, Wang B, Hay EB et al (2009) Discovery of ZIP transporters that participate in cadmium damage to testis and kidney. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:250–257
Houtman JP (1993) Prolonged low-level cadmium intake and atherosclerosis. Sci Total Environ 138:31–36
Jamall IS, Naik M, Sprowls JJ et al (1989) A comparison of the effects of dietary cadmium on heart and kidney antioxidant enzymes: evidence for the greater vulnerability of the heart to cadmium toxicity. J Appl Toxicol 9:339–345
Jung YS, Jeong EM, Park EK et al (2008) Cadmium induces apoptotic cell death through p38 MAPK in brain microvessel endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol 578:11–18
Kadar A, Glasz T (2001) Development of atherosclerosis and plaque biology. Cardiovasc Surg 9:109–121
Kaji T (2004) Cell biology of heavy metal toxicity in vascular tissue. Yakugaku Zasshi 124:113–120
Kaji T, Mishima A, Koyanagi E et al (1992) Possible mechanism for zinc protection against cadmium cytotoxicity in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Toxicology 76:257–270
Kaji T, Mishima A, Yamamoto C et al (1993a) Zinc protection against cadmium-induced destruction of the monolayer of cultured vascular endothelial cells. Toxicol Lett 66:247–255
Kaji T, Yamamoto C, Tsubaki S et al (1993b) Metallothionein induction by cadmium, cytokines, thrombin and endothelin-1 in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Life Sci 53:1185–1191
Kaji T, Mishima A, Yamamoto C et al (1996) Bismuth induces metallothionein but does not protect against cadmium cytotoxicity in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 56:630–634
Kara H, Karatas F, Canatan H et al (2005) Effects of exogenous metallothionein on acute cadmium toxicity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 104:223–232
Kisling GM, Kopp SJ, Paulson DJ et al (1993) Cadmium-induced attenuation of coronary blood flow in the perfused rat heart. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 118:58–64
Knoflach M, Kiechl S, Penz D et al (2009) Cardiovascular risk factors and atherosclerosis in young women: atherosclerosis risk factors in female youngsters (ARFY study). Stroke 40:1063–1069
Kolakowski J, Baranski B, Opalska B (1983) Effect of long-term inhalation exposure to cadmium oxide fumes on cardiac muscle ultrastructure in rats. Toxicol Lett 19:273–278
Kundu S, Sengupta S, Chatterjee S et al (2009) Cadmium induces lung inflammation independent of lung cell proliferation: a molecular approach. J Inflamm (Lond) 6:19
Kyselovic J, Martinka P, Batova Z et al (2005) Calcium channel blocker inhibits Western-type diet-evoked atherosclerosis development in ApoE-deficient mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:320–328
Lag M, Westly S, Lerstad T et al (2002) Cadmium-induced apoptosis of primary epithelial lung cells: involvement of Bax and p53, but not of oxidative stress. Cell Biol Toxicol 18:29–42
Lee WK, Thevenod F (2008) Novel roles for ceramides, calpains and caspases in kidney proximal tubule cell apoptosis: lessons from in vitro cadmium toxicity studies. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1323–1332
Lepeshkevich SV, Dzhagarov BM (2009) Effect of zinc and cadmium ions on structure and function of myoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794:103–109
Liu F, Jan KY (2000) DNA damage in arsenite- and cadmium-treated bovine aortic endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 28:55–63
Majumder S, Muley A, Kolluru GK et al (2008) Cadmium reduces nitric oxide production by impairing phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Biochem Cell Biol 86:1–10
Mallika V, Goswami B, Rajappa M (2007) Atherosclerosis pathophysiology and the role of novel risk factors: a clinicobiochemical perspective. Angiology 58:513–522
Martynowicz H, Skoczynska A, Wojakowska A et al (2004) Serum vasoactive agents in rats poisoned with cadmium. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 17:479–485
Messner B, Knoflach M, Seubert A et al (2009) Cadmium is a novel and independent risk factor for early atherosclerosis mechanisms and in vivo relevance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1392–1398
Miller KA, Siscovick DS, Sheppard L et al (2007) Long-term exposure to air pollution and incidence of cardiovascular events in women. N Engl J Med 356:447–458
Mlynek V, Skoczynska A (2005) The proinflammatory activity of cadmium. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 59:1–8
Moll UM, Wolff S, Speidel D et al (2005) Transcription-independent pro-apoptotic functions of p53. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:631–636
Nakagawa H, Nishijo M (1996) Environmental cadmium exposure, hypertension and cardiovascular risk. J Cardiovasc Risk 3:11–17
Navas-Acien A, Silbergeld EK, Sharrett R et al (2005) Metals in urine and peripheral arterial disease. Environ Health Perspect 113:164–169
Ozturk IM, Buyukakilli B, Balli E et al (2009) Determination of acute and chronic effects of cadmium on the cardiovascular system of rats. Toxicol Mech Methods 19:308–317
Park SL, Kim YM, Ahn JH et al (2009) Cadmium stimulates the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and JNK activation in cerebrovascular endothelial cells. J Pharmacol Sci 110:405–409
Pearce LL, Wasserloos K, St Croix CM et al (2000) Metallothionein, nitric oxide and zinc homeostasis in vascular endothelial cells. J Nutr 130:1467S–1470S
Pearson CA, Lamar PC, Prozialeck WC (2003) Effects of cadmium on E-cadherin and VE-cadherin in mouse lung. Life Sci 72:1303–1320
Peters JL, Perlstein TS, Perry MJ et al (2010) Cadmium exposure in association with history of stroke and heart failure. Environ Res
Plusquin M, Nawrot TS, Staessen JA (2005) Peripheral arterial disease and metals in urine and blood. Environ Health Perspect 113:A510–A511; author reply A511
Prentice RC, Hawley PL, Glonek T et al (1984) Calcium-dependent effects of cadmium on energy metabolism and function of perfused rat heart. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 75:198–210
Prozialeck WC, Edwards JR, Woods JM (2006) The vascular endothelium as a target of cadmium toxicity. Life Sci 79:1493–1506
Prozialeck WC, Edwards JR, Nebert DW et al (2008) The vascular system as a target of metal toxicity. Toxicol Sci 102:207–218
Rogalska J, Brzoska MM, Roszczenko A et al (2009) Enhanced zinc consumption prevents cadmium-induced alterations in lipid metabolism in male rats. Chem Biol Interact 177:142–152
Ross R (1995) Cell biology of atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Physiol 57:791–804
Ross R (1997) Cellular and molecular studies of atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis 131(Suppl):S3–S4
Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340:115–126
Ross R, Glomset JA (1973) Atherosclerosis and the arterial smooth muscle cell: proliferation of smooth muscle is a key event in the genesis of the lesions of atherosclerosis. Science 180:1332–1339
Sacerdote FL, Cavicchia JC (1983) Ultrastructural effects of cadmium on the rat epididymis. Int J Androl 6:533–540
Sarkar S, Yadav P, Trivedi R et al (1995) Cadmium-induced lipid peroxidation and the status of the antioxidant system in rat tissues. J Trace Elem Med Biol 9:144–149
Schutte R, Nawrot T, Richart T et al (2008) Arterial structure and function and environmental exposure to cadmium. Occup Environ Med 65:412–419
Shen JB, Jiang B, Pappano AJ (2000) Comparison of L-type calcium channel blockade by nifedipine and/or cadmium in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:562–570
Shukla A, Shukla GS, Srimal RC (1996) Cadmium-induced alterations in blood-brain barrier permeability and its possible correlation with decreased microvessel antioxidant potential in rat. Hum Exp Toxicol 15:400–405
Simovich MJ, Conrad ME, Umbreit JN et al (2002) Cellular location of proteins related to iron absorption and transport. Am J Hematol 69:164–170
Skalen K, Gustafsson M, Rydberg EK et al (2002) Subendothelial retention of atherogenic lipoproteins in early atherosclerosis. Nature 417:750–754
Steffensen IL, Mesna OJ, Andruchow E et al (1994) Cytotoxicity and accumulation of Hg, Ag, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in human peripheral T and B lymphocytes and monocytes in vitro. Gen Pharmacol 25:1621–1633
Subramanyam G, Bhaskar M, Govindappa S (1992) The role of cadmium in induction of atherosclerosis in rabbits. Indian Heart J 44:177–180
Szuster-Ciesielska A, Lokaj I, Kandefer-Szerszen M (2000a) The influence of cadmium and zinc ions on the interferon and tumor necrosis factor production in bovine aorta endothelial cells. Toxicology 145:135–145
Szuster-Ciesielska A, Stachura A, Slotwinska M et al (2000b) The inhibitory effect of zinc on cadmium-induced cell apoptosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in cell cultures. Toxicology 145:159–171
Tedgui A, Mallat Z (2001) Apoptosis as a determinant of atherothrombosis. Thromb Haemost 86:420–426
Teleman O, Drakenberg T, Forsen S et al (1983) Calcium and cadmium binding to troponin C. Evidence for cooperativity. Eur J Biochem 134:453–457
Tellez-Plaza M, Navas-Acien A, Crainiceanu CM et al (2008) Cadmium exposure and hypertension in the 1999–2004 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Environ Health Perspect 116:51–56
Tomera JF, Lilford K, Kukulka SP et al (1994) Divalent cations in hypertension with implications to heart disease: calcium, cadmium interactions. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 16:97–107
Wang Y, Fang J, Leonard SS et al (2004) Cadmium inhibits the electron transfer chain and induces reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 36:1434–1443
Wang SH, Shih YL, Kuo TC et al (2009a) Cadmium toxicity toward autophagy through ROS-activated GSK-3beta in mesangial cells. Toxicol Sci 108:124–131
Wang SH, Shih YL, Lee CC et al (2009b) The role of endoplasmic reticulum in cadmium-induced mesangial cell apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact 181:45–51
WHO (2009) Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). In: WHO (ed). Fact sheet N 317. WHO
Wolf MB, Baynes JW (2007) Cadmium and mercury cause an oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction. Biometals 20:73–81
Wolff NA, Lee WK, Abouhamed M et al (2008) Role of ARF6 in internalization of metal-binding proteins, metallothionein and transferrin, and cadmium-metallothionein toxicity in kidney proximal tubule cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 230:78–85
Woods JM, Leone M, Klosowska K et al (2008) Direct antiangiogenic actions of cadmium on human vascular endothelial cells. Toxicol In Vitro 22:643–651
Xu G, Zhou G, Jin T et al (1999) Apoptosis and p53 gene expression in male reproductive tissues of cadmium exposed rats. Biometals 12:131–139
Yamamoto C, Kaji T, Sakamoto M et al (1996) Effects of cadmium on the release of tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 from cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts. Toxicology 106:179–185
Yang PM, Chen HC, Tsai JS et al (2007) Cadmium induces Ca2+-dependent necrotic cell death through calpain-triggered mitochondrial depolarization and reactive oxygen species-mediated inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activity. Chem Res Toxicol 20:406–415
Yoopan N, Watcharasit P, Wongsawatkul O et al (2008) Attenuation of eNOS expression in cadmium-induced hypertensive rats. Toxicol Lett 176:157–161
Yuan C, Kadiiska M, Achanzar WE et al (2000) Possible role of caspase-3 inhibition in cadmium-induced blockage of apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 164:321–329
Zikic RV, Stajn AS, Ognjanovic BI et al (1998) The effect of cadmium and selenium on the antioxidant enzyme activities in rat heart. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 17:259–264
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank Mrs. Rajam Csordas-Iyer for correction of the English language. This project was supported by the Austrian National Bank (Project # 12697 to D.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Messner, B., Bernhard, D. Cadmium and cardiovascular diseases: cell biology, pathophysiology, and epidemiological relevance. Biometals 23, 811–822 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9314-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9314-4