Abstract
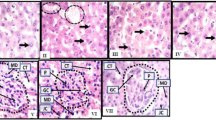
Bromobenzene is a well-known environmental toxin which causes liver and kidney damage through CYP450-mediated bio-activation to generate reactive metabolites and, consequently, oxidative stress. The present study aimed to evaluate the possible protective role of withaferin A against bromobenzene-induced liver and kidney damage in mice. Withaferin A (10 mg/kg) was administered orally to the mice for 8 days before intragastric intubation of bromobenzene (10 mmol/kg). As results of this experiment, the levels of liver and kidney functional markers, lipid peroxidation, and cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β) presented an increase and there was a decrease in anti-oxidant activity in the bromobenzene-treated group of mice. Pre-treatment with withaferin A not only significantly decreased the levels of liver and kidney functional markers and cytokines but also reduced oxidative stress, as evidenced by improved anti-oxidant status. In addition, the mitochondrial dysfunction shown through the decrease in the activities of mitochondrial enzymes and imbalance in the Bax/Bcl-2 expression in the livers and kidneys of bromobenzene-treated mice was effectively prevented by pre-administration of withaferin A. These results validated our conviction that bromobenzene caused liver and kidney damage via mitochondrial pathway and withaferin A provided significant protection against it. Thus, withaferin A may have possible usage in clinical liver and kidney diseases in which oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction may be existent.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amacher DE. A toxicologist’s guide to biomarkers of hepatic response. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2002;21:253–62.
Bargagna-Mohan P, Paranthan RR, Hamza A, Dimova N, Trucchi B, Srinivasan C, et al. Withaferin A targets intermediate filaments glial fibrillary acidic protein and vimentin in a model of retinal gliosis. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:7657–69.
Bell JL, Baron DN. A colorimetric method for determination of isocitrate dehydrogenase. Clin Chem Acta. 2001;5:740–7.
Berghe WV, Sabbe L, Kaileh M, Haegeman G, Heyninck K. Molecular insight in the multifunctional activities of withaferin A. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;84(10):1282–91.
Bonting SL. Presence of enzyme system in mammalian tissues. In: Bilter EE, editor. Membrane and ion transport. London: Wiley Inter Science; 1970. p. 257–63.
Bruchajzer E, Szymanska J, Piotrowski JK. Acute and subacute nephrotoxicity of 2-bromophenol in rats. Toxicol Lett. 2002;134:245–52.
Chen G. Goeddel DV.TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science. 2002;296:1634–5.
Dey D, Sunetra C, Nitin A, Deepa C. Acute and chronic toxicity, cytochrome P450 enzyme inhibition, and hERG channel blockade studies with a polyherbal, ayurvedic formulation for inflammation. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 1–9.
Dykens JA, Will Y. The significance of mitochondrial toxicity testing in drug development. Drug Discov Today. 2008;12:777–85.
Evans DJ. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase of E. coli activation by calcium ions and inhibition by monovalent cations. J Bacteriol. 1969;100(2):914–22.
Fiske CH, Subbarow Y. The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem. 1925;66:375–400.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972;18:499–502.
Gaur U, Aggarwal BB. Regulation of proliferation, survival and apoptosis by members of the TNF superfamily. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;66:1403–8.
Gilmore TD. Introduction to NF-jB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene. 2006;25:6680–4.
Gopi S, Setty OH. Beneficial effect of the administration of Hemidesmus indicus against bromobenzene induced oxidative stress in rat liver mitochondria. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;127:200–20.
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB. Glutathione-S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1974;249:7130–9.
Hamed MA, El-Rigal NS, Ali SA. Effects of black seed oil on resolution of hepato-renal toxicity induced by bromobenzene in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17:569–81.
Heijne WHM, Stierum RH, Slijper M, Bladeren PJ, Ommen B. Toxicogenomics of bromobenzene hepatotoxicity: a combined transcriptomics and proteomics approach. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;65:857–75.
Heijne WH, Slitt AL, van Bladeren PJ, Groten JP, Klaassen CD, Stierum RH, et al. Bromobenzene-induced hepatotoxicity at the transcriptome level. Toxicol Sci. 2004;79(2):411–22.
Hjertan S, Pan H. Purification and characterization of two forms of a low affinity Ca2+-ATPase from erythrocyte membranes. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1983;728(2):281–8.
Johnson D, Lardy H. Isolation of liver or kidney mitochondria. In: Methods in enzymology. London: Academic; 1981. p. 94–96.
Kaushal R, Dave KR, Katyare SS. Paracetamol hepatotoxicity and microsomal function. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 1999;7:67–74.
Koen YM, Williams TD, Hanzlik RP. Identification of three protein targets for reactive metabolites of bromobenzene in rat liver cytosol. Chem Res Toxicol. 2000;13(12):1326–35.
Lind CL, Gandolfi AJ. Hepatoprotection by dimethyl sulfoxide. II. Characterization of optimal dose and the latest time of administration for effective protection against chloroform and bromobenzene induced injury. Exp Toxic Pathol. 1999;51:537–43.
Liu X, Qi W, Cooke LS, Kithsiri Wijeratne EM, Xu YM, Marron MT, et al. An analog of withaferin A activates the MAPK and glutathione “stress” pathways and inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Invest. 2011;29(10):668–75. doi:10.3109/07357907.2011.626478.
Mahima V, Rasool M, Sabina EP. Amelioration of bromobenzene hepatotoxicity by Withania somnifera pretreatment: role of mitochondrial oxidative stress. Toxicol Rep. 2014a;1:629–38.
Mahima V, Rasool MK, Sabina EP. Protective effect of Withania somnifera against bromobenzene-induced nephrotoxicity and mitochondrial oxidative stress in rats. Ren Fail. 2014b;36(7):1095–103.
Marklund SL, Marklund G. Involvement of superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem. 1974;47:469–74.
Mehler AH, Kornberg A, Grisolia S, Ochoa S. The enzymatic mechanism of oxidation-reductions between malate or isocitrate and pyruvate. J Biol Chem. 1948;174:961–77.
Minakami S, Ringler RL, Singer TP. Studies on the respiratory chain-linked dihydrodiphosphopyridine nucleotide dehydrogenase. I. Assay of the enzyme in particulate and in soluble preparation. J Biol Chem. 1962;237:569–76.
Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B. Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione-S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1979;582:67–78.
Ohinishi T, Suzuki T, Suzuki Y, Ozawa K. A comparative study of plasma membrane Mg2+-ATPase activities in normal, regenerating and malignant cells. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1982;684(1):67–74.
Ohkawa H, Ohish N, Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid. Anal Biochem. 1997;95:351–8.
Pearl W, Cascarano J, Zweifach BW. Microdetermination of cytochrome oxidase in rat tissues by the oxidation of N-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine or ascorbic acid. J Histochem Cytochem. 1963;2:102–4.
Ravirajsinh NJ, Nathalie HU, Suchismita D, Sandeep K, Neeraj KS. Withaferin-A reduces acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015;97:122–32.
Reed LJ, Mukherjee RB. α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex from Escherichia coli. In: Colowick SP, Kaplon NO, editors. Methods in enzymology, vol. 13. New York: Academic; 1969. p. 53–61.
Rotruk JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra WG. Selenium, biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase purification and assay. Science. 1973;17:588–90.
Sabina EP, Chandal S, Rasool MK. Inhibition of monosodium urate crystal-induced inflammation by withaferin A. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2008;11:46–55.
Sinha AK. Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem. 1974;147:389–94.
Slater EC, Bonner WDJ. The effect of fluoride on succinic oxidase system. Biochemistry. 1952;52:185–95.
So-Jung P, Kufareva I, Abagyan R. Improved docking, screening and selectivity prediction for small molecule nuclear receptor modulators using conformational ensembles. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2010;24:459–71.
Sunderman WF, Nomoto S. Measurement of human serum ceruloplasmin by its p-phenylenediamine oxidase activity. Clin Chem. 1970;16(11):903–10.
Szymanaska JA. Hepatotoxicity of brominated benzenes: relationship between chemical structure and hepatotoxic effects in acute intoxication of mice. Arch Toxicol. 1998;72:97–103.
Tsai CF, Hsu YW, Chen WK, Chang WH, Yen CC, Ho YH, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of electrolyzed reduced water against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009;27:2031–6.
Xu C, Li CYT, Kong ANT. Induction of phase I, II and III drug metabolism/transport by xenobiotics. Arch Pharm Res. 2005;28(3):249–68.
Yang J, Dongmei L, Weixin J, Hans-Uwe D, Lan WB. Effects of cadmium on lipid storage and metabolism in the freshwater crab Sinopotamon henanense. Plos One. 2013;8(10).
Yokota Y, Bargagna-Mohan P, Ravindranath PP, Kim KB, Mohan R. Development of withaferin A analogs as probes of angiogenesis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006;16:2603–7.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the VIT University for the infrastructure and support provided for the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Experimental procedure for the present study has been approved by the ethical committee (VIT/IAEC/VII th/17) of the VIT University, Vellore, India.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vedi, M., Sabina, E.P. Assessment of hepatoprotective and nephroprotective potential of withaferin A on bromobenzene-induced injury in Swiss albino mice: possible involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation. Cell Biol Toxicol 32, 373–390 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-016-9340-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-016-9340-2