Summary
-
1.
We have investigated the effect of the volatile anesthetic sevoflurane on acetylcholine (ACh) release from rat brain cortical slices.
-
2.
The release of [3H]-ACh into the incubation fluid was studied after labeling the tissue ACh with [methyl-3H]-choline chloride.
-
3.
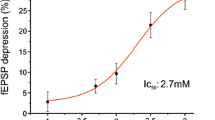
We observed that sevoflurane induced an increase on the release of ACh that was dependent on incubation time and anesthetic concentration. The sevoflurane-induced ACh release was not blocked by tetrodotoxin (TTX) and therefore was independent of sodium channels. In addition, the sevoflurane effect was not blocked by ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether (EGTA) or cadmium (Cd2+), thus independent of extracellular calcium.
-
4.
The sevoflurane-induced ACh release was inhibited by 1,2-bis (2-aminophenoxy) ethane-N,N,N’,N’-tetra-acetic acid (BAPTA-AM), suggestingthe involvement of intracellular calcium-sensitive stores in the process. Dantrolene, an inhibitor of ryanodine receptors, had no effect but 2-aminoethoxydiphenylborate (2-APB), a membrane-permeable inhibitor of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor inhibited the sevoflurane-induced release of ACh.
-
5.
It is concluded that sevoflurane-induced release of ACh in brain cortical slices involves the mobilization of calcium from IP_{3}-sensitive calcium stores.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi, M., Ikemoto, Y., Kubo, K., and Takuma, C. (1992) Seizure-like movements during induction of anaesthesia with sevoflurane. Br. J. Anaesth. 68:214–215
Adachi, Y. U., Watanabe, H., Higuchi, T., Satoh, T., and Zsilla, G. (2001). Halothane enhances acetylcholine release by decreasing dopaminergic activity in rat striatal slices. Neurochem. Int. 40:189–193.
Adler, E. M., Augustine, G. J., Duffy S. N., and Chariton M. P. (1991). Alien intracellular calcium chelator attenuate neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. J. Neurosci. 11:1496–1507.
Bazil, C. W., and Minneman, K. P. (1989a). Effects of clinically effective concentrations of halothane on adrenergic and cholinergic synapses in rat brain in vitro, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 248:143–148.
Bazil, C. W., and Minneman, K. P. (1989b). Clinical concentrations of volatile anesthetics reduce depolarization-evoked release of [3H]-norepinephrine, but not [3H]-acetylcholine, from rat cerebral cortex. J. Neurochem. 53:962–965.
Bertorelli, A., Hallstrom, A., Hurd, Y. L., Karlsson, S., Consolo, S., and Ungerstedt, U. (1990). Anaesthesia effects on in vivo acetylcholine transmission: Comparison of radioenzymatic and HPLC assays. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 175:79–83.
Casali, T. A. A., Gomez, R. S., Moraes-Santos, T., Romano-Silva, M. A., Prado, M. A. M., and Gomez, M. V. (1997). Different effects of reducing agents on ω –conotoxin GVIA inhibition of [3H]-acetylcholine release from cortical slices and guinea-pig myenteric plexus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 120:88–92.
Fox, A. P., Nowycky, M. C., and Tsien R. W. (1987). Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 394:149–172.
Goldberg, A. M., and McCaman, R. E. (1973). The determination of picomole amounts of acetylcholine in mammalian brain. J. Neurochem. 20:1–8.
Gomez, R. S., Gomez, M. V., and Prado, M. A. M. (1996) Inhibition of Na+, K+,-ATPase by ouabain opens calcium channles coupled to acetylcholine release in guinea pig myenteric plexus. J. Neurochem. 66:1440–1447.
Gomez, R. S., Prado, M. A. M., Carazza, F., and Gomez, M. V. (1999). Halothane enhances exocytosis of [3H]-acetylcholine without increasing calcium influx in rat brain cortical slices. Br. J. Pharmacol. 127:679–684.
Gomez, R. S., Gomez, M. V., and Prado, M. A. M. (2000). The effect of isoflurane on the release of [3H]-acetylcholine from rat brain cortical slices. Brain Res. Bull. 52:263–267.
Gomez, R. S., Guatimosim, C., Barbosa, Jr. J., Massensini, A. R., Gomez, M. V., and Prado, M. A. M. (2001). Halothane induced intracellular calcium release in cholinergic cells. Brain Res. 921:106–114.
Griffiths, R., Greiff, J. M. C., Haycock, J., Elton, C. D., Rowbotham, D. J., and Norman, R. I. (1995). Inhibition by halothane of potassium-stimulated acetylcholine release from rat cortical slices. Br. J. Pharmacol. 116:2310–2314.
Griffiths, R., and Norman, R. I. (1993). Effects of anaesthetics on uptake, synthesis and release of transmitters. Br. J. Anaesth. 71:96–107.
Hossain, M. D., and Evers, A. S. (1994). Volatile anesthetic-induced efflux of calcium from IP3-gated stores in clonal (GH3) pituitary cells. Anesthesiology 80:1379–1389.
Johnson, G. V. W., and Hartzell, C. R. (1985). Choline uptake, acetylcholine synthesis and release, and halothane effects in sinaptosomes. Anesth. Analg. 64:395–399.
Katsuoka, M., and Ohnishi, S. T. (1989). Inhalation anaesthetics decrease calcium content of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Br. J. Anaesth. 62:669–673.
Keifer, J. C., Baghdoyan, H. A., Becker, L., and Lydic, R. (1994). Halothane decreases pontine acetylcholine release and increased EEG spindles. Neuroreport 31:577–580.
Kindler, C. H., Eilers, P., Donohoe, S., Ozer, S., and Bickler, P. E. (1999). Volatile anesthetics increase intracellular calcium in cerebrocortical and hippocampal neuron. Anesthesiology 90:1137–1145.
Komatsu, H., Taie, S., Endo, S., Fukuda, K., Ueki, M., Nogaya, J., and Ogli, K. (1994). Electrical seizures during sevoflurane anesthesia in two pediatric patients with epilepsy. Anesthesiology 81:1535–1537.
Kudoh, A., and Matsuki, A. (2000). Sevoflurane stimulates inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate in skeletal muscle. An esth. Analg. 91:440–445.
Lynch, C., and Frazer, M. J. (1994). Anesthetic alteration of ryanodine binding by cardiac calcium release channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1194:109–117.
Maruyama, S., Nakade, T., Kann, T., and Mikoshiba, K. (1997). 2-APB, 2- aminoethoxydiphenylborate, a membrane penetrable modulator of Ins(1,4,5)P3-induced Ca2+ release. J. Biochem. 122:495–505.
Miller, M. S., and Gandolfi, A. J. (1979). A rapid, sensitive method for quantifying enflurane in whole blood. Anesthesiology 51:542–544.
Modica, P. A., Tempelhoff, R., and White, P. F. (1990). Pro- and anticonvulsant effects of anesthetics (part I). Anesth. Analg. 70:303–315.
Moe, M. C., Berg-Johnsen, J., Larsen, G. A., Kampenhaug, E. B., and Vinje, M. L. (2003). The effect of isoflurane and sevoflurane on cerebrocortical presynaptic Ca2+ and protein kinase C activity. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 15:209–214.
Narahashi, J., Moore, J., and Scott, W. R. (1964). Tetrodotoxin blockage of sodium conductance increase in lobster giant axon. J. Gen. Phsyiol. 147:965–974.
Ohta, T., Ito, S., and Ohga, A. (1990). Inhibitory action of dantrolene on Ca-induced Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum in guinea pig skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 178:11–19.
Peppiatt, C. M., Collins, T. J., Mackenzie, I., Conway, S. J., Holmes, A. B., Bootman, M. D., Berridge, M. J., Seo, J. T., and Roderick, H. L. (2003). 2-Aminoethoxydephenylborate (2-APB) antagonizes inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate-induced calcium release, inhibits calcium pumps and has a use-dependent and slowly reversible action on store-operated calcium entry channel. Cell Calcium 34:97–108.
Pocock, G., and Richards, C. D. (1996). Excitatory and inhibitory synaptic mechanism in anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 71:134–147.
Prado, M. A. M., Gomez, M. V., and Collier, B. (1993). Mobilization of a vesamicol-insensitive pool of acetylcholine from a sympathetic ganglion by ouabain. J. Neurochem. 61:45–56.
Shichino, M. Murakawa, T., Adachi, T., Arai, Y., Miyazaki, Y., and Mori, K. (1998). Effects of inhalation anaesthetics on the release of acetylcholine in the rat cerebral cortex in vivo. Br. J. Anaesth. 80:365–370.
Shichino, T., Murakawa, T., Adachi, T., Arai, S., Nakao, T., Shinomura, J., Kurata, J., and Mori, K. (1997) Effects of isoflurane on in vivo release of acetylcholine in the rat cerebral cortex and striatum. Acta. Anaesthesiol. Scand. 41:1335–1340.
Shichino, M., Murakawa, T., Adachi, T., Arai, Y., Miyazaki, H., Segawa, H., Fukuda, K., and Mori, K. (2002). Effects of xenon on acetylcholine release in the rat cerebral cortex in vivo. Br. J. Anaesth. 88:866–868.
Schotten, M., Greiser, V., Braun, V., Karlein, F., Schoendube, P., and Hanrath, P. (2001). Effect of volatile anesthetics on the force-frequency relation in human ventricular myocardium. Anesthesiology 95:1160–1168.
Taguchi, K., Andresen, M. J., and Hentall, I. D. (1991). Acetylcholine release from the midbrain interpeduncular nucleous during anesthesia. Neuroreport 2:789–792.
Weldon, B. C., Bell, M., and Craddock, T. (2004). The effect of caudal analgesia on emergence agitation in children after sevoflurane versus halothane anesthesia. Anesth. Analg. 98:321–326.
Wells, L. T., and Rasch, D. K. (1999). Emergence “delirium” after sevoflurane anesthesia: A paranoid delusion? Anesth. Analg. 88:1308–1310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, J.H., Gomez, R.S., Pinheiro, A.C.N. et al. Acetylcholine Release Induced by the Volatile Anesthetic Sevoflurane in Rat Brain Cortical Slices. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25, 807–818 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-005-4934-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-005-4934-x