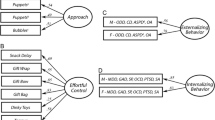
Abstract
Co-occurring internalizing and externalizing disorders are moderately prevalent in children, adolescents, and adults (Anderson, Williams, McGee, & Silva, 1987; McConaughy & Skiba, 1994), but much remains to be understood regarding why some children show “pure” versus co-occurring internalizing and externalizing symptoms. One possible influence that has previously not been considered is the failure to attain socio-developmental milestones, which paradoxically may prevent the development of co-occurring symptoms for some children. The present study proposes a model in which failure to attain relevant socio-developmental milestones might explain why some children may not develop heterotypic co-occurring symptoms. Specifically, it is proposed that specific clusters of internalizing symptoms (i.e., high social anxiety, withdrawal, and inhibition) and externalizing symptoms (i.e., high impulsivity, hyperactivity, and emotional reactivity) may be associated with the failure to attain socio-developmental milestones (i.e., poor peer relations for anxious children, lack of self-reflection and evaluation for impulsive/reactive children) that, in turn, may prevent subgroups of children from developing co-occurring, heterotypic symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, C., & Hammen, C. (1993). Psychosocial outcomes of children of unipolar depressed, bipolar, medically ill, and normal women: A longitudinal study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 61, 448–454.
Anderson, J., Williams, S., McGee, R. & Silva, P. (1987). DSM-III disorders in preadolescent children: Prevalence in a large sample from the general population. Archives of General Psychiatry, 44, 69–76.
Angold, A., & Costello, E. (1992). Comorbidity in children and adolescents with depression. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 1, 31–51.
Angold, A., & Costello, E. (1993). Depressive comorbidity in children and adolescents: Empirical, theoretical, and methodological issues. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 150, 1779–1791.
Angold, A., Costello, E., & Erkanli, A. (1999). Comorbidity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 40(1), 57–87.
Bates, J., Petit, G., Dodge, K., & Ridge, B. (1998). Interaction of temperamental resistance to control and restrictive parenting in the development of externalizing behavior. Developmental Psychology, 34(5), 982–995.
Baumeister, R., Smart, L., & Boden, J. (1996). Relation of threatened egotism to violence and aggression: The dark side of high self-esteem. Psychological Review, 103(1), 5–33.
Beidel, D., & Turner, S. (1997). At risk for anxiety: I. Psychopathology in the offspring pure vs. co-occurring 37 of anxious parents. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36, 918–924.
Beyers, J., & Loeber, R. (2003). Untangling developmental relations between depressed mood and delinquency in male adolescents. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 31(3), 247–266.
Biederman, J., Faraone, S., Mick, E., & Lelon, E. (1995). Psychiatric comorbidity among referred juveniles with major depression: Fact or artifact. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 34(5), 579–591.
Biederman, J., Newcorn, J., & Sprich, S. (1991). Comorbidity of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder with conduct, depressive, anxiety and other disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry, 148, 564–577.
Bogels, S., & Zigerman, D. (2000). Dysfunctional cognitions in children with social phobia, separation anxiety disorder, and generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28(2), 205–216.
Cairns, R., Cairns, B., Neckerman, H., Gest, S., & Gariepy, J. (1988). Social networks and aggressive behavior: Peer support or peer rejection? Developmental Psychology, 24, 815–823.
Calkins, S., Gill, K., & Wilford, A. (1999). Externalizing problems in two year olds: Implications for patterns of social behavior and peers' responses to aggression. Early Education and Development, 10(3), 267–288.
Campbell, S. (1994). Hard-to-manage preschool boys: Externalizing behavior, social pure vs. co-occurring 38 competence and family context at two-year follow-up. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 22, 147–166.
Capaldi, D. (1992). Co-occurrence of conduct problems and depressive symptoms in early adolescent boys: II. A 2-year follow-up at Grade 8. Development and Psychopathology, 4, 125–144.
Caron, C., & Rutter, M. (1991). Comorbidity in child psychopathology: Concepts, issues and research strategies. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 32(7), 1063–1080.
Coie, J., & Dodge, K. (1988). Multiple sources of data on social behavior and social status in the school: A cross-age comparison. Child Development, 59, 815–829.
Coie, J., Lochman, J., Terry, R., & Hyman, C. (1992). Predicting early adolescent disorder from childhood aggression and peer rejection. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60(5), 783–792.
Colder, C., Lochman, J., & Wells, K. (1997). The moderating effects of children's fear and activity level on relations between parenting practices and childhood symptoms. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 25, 251–263.
Cole, D., & Carpentieri, S. (1990). Social status and the comorbidity of child depression and conduct disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 58(6), 748–757.
Connor, D., Edwards, G., Fletcher, K., Baird, J., Barkley, R., & Steingard, R. (2003). Correlates of comorbid psychopathology in children with ADHD. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 42(2), 193–200.
Costello, E., Angold, A., Burns, B., Stangl, D., Tweed, D., Erkanli, A., Worthman, C. (1996). The Great Smoky Mountains Study of youth: Goals, design, methods, and the prevalence of DSM-III-R disorders. Archives of General Psychiatry, 53(12), 1129–1136.
Costello, E., Costello, A., Edelbrock, C., Burns, B., Dulcan, M., Brent, D., & Janiszewski, S. (1988). Psychiatric disorders in pediatric primary care: prevalence and risk factors. Archives of General Psychiatry, 45, 1107–1116.
Crick, N., & Ladd, G. (1993). Children's perceptions of their peer experiences: Attributions, loneliness, social anxiety, and social avoidance. Developmental Psychology, 29, 244–254.
Cunningham, C. E., Siegel, L. S., & Offord, D. R. (1991). A dose-response analysis of the effects of methylphenidate on the peer interactions and simulated classroom performance of ADD children with and without conduct problems. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 32, 439–452.
Dadds, M., Barrett, P., Rapee, R., & Ryan, S. (1996). Family process and child anxiety and aggression: An observational analysis. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 24(6), 715–734.
Dadds, M., Sanders, M., Morrison, M., & Rebgetz, M. (1992). Childhood depression and conduct disorder: II. An analysis of family interaction patterns in the home. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 101(3), 505–513.
Daleiden, E., & Vasey, M. (1997). An information-processing perspective on childhood anxiety. Clinical Psychology Review, 17(4), 407–429.
DeKlyen, M., Speltz, M., & Greenberg, M. (1998). Fathering and early onset conduct problems: Positive and negative parenting, father-son attachment, and the marital context. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 1, 3–21.
Dodge, K., & Frame, C. (1982). Social cognitive biases and deficits in aggressive boys. Child Development, 53, 620–635.
Dubow, E. (1988). Aggressive behavior and peer social status of elementary school children. Aggressive Behavior, 14, 315–324.
Edens, J., Cavell, T., & Hughes, J. (1999). The self-systems of aggressive children: A cluster-analytic investigation. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 40(3), 441–453.
Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R., Guthrie, I., & Reiser, M. (2000). Dispositional emotionality and regulation: Their role in predicting quality of social functioning. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78, 136–157.
Epkins, C. (2000). Cognitive specificity in internalizing and externalizing problems in community and clinic-referred children. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 29(2), 199–208.
Felson, R. (1989). Parents and the reflected appraisal process: A longitudinal analysis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 56, 965–971.
Fergusson, D., Lynskey, M., & Horwood, L. (1996). Factors associated with continuity and change in disruptive behavior patterns between childhood and adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 24, 533–553.
France-Kaatrude, A., & Smith, W. (1985). Social comparison, task motivation, and the pure vs. co-occurring 41 development of self-evaluative standards in children. Developmental Psychology, 21(6), 1080–1089.
French, D. (1988). Heterogeneity of peer-rejected boys: Aggressive and nonaggressive subtypes. Child Development, 59, 976–985.
Frick, P., & Ellis, M. (1999). Callous-unemotional traits and subtypes of conduct disorder. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 2(3), 149–168.
Frick, P. Lilienfeld, S., Ellis, M., Loney, B., & Silverthorn, P. (1999). The association between anxiety and psychopathy dimensions in children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 27(5), 382–392.
Gabel, S., Schmitz, S., & Fulker, D. (1996). Comorbidity in hyperactive children: Issues related to selection bias, gender, severity, and internalizing symptoms. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 27, 15–28.
Gazelle, H., & Ladd, G. (2003). Anxious solitude and peer exclusion: A diathesis-stress model of internalizing trajectories in childhood. Child Development, 74(1), 257–279.
Gilliom, M., & Shaw, D. S. (2004). Co-development of externalizing and internalizing problems in early childhood. Development and Psychopathology, 16(2), 313–333.
Ginsburg, G., LaGreca, A., & Silverman, W. (1998). Social anxiety in children with anxiety disorders: Relation with social and emotional functioning. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 26(3), 175–186.
Gjone, J., & Stevenson, J. (1997). The association between internalizing and externalizing behavior in childhood and early adolescence: Genetic or pure vs. co-occurring 42 environmental common influences? Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 25(4), 277–297.
Goodman, S., Adamson, L., Rinti, J., & Cole, S. (1994). Mother's expressed attitudes: Associations with maternal depression and children's self-esteem and psychopathology. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 33, 1265–1274.
Goodyer, I., Wright, C., & Altham, P. (1989). Recent friendships in anxious and depressed school age children. Psychological Medicine, 19, 165–174.
Guerin, D., Gottfriend, A., & Thomas, C. (1997). Difficult temperament and behaviour problems: A longitudinal study from 1.5 to 12 years. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 21, 71–90.
Guerra, N., Huesmann, L., Tolan, P., Van Acker, R., & Eron, L. (1995). Stressful events and individual beliefs as correlates of economic disadvantage and aggression among urban children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 63, 518–528.
Haapasalo, J., & Tremblay, R. (1994). Physically aggressive boys from ages 6 to 12: Family background, parenting behavior, and prediction of delinquency. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62(5), 1044–1052.
Hammen, C., & Compas, B. (1994). Unmasking unmasked depression in children and adolescents: The problem of comorbidity. Clinical Psychology Review, 14, 585–603.
Hammen, C., & Zupan, B. (1984). Self-schemas, depression, and the processing of pure vs. co-occurring 43 personal information in children. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 37, 598–608.
Hankin, B., & Abramson, L. (2001). Development of gender differences in depression: An elaborated cognitive vulnerability-transactional stress theory. Psychological Bulletin, 127, 773–796.
Hecht, D., Inderbitzen, H., & Bukowski, A. (1998). The relationship between peer status and depressive symptoms in children and adolescents. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 26(2), 153–161.
Heim, C & Nemeroff, C. (1999). The impact of early adverse experiences on brain systems involved in the pathophysiology of anxiety and affective disorders. Biological Psychiatry, 46(11), 1509–1522.
Henry, B., Caspi, A., Moffitt, T., & Silva, P. (1996). Temperamental and familial predictors of violent and nonviolent criminal convictions: Age 3 to age 18. Developmental Psychology, 32, 614–623.
Hinshaw, S. (1992). Academic underachievement, attention deficits, and aggression: Comorbidity and implications for intervention. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60, 893–903.
Hoza, B., Pelham, W. E., Dobbs, J., Owens, J. S., & Pillow, D. R. (2002). Do boys with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder have positive illusory self-concepts? Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 111, 268–278.
Hoza, B., Pelham, W. E., Milich, R., Pillow, D., & McBride, K. (1993). The self-perceptions and attributions of attention deficit hyperactivity disordered and pure vs. co-occurring 44 nonreferred boys. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 21, 271–286.
Hughes, J., Cavell, T., & Grossman, P. (1997). A positive view of self: Risk or protection for aggressive children? Development and Psychopathology, 9, 75–94.
Ialongo, N., Edelsohn, G., Werthamer-Larsson, L., & Crockett, L. (1996). The course of aggression in first-grade children with and without comorbid anxious symptoms. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 24(4), 445–456.
Jensen, P. (2003). Comorbidity and child psychopathology: Recommendations for the next decade. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 31(3), 293–300.
Jensen, J., Burke, N., & Garfinkel, B. (1988), Depression and symptoms of attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 27, 742–747.
Jensen, P., Martin, D., & Cantwell, D. (1997). Comorbidity in ADHD: Implications for research, practice, and DSM-V. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36(8), 1065–1079.
Jensen, P., Shervette, R., Xenakis, S., & Richters, J. (1993). Anxiety and depressive disorders in attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity: New findings. American Journal of Psychiatry, 150, 1203–1209.
Joiner, T., Cantanzaro, S., & Laurent, J. (1996). Tripartite structure of positive and negative affect, depression, and anxiety in child and adolescent psychiatric inpatient. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 105(3), 401–409.
Juvonen, J. (1991). Deviance, perceived responsibility, and negative peer reactions. Developmental Psychology, 27(4), 672–681.
Katz, L., & Gottman, J. (1993). Patterns of marital conflict predict children's internalizing and externalizing behaviors. Developmental Psychology, 29, 940–950.
Kazdin, A. (1992). Overt and covert antisocial behavior: Child and family characteristics among psychiatric inpatient children. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 1, 3–20.
Keiley, M., Lofthouse, N., Bates, J., Dodge, K., & Petit, G. (2003). Differential risks of covarying and pure components in mother and teacher reports of externalizing and internalizing behavior across ages 5 to 14. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 31(3), 267–283.
Kendall, P., Stark, K., & Adam, T. (1990). Cognitive deficit or cognitive distortion in childhood depression. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 18, 255–270.
Kennedy, E., Spence, S., Hensley, R. (1989). An examination of the relationship between childhood depression and social competence among primary school children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 30, 561–573.
Kerig, P. (1998). Moderators and mediators of the effects of interparental conflict on children's adjustment. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 26(3), 199–213.
Kim, I., Ge, X., Brody, G., Conger, R., Gibbons, F., & Simons, R. (2003). Parenting behaviors and the occurrence and co-occurrence of depressive symptoms and conduct problems among African American children. Journal of Family Psychology, 17(4), 571–583.
Klein, D., & Riso, L. (1993). Psychiatric disorders: Problems of boundaries and comorbidity. In C. Costello (Ed.), Basic issues in psychopathology (Vol. IX, pp. 19–66). New York: Guilford.
Kovacs, M. (1990). Comorbid anxiety disorders in childhood-onset depression. In J. Maser & C. Cloninger (Eds.), Comorbidity of mood and anxiety disorders (pp. 271–282). Washington: DCL American Psychiatric Press.
Kovacs, M., & Devlin, B. (1998). Internalizing disorders in childhood. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 1, 47–63.
Kovacs, M., Devlin, B., Pollock, M., Richards, C., & Mukerji, P. (1997). A controlled family history study of childhood-onset depressive disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 54(7), 613–623.
Kovacs, M., Paulauskas, S., Gatsonis, C., & Richards, C. (1988). Depressive disorders in childhood: III. A longitudinal study of comorbidity with and risk for conduct disorders. Journal of Affective Disorders, 15, 205–217.
Lahey, B., & Carlson, C. (1991). Validity of the diagnostic category of attention deficit disorder without hyperactivity: A review of the literature. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 24, 110–120.
Lahey, B., Loeber, R., Burke, J., Rathouse, P., & McBurnett, K. (2002). Waxing and waning in concert: Dynamic comorbidity of conduct disorder with other disruptive and emotional problems over 7 years among clinic-referred boys. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 111(4), 556–567.
Lahey, B., Loeber, R., Frick, E., Applegate, B., Zhang, Q., Green, S., Russo, M. (1995). Four-year longitudinal study of conduct disorder in boys: Patterns and predictors of persistence. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 104(1), 83–93.
Lahey, B., Schaughency, E., Frame, C., & Strauss, C. (1985). Teacher ratings of attention problems in children experimentally classified as exhibiting attention deficit disorder with and without hyperactivity. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 24, 613–616.
Lahey, B., Schaughency, E., Hynd, G., Carlson, C., & Nieves, N. (1987). Attention deficit disorder with and without hyperactivity: Comparison of behavioral characteristics of clinic-referred children. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 26, 718–723.
Lahey, B., Schaughency, E., Strauss, C., & Strauss, C. (1984). Are attention deficit disorders with and without hyperactivity similar or dissimilar disorders? Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 23, 302–309.
Lahey, B. Waldman, I., & McBurnett, K. (1999). The development of antisocial behavior: An integrative causal model. Journal of Child Psychology & Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 40(5), 669–682.
Landau, S., & Milich, R. (1988). Social communication patterns of attention deficit disordered boys. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 16, 69–81.
Lemerise, E. A., & Arsenio, W. F. (2000). An integrated model of emotion processes and cognition in social information processing. Child Development, 71(1), 107–118.
Lilienfeld, S. (2003). Comorbidity between and within childhood externalizing and internalizing disorders: Reflections and directions. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 31(3), 285–291.
Lochman, J., & Dodge, K. (1994). Social-cognitive processes of severely violent, moderately aggressive, and nonaggressive. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62(2), 366–374.
Loeber, R., Burke, J., Lahey, B., Winters, A., & Zera, M. (2000a). Oppositional defiant and conduct disorder: A review of the past 10 years, part 1. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 39(12), 1468–1484.
Loeber, R., Green, S., Lahey, B., Frick, P., & McBurnett, K. (2000b). Findings on disruptive behavior disorders form the first decade of the Developmental Trends Study. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 3, 37–60.
Loeber, R., & Keenan, K. (1994). Interaction between conduct disorder and its comorbid conditions: Effects of age and gender. Clinical Psychology Review, 14(6), 497–523.
Lonigan, C., Carey, M., & Finch, A. (1994). Anxiety and depression in children and adolescents: Negative affectivity and the utility of self-reports. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62(5), 1000–1008.
Loss, N., Beck, S., & Wallace, A. (1995). Distressed and nondistressed third- and sixth-grade children's self-reports of life events and impact and concordance with mothers. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 23, 397–409.
Mac Kinnon-Lewis, C., Volling, B., Lamb, M., Dechman, K., Rabiner, D., & Curtner, M. (1994). A cross-contextual analysis of boys' social competence: From family to school. Developmental Psychology, 30(3), 325–333.
Manassis, K., & Hood, J. (1998). Individual and familial predictors of impairment in childhood anxiety disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 37(4), 428–443.
March, J., Swanson, J., Arnold, E., Hoza, B., Conners, K., Hinshaw, S., et al. (2000). Anxiety as a predictor and outcome variable in the Multimodal Treatment Study of Children with ADHD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28(6), 527–554.
McCabe, K., Hough, R., Wood, P., & Yeh, M. (2001). Childhood and adolescent onset conduct disorder: A test of the developmental taxonomy. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 29, 305–316.
McCauley, E., Mitchell, J., Burke, P., & Moss, S. (1988). Cognitive attributes of depression in children and adolescents. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 56, 903–908.
McConaughy, S., & Achenbach, T. (1994). Comorbidity of empirically based syndromes in matched general populations and clinical samples. Journal of Child Psychiatry and Psychology, 35, 1141–1157.
McConaughy, S., & Skiba, R. (1994). Comorbidity of externalizing and internalizing problems. School Psychology Review, 22(3), 421–436.
McLeod, J., & Shanahan, M. (1996). Trajectories of poverty and children's mental health. Journal of Health & Social Behavior, 37(3), 207–220.
Meller, W., & Borchardt, C. (1996). Comorbidity of major depression and conduct disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 39, 123–126.
Mesman, J., & Koot, H. (2000). Child-reported depression and anxiety in preadolescence: II. Preschool predictors. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 39(11), 1379–1386.
Messer, S., & Beidel, D. (1994). Psychosocial correlates of childhood anxiety disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 33, 975–983.
Milch-Reich, S., Campbell, S. B., Pelham, W. E., Connelly, L. M., & Geva, D. (1999). Developmental and individual differences in children's on-line representations of dynamic social events. Child Development, 70, 413–431.
Moffitt, T., Caspi, A., Dickson, N., Silva, P., & Stanton, W. (1996). Childhood-onset versus adolescent-onset antisocial conduct problems in males: Natural history from ages 3 to 18 years. Development and Psychopathology, 8, 399–424.
Mufson, L., Aidala, A., & Warner, V. (1994). Social dysfunction and psychiatric disorder in mothers and their children. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 33(9), 1256–1265.
Munir, K., Biederman, J., & Knee, D. (1987). Psychiatric comorbidity in patients with attention deficit disorder: A controlled study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 26, 844–848.
Newman, D., Moffitt, T., Caspi, A., & Silva, P. (1998). Comorbid mental disorders: Implications for treatment and sample selection. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 107(2), 305–311.
Nottelmann, E., & Jensen, P. (1995). Comorbidity of disorders in children and adolescents: Developmental perspectives. Advances in Clinical Child Psychology, 17, 109–155.
O'Brien, B., & Frick, P. (1996). Reward dominance: Associations with anxiety, conduct problems, and psychopathy in children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 24, 223–240.
O'Connor, T., McGuire, S., Reiss, D., Hetherington, E., & Plomin, R. (1998). Co-occurrence of depressive symptoms and antisocial behavior in adolescence: A common genetic liability. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 107(1), 27–37.
Owens, J. S., & Hoza, B. (2003). The Role of Inattention and Hyperactivity/Impulsivity in the Positive Illusory Bias. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 71(4), 680–691.
Patterson, G., DeBaryshe, B., & Ramsey, E. (1989). A developmental perspective on antisocial behavior. American Psychologist, 44(2), 329–335.
Patterson, G., & Stoolmiller, M. (1991). Replications of a dual failure model for boys' depressed mood. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 59(4), 491–498.
Perrin, S., & Last, C. (1996). Relationship between ADHD and anxiety in boys: Results from a family study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35(8), 988–996.
Pfiffner, L., McBurnett, K., Lahey, B., Loeber, R., Green, S., Frick, P., & Rathouz, P. (1999). Association of parental psychopathology to the comorbid disorders of boys with attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 67(6), 881–893.
Pliszka, R. (1989). Effect of anxiety on cognition, behavior, and stimulant response in ADHD. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 28, 882–887.
Pliszka, R. (1992). Comorbidity of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and overanxious disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 31(2), 197–203.
Pope, A., Bierman, K., & Mumma, G. (1991). Aggression, hyperactivity, and inattention-immaturity: Behavior dimensions associated with peer rejection in elementary school boys. Developmental Psychology, 27, 663–671.
Prieto, S., Cole, D., & Tageson, C. (1992). Depressive self-schemas in clinic and nonclinic children. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 16, 521–534.
Puig-Antich, J., Lukens, E., Davies, M., Goetz, D., Brennan-Quattrock, J., Todak, G. (1985). Psychosocial functioning in prepubertal major depressive disorders. II. Interpersonal relationships after sustained recovery from affective episode. Archives of General Psychiatry, 42, 511–517.
Renouf, A., Kovacs, M., & Mukerji, P. (1997). Relationship of depressive, conduct, and comorbid disorders and social functioning in childhood. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36, 998–1004.
Renken, B., Egeland, B., Marvinney, D., Mangelsdorf, S., & Sroufe, A. (1989). Early childhood antecedents of aggression and passive-withdrawal in early elementary school. Journal of Personality, 57, 257–281.
Renouf, A., Kovacs, M., & Mukerji, P. (1997). Relationship of depressive, conduct, and comorbid disorders and social functioning in childhood. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(7), 998–1004.
Rubin, K. (1993). The Waterloo Longitudinal Project: Correlates and consequences of social withdrawal from childhood to adolescence. In K. H. Rubin & J. B. Asendorpf (Eds.), Social withdrawal, inhibition, and shyness in childhood (pp. 291–314). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Rubin, K., Hymel, S., & Mills, R. (1989). Sociability and social withdrawal in childhood: Stability and outcomes. Journal of Personality, 57(2), 237–255.
Rubin, K., & Mills, R. (1988). The many faces of social isolation in childhood. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 56, 916–924.
Rudolph, K., Hammen, C., & Burge, D. (1994). Interpersonal functioning and depressive symptoms in childhood: addressing the issues of specificity and comorbidity. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 22(3), 355–372.
Russo, M., & Beidel, D. (1994). Comorbidity of childhood anxiety and externalizing disorders: Prevalence, associated characteristics, and validation issues. Clinical Psychology Review, 14, 199–221.
Russo, M., Lahey, B., Christ, M., Frick, P., McBurnett, K., Walker, J., Loeber, R., Stouthamer-Loeber, M., & Green, S. (1991). Preliminary development of a Sensation Seeking Scale for Children. Personality and Individual Differences, 12, 399–405.
Sacco, W., & Graves, D. (1984). Childhood depression, interpersonal problem-solving, and self-ratings of performance. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 13, 10–15.
Sanders, M., Dadds, M., Johnson, B., & Cash, R. (1992). Childhood depression and conduct disorder: I. Behavioral, affective, and cognitive aspects of family problem-solving interactions. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 101, 495–504.
Schachar, R., & Logan, G. (1990). Impulsivity and inhibitory control in normal development and childhood psychopathology. Developmental Psychology, 26(5), 710–720.
Seligman, L., & Ollendick, T. (1998). Comorbidity of anxiety and depression in children and adolescents: An integrative review. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 1(2), 125–144.
Shaw, D., Keenan, K., & Vondra, J. (1994). The developmental precursors of antisocial behavior: Ages 1–3. Developmental Psychology, 30, 355–364.
Shaw, D., Owens, E., Giovanelli, J., & Winslow, E. (2001). Infant and toddler pathways leading to early externalizing disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40, 36–43.
Shaw, D., Winslow, E., Owens, E., Vondra, J., Cohn, J., & Bell, R. (1998). The development of early externalizing problems among children from low-income families: A transformational perspective. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 26, 95–107.
Silberg, J., Rutter, M., & Eaves, L. (2001). Genetic and environmental influences on the temporal association between earlier anxiety and later depression in girls. Society of Biological Psychiatry, 49, 1040–1049.
Simic, M., & Fombone, E. (2001). Depressive conduct disorder: symptom patterns and correlates in referred children and adolescents. Journal of Affective Disorders, 62, 175–185.
Stewart, S., & Rubin, K. (1995). The social problem solving skills of anxious-withdrawn children. Development and Psychopathology, 7, 323–336.
Stipek, D. (1987). Emotional responses to objective and normative performance feedback. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 8(2), 183–195.
Strauss, C., Frame, C., & Forehand, R. (1987). Psychosocial impairment associated with anxiety in children. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 16, 235–239.
Strauss, C., Lahey, B., Frick, P., Frame, C., & Hynd, G. (1988). Peer social status of children with anxiety disorders. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 56, 137–141.
Thomas, J., & Guskin, K. (2001). Disruptive behavior in young children: What does it mean? Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychology, 40(1), 44–51.
Tolan, P., & Henry, D. (1996). Patterns of psychopathology among urban poor children: Comorbidity and aggression effects. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 64(5), 1094–1099.
Turner, S., Beidel, D., & Costello, A. (1987). Psychopathology in the offspring of anxiety disorders patients. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 55, 229–235.
Turner, J., & Cole, D. (1994). Developmental differences in cognitive diatheses for child depression. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 22(1), 15–33.
Verhulst, F., & van der Ende, J. (1993). “Comorbidity” in an epidemiological sample: A longitudinal perspective. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 34, 767–783.
Waas, G. (1988). Social attributional biases of peer-rejected and aggressive children. Child Development, 59, 969–975.
Walker, J., Lahey, B., Russo, M., Frick, P., Christ, M., McBurnett, K., et al. (1991). Anxiety, inhibition, and conduct disorder in children: Relations to social impairment. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 30, 187–191.
Watson, D., & Clark, L. (1984). Negative affectivity: The disposition to experience aversive emotional states. Psychological Bulletin, 98, 219–235.
Weiss, B., & Catron, T. (1994). Specificity of the comorbidity of aggression and depression in children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 22, 389–402.
Weissman, M. (1988). The epidemiology of anxiety disorders: Rates, risks, and familial patterns. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 22, 99–114.
Weissman, M., Wolk, S., Wickramartne, P., Goldstein, R., Adams, P., Greenwald, S., et al. (1999). Children with prepubertal-onset major depressive disorder and anxiety grown up. Archives of General Psychiatry, 56, 794–801.
Wierzbicki, M., & McCabe, M. (1988). Social skills and subsequent depressive symptoms in children. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 17, 203–208.
Wiesner, M. (2003). A longitudinal latent variable analysis of reciprocal relations between depressive symptoms and delinquency during adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 112, 633–645.
Woodword, L., Taylor, E., & Downey, L. (1998). The parenting and family functioning of children with hyperactivity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 39(2), 161–169.
Wright, J., Zakriski, A., & Drinkwater, M. (1999). Developmental psychopathology and the reciprocal patterning of behavior and environment: Distinctive situational and behavioral signatures of internalizing, externalizing, and mixed-syndrome children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 67, 95–107.
Youngstrom, E., Findling, R., & Calabrese, J. (2003). Who are the comorbid adolescents? Agreement between psychiatric diagnosis, youth, parent, and teacher report. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 31(3), 231–245.
Zahn-Waxler, C., Klimes, D. B., & Slattery, M. (2000). Internalizing problems of childhood and adolescence: Prospects, pitfalls, and progress in understanding the development of anxiety and depression. Development and Psychopathology, 12, 443–466.
Zakriski, A., & Coie, J. (1996). A comparison of aggressive-rejected and nonaggressive-rejected children's interpretations of self-directed and other-directed rejection. Child Development, 67, 1048–1070.
Zoccolillo, M. (1993). Gender and the development of conduct disorder. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 65–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oland, A.A., Shaw, D.S. Pure Versus Co-occurring Externalizing and Internalizing Symptoms in Children: The Potential Role of Socio-Developmental Milestones. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 8, 247–270 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-005-8808-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-005-8808-z