Abstract
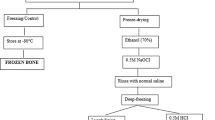
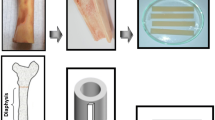
New sterilization methods for human bone allografts may lead to alterations in bone mechanical properties, which strongly influence short- and medium-term outcomes. In many sterilization procedures, bone allografts are subjected to gamma irradiation, usually with 25 KGy, after treatment and packaging. We used speed-of-sound (SOS) measurements to evaluate the effects of gamma irradiation on bone. All bone specimens were subjected to the same microbial inactivation procedure. They were then separated into three groups, of which one was treated and not irradiated and two were exposed to 10 and 25 KGy of gamma radiation, respectively. SOS was measured using high- and low-frequency ultrasound beams in each orthogonal direction. SOS and Young modulus were altered significantly in the three groups, compared to native untreated bone. Exposure to 10 or 25 KGy had no noticeable effect on the study variables. The impact of irradiation was small compared to the effects of physical or chemical defatting. Reducing the radiation dose used in everyday practice failed to improve graft mechanical properties in this study.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abendstein W, Hyatt GW (1970) Ultrasonics and selected properties of bone. Clin Orthop Rel Res 69:294–301
Ashman RB, Corin JD, Turner CH (1987) Elastic properties of cancellous bone: measurement by an ultrasonic technique. J Biomech 20:979–986
Anderson MJ, Keyak JH, Skinner HB (1992) Compressive mechanical properties of human cancellous bone after gamma irradiation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 74(5):747–752
Brown TD, Ferguson AB (1980) Mechanical property distributions in the cancellous bone of the human proximal femur. Acta Orthop Scand 31:429–437
Carter D, Hayes WC (1976) Bone compressive strength: the influence of density and strain rate. Science 194:1174–1175
Chappard D, Fressonnet C, Genty C, Baslé MF, Rebel A (1993) Fat in bone xenografts: importance of the purification procedures on cleanliness, wettability and biocompatibility. Biomaterials 14:507–512
Cornu O, Banse X, Docquier PL, Luyckx S, Delloye C (2000) Effect of freeze drying and gamma irradiation on the mechanical properties of human cancellous bone. J Orthop Res 18:426–431
Crowninshield RD, Brand RA, Pedersen DR (1983) A stress analysis of acetabular reconstruction in protrusio acetabuli. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65A:495–499
Deligianni DD, Maris A, Missirlis YF (1994) Stress relaxation behaviour of trabecular bone specimens. J Biomech 27:1469–1476
Grieb TA, Forng RY, Stafford RE, Lin J, Almeida J, Bogdansky S, Ronholdt C, Drohan WN, Burgess WH (2005) Effective use of optimized, high dose (50 KGy) gamma irradiation for pathogen inactivation of human bone allograft. Biomaterials 26:2033–2042
Kalus U, Muller H, Baudisch H, Birkhahn HJ, Von Versen R, Hansen A, Pruss A (2005) A Method for the determination of the residual chloroform in defatted bone transplants. Cell Tissue Bank 6:71–75
Hodgkinson R, Njeh CF, Currey JD, Langton CM (1997) The ability of ultrasound velocity to predict the stiffness of cancellous bone in vitro. Bone 21:183–190
Loty B, Courpied JP, Tomeno B, Postel M, Forest M, Abelanet R (1990) Radiation sterilized bone allografts. Int Orthop 14:237–242
Mitton D, Rappeneau J, Bardonnet R (2005) Effect of a supercritical CO2 based treatment on mechanical properties of human cancellous bone. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 15:264–269
Mroz TE, Lin EL, Summit MC, Bianchi JR, Keesling JE, Roberts M, Vangness CT, Wang JC (2006) Biomechanical analysis of allograft bone treated with a novel tissue sterilization process. Spine 6:34–39
Njeh CF, Kuo CW, Langton CM, Atrah HL, Boivin CM (1997) Prediction of human femoral bone strength using ultrasound velocity and BMD: an in vitro study. Osteoporos Int 7:471–77
Oonishi Hironibu, Isha Hideo, Hasegawa Tatsuhiko (1983) Mechanical analysis of the human pelvis and its application to the artificial hip joint—By means of the three dimensional finite element method. J Biomech 16:427–444
Poumarat G, Squire P (1993) Comparison of mechanical properties of human, bovine bone and a new processed xenograft. Biomaterials 14:337–340
Smith CB, Smith DA (1976) Relation between age, mineral density and mechanical properties of human femoral compacta. Acta Orthop Scand 47:496–402
Smith RA, Ingels J, Locheness JJ, Dutkowsky JP, Pifer LL (2001) Gamma irradiation of HIV-1. J Orthop Res 19:815–819
Vastel L, Meunier A, Siney H, Sedel L, Courpied JP (2004) Effect of different sterilization methods on the mechanical properties of human cancellous bone allografts. Biomaterials 25:2105–2110
Weaver JK, Chalmers J (1966) Cancellous bone: its strength and changes with aging and an evaluation of some methods for measuring its mineral contents. J Bone Joint Surg Am 48A:289–299
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vastel, L., Masse, C., Crozier, E. et al. Effects of gamma irradiation on mechanical properties of defatted trabecular bone allografts assessed by speed-of-sound measurement. Cell Tissue Banking 8, 205–210 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-006-9030-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-006-9030-z