Summary
1. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) is an extremely abundant glycolytic enzyme, and exemplifies the class of proteins with multiple, seemingly unrelated functions. Recent studies indicate that it is a major intracellular messenger mediating apoptotic cell death. This paper reviews the GAPDH cell death cascade and discusses its clinical relevance.
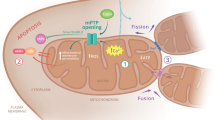
2. A wide range of apoptotic stimuli activate NO formation, which S-nitrosylates GAPDH. The S-nitrosylation abolishes catalytic activity and confers upon GAPDH the ability to bind to Siah, an E3-ubiquitin-ligase, which translocates GAPDH to the nucleus. In the nucleus, GAPDH stabilizes the rapidly turning over Siah, enabling it to degrade selected target proteins and affect apoptosis.
3. The cytotoxicity of mutant Huntingtin (mHtt) requires nuclear translocation which appears to be mediated via a ternary complex of GAPDH—Siah—mHtt. The neuroprotective actions of the monoamine oxidase inhibitor R-(—)-deprenyl (deprenyl) reflect blockade of GAPDH—Siah binding. Thus, novel cytoprotective therapies may emerge from agents that prevent GAPDH—Siah binding.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bae, B. I., Xu, H., Igarashi, S., Fujimuro, M., Agrawal, N., Taya, Y., Hayward, S. D., Moran, T. H., Montell, C., Ross, C. A., Snyder, S. H., and Sawa, A. (2005). p53 mediates cellular dysfunction and behavioral abnormalities in Huntington's disease. Neuron 47:29–41.
Bae, B. I., Hara, M. R., Cascio, M. B., Wellington, C. L., Hayden, M. R., Ross, C. A., Ha, H. C., Li, X. J., Snyder, S. H., and Sawa, A. (2006). Mutant Huntingtin: Nuclear translocation and cytotoxicity mediated by GAPDH. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103:3405–3409.
Birkmayer, W., Knoll, J., Riederer, P., Youdim, M. B., Hars, V., and Marton, J. (1985). Increased life expectancy resulting from addition of l-deprenyl to Madopar treatment in Parkinson's disease: A longterm study. J. Neural. Transm. 64:113–127.
Boehning, D., Patterson, R. L., Sedaghat, L., Glebova, N. O., Kurosaki, T., and Snyder, S. H. (2003). Cytochrome c binds to inositol (1,4,5) trisphosphate receptors, amplifying calcium-dependent apoptosis. Nat. Cell. Biol. 5:1051–1061.
Brown, V. M., Krynetski, E. Y., Krynetskaia, N. F., Grieger, D., Mukatira, S. T., Murti, K. G., Slaughter, C. A., Park, H. W., and Evans, W. E. (2004). A novel CRM1-mediated nuclear export signal governs nuclear accumulation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase following genotoxic stress. J. Biol. Chem. 279:5984–5992.
Brune, B., and Lapetina, E. G. (1989). Activation of a cytosolic ADP-ribosyltransferase by nitric oxide-generating agents. J. Biol. Chem. 264:8455–8458.
Burke, J. R., Enghild, J. J., Martin, M. E., Jou, Y. S., Myers, R. M., Roses, A. D., Vance, J. M., and Strittmatter, W. J. (1996). Huntingtin and DRPLA proteins selectively interact with the enzyme GAPDH. Nat. Med. 2:347–350.
Chen, M., Ona, V. O., Li, M., Ferrante, R. J., Fink, K. B., Zhu, S., Bian, J., Guo, L., Farrell, L. A., Hersch, S. M., Hobbs, W., Vonsattel, J. P., Cha, J. H., and Friedlander, R. M. (2000). Minocycline inhibits caspase-1 and caspase-3 expression and delays mortality in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington disease. Nat. Med. 6:797–801.
Dawson, V. L., Dawson, T. M., Bartley, D. A., Uhl, G. R., and Snyder, S. H. (1993). Mechanisms of nitric oxide-mediated neurotoxicity in primary brain cultures. J. Neurosci. 13:2651–2661.
Dawson, V. L., Dawson, T. M., London, E. D., Bredt, D. S., and Snyder, S. H. (1991). Nitric oxide mediates glutamate neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88:6368–6371.
Della, N. G., Senior, P. V., and Bowtell, D. D. (1993). Isolation and characterisation of murine homologues of the Drosophila seven in absentia gene (sina). Development 117:1333–1343.
Fiucci, G., Beaucourt, S., Duflaut, D., Lespagnol, A., Stumptner-Cuvelette, P., Geant, A., Buchwalter, G., Tuynder, M., Susini, L., Lassalle, J. M., Wasylyk, C., Wasylyk, B., Oren, M., Amson, R., and Telerman, A. (2004). Siah-1b is a direct transcriptional target of p53: Identification of the functional p53 responsive element in the siah-1b promoter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101:3510–3515.
Fukushima, T., Zapata, J. M., Singha, N. C., Thomas, M., Kress, C. L., Krajewska, M., Krajewski, S., Ronai, Z., Reed, J. C., and Matsuzawa, S. (2006). Critical function for SIP, a ubiquitin E3 ligase component of the beta-catenin degradation pathway, for thymocyte development and G1 checkpoint. Immunity 24:29–39.
Graven, K. K., Troxler, R. F., Kornfeld, H., Panchenko, M. V., and Farber, H. W. (1994). Regulation of endothelial cell glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase expression by hypoxia. J. Biol. Chem. 269:24446–24453.
Hantraye, P., Brouillet, E., Ferrante, R., Palfi, S., Dolan, R., Matthews, R. T., and Beal, M. F. (1996). Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase prevents MPTP-induced parkinsonism in baboons. Nat. Med. 2:1017–1021.
Hara, M. R., Agrawal, N., Kim, S. F., Cascio, M. B., Fujimuro, M., Ozeki, Y., Takahashi, M., Cheah, J. H., Tankou, S. K., Hester, L. D., Ferris, C. D., Hayward, S. D., Snyder, S. H., and Sawa, A. (2005). S-nitrosylated GAPDH initiates apoptotic cell death by nuclear translocation following Siah1 binding. Nat. Cell. Biol. 7:665–674.
Hara, M. R., Thomas, B., Cascio, M. B., Bae, B. I., Hester, L. D., Dawson, V. L., Dawson, T. M., Sawa, A., and Snyder, S. H. (2006). Neuroprotection by pharmacologic blockade of the GAPDH death cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103:3887–3889.
Hu, G., and Fearon, E. R. (1999). Siah-1 N-terminal RING domain is required for proteolysis function, and C-terminal sequences regulate oligomerization and binding to target proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:724–732.
Ignarro, L. J. (1990). Haem-dependent activation of guanylate cyclase and cyclic GMP formation by endogenous nitric oxide: A unique transduction mechanism for transcellular signaling. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 67:1–7.
Ishitani, R., and Chuang, D. M. (1996). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase antisense oligodeoxynucleotides protect against cytosine arabinonucleoside-induced apoptosis in cultured cerebellar neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93:9937–9941.
Ishitani, R., Kimura, M., Sunaga, K., Katsube, N., Tanaka, M., and Chuang, D. M. (1996a). An antisense oligodeoxynucleotide to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase blocks age-induced apoptosis of mature cerebrocortical neurons in culture. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 278:447–454.
Ishitani, R., Sunaga, K., Hirano, A., Saunders, P., Katsube, N., and Chuang, D. M. (1996b). Evidence that glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is involved in age-induced apoptosis in mature cerebellar neurons in culture. J. Neurochem. 66:928–935.
Jaffrey, S. R., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Ferris, C. D., Tempst, P., and Snyder, S. H. (2001). Protein S-nitrosylation: A physiological signal for neuronal nitric oxide. Nat. Cell. Biol. 3:193–197.
Jenner, P. (2004). Preclinical evidence for neuroprotection with monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 63:S13– S22.
Koshy, B., Matilla, T., Burright, E. N., Merry, D. E., Fischbeck, K. H., Orr, H. T., and Zoghbi, H. Y. (1996). Spinocerebellar ataxia type-1 and spinobulbar muscular atrophy gene products interact with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Hum. Mol. Genet. 5:1311–1318.
Kragten, E., Lalande, I., Zimmermann, K., Roggo, S., Schindler, P., Muller, D., van Oostrum, J., Waldmeier, P., and Furst, P. (1998). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, the putative target of the antiapoptotic compounds CGP 3466 and R-(−)-deprenyl. J. Biol. Chem. 273:5821–5828.
Kudo, N., Matsumori, N., Taoka, H., Fujiwara, D., Schreiner, E. P., Wolff, B., Yoshida, M., and Horinouchi, S. (1999). Leptomycin B inactivates CRM1/exportin 1 by covalent modification at a cysteine residue in the central conserved region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96:9112–9117.
Liani, E., Eyal, A., Avraham, E., Shemer, R., Szargel, R., Berg, D., Bornemann, A., Riess, O., Ross, C. A., Rott, R., and Engelender, S. (2004). Ubiquitylation of synphilin-1 and alpha-synuclein by SIAH and its presence in cellular inclusions and Lewy bodies imply a role in Parkinson's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101:5500–5505.
Liberatore, G. T., Jackson-Lewis, V., Vukosavic, S., Mandir, A. S., Vila, M., McAuliffe, W. G., Dawson, V. L., Dawson, T. M., and Przedborski, S. (1999). Inducible nitric oxide synthase stimulates dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson disease. Nat. Med. 5:1403–1409.
Matsuzawa, S. I., and Reed, J. C. (2001). Siah-1, SIP, and Ebi collaborate in a novel pathway for beta-catenin degradation linked to p53 responses. Mol. Cell. 7:915–926.
McDonald, L. J., and Moss, J. (1993). Stimulation by nitric oxide of an NAD linkage to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90:6238–6241.
Meyer-Siegler, K., Mauro, D. J., Seal, G., Wurzer, J., deRiel, J. K., and Sirover, M. A. (1991). A human nuclear uracil DNA glycosylase is the 37-kDa subunit of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88:8460–8464.
Mohr, S., Stamler, J. S., and Brune, B. (1996). Posttranslational modification of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase by S-nitrosylation and subsequent NADH attachment. J. Biol. Chem. 271:4209–4214.
Morgenegg, G., Winkler, G. C., Hubscher, U., Heizmann, C. W., Mous, J., and Kuenzle, C. C. (1986). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a nonhistone protein and a possible activator of transcription in neurons. J. Neurochem. 47:54–62.
Moriyoshi, K., Iijima, K., Fujii, H., Ito, H., Cho, Y., and Nakanishi, S. (2004). Seven in absentia homolog 1A mediates ubiquitination and degradation of group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101:8614–8619.
Nagano, Y., Yamashita, H., Takahashi, T., Kishida, S., Nakamura, T., Iseki, E., Hattori, N., Mizuno, Y., Kikuchi, A., and Matsumoto, M. (2003). Siah-1 facilitates ubiquitination and degradation of synphilin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 278:51504–51514.
Nagata, E., Luo, H. R., Saiardi, A., Bae, B, I., Suzuki, N., and Snyder, S. H. (2005). Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase-2, a physiologic mediator of cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 280:1634–1640.
Patterson, R. L., van Rossum, D. B., Kaplin, A. I., Barrow, R. K., and Snyder, S. H. (2005). Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor/GAPDH complex augments Ca2+ release via locally derived NADH. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102:1357–1359.
Przedborski, S., Jackson-Lewis, V., Yokoyama, R., Shibata, T., Dawson, V. L., and Dawson, T. M. (1996). Role of neuronal nitric oxide in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93:4565–4571.
Sawa, A., Khan, A. A., Hester, L. D., and Snyder, S. H. (1997). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: Nuclear translocation participates in neuronal and nonneuronal cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94:11669–11674.
Sawa, A., Wiegand, G. W., Cooper, J., Margolis, R. L., Sharp, A. H., Lawler, J. F.Jr., Greenamyre, J. T., Snyder, S. H., and Ross, C. A. (1999). Increased apoptosis of Huntington disease lymphoblasts associated with repeat length-dependent mitochondrial depolarization. Nat. Med. 5:1194–1198.
Senatorov, V. V., Charles, V., Reddy, P. H., Tagle, D. A., and Chuang, D. M. (2003). Overexpression and nuclear accumulation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington's disease. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 22:285–297.
Sharpless, N. E., and DePinho, R. A. (2002). p53: Good cop/bad cop. Cell 110:9–12.
Singh, R., and Green, M. R. (1993). Sequence-specific binding of transfer RNA by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Science 259:365–368.
Sourisseau, T., Desbois, C., Debure, L., Bowtell, D. D., Cato, A. C., Schneikert, J., Moyse, E., and Michel, D. (2001). Alteration of the stability of Bag-1 protein in the control of olfactory neuronal apoptosis. J. Cell. Sci. 114:1409–1416.
Sundararaj, K. P., Wood, R. E., Ponnusamy, S., Salas, A. M., Szulc, Z., Bielawska, A., Obeid, L. M., Hannun, Y. A., and Ogretmen, B. (2004). Rapid shortening of telomere length in response to ceramide involves the inhibition of telomere binding activity of nuclear glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 279:6152–6162.
Tatton, N. A. (2000). Increased caspase 3 and Bax immunoreactivity accompany nuclear GAPDH translocation and neuronal apoptosis in Parkinson's disease. Exp. Neurol. 166:29–43.
Tokunaga, K., Nakamura. Y., Sakata, K., Fujimori, K., Ohkubo, M., Sawada, K., and Sakiyama, S. (1987). Enhanced expression of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene in human lung cancers. Cancer Res. 47:5616–5619.
Vogelstein, B., Lane, D., and Levine, A. J. (2000). Surfing the p53 network. Nature 408:307–310.
Waldmeier, P. C., Boulton, A. A., Cools, A. R., Kato, A. C., and Tatton, W. G. (2000). Neurorescuing effects of the GAPDH ligand CGP 3466B. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 60:197–214.
Yamaji, R., Fujita, K., Takahashi, S., Yoneda, H., Nagao, K., Masuda, W., Naito, M., Tsuruo, T., Miyatake, K., Inui, H., and Nakano, Y. (2003). Hypoxia up-regulates glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in mouse brain capillary endothelial cells: involvement of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1593:269–276.
Zhang, J., and Snyder, S. H. (1992). Nitric oxide stimulates auto-ADP-ribosylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89:9382–9385.
Zheng, L., Roeder, R. G., and Luo, Y. (2003). S phase activation of the histone H2B promoter by OCA-S, a coactivator complex that contains GAPDH as a key component. Cell 114:255–266.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by USPHS grants DA-00266 and Research Scientist AwardDA00074 (SHS). We thank Dr. Akira Sawa, Dr. Byoung-Il Bae, and Matthew B. Cascio for their helpful comments. We thank Dr. Peter Waldmeier for providing us TCH346.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hara, M.R., Snyder, S.H. Nitric Oxide–GAPDH–Siah: A Novel Cell Death Cascade. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26, 525–536 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9011-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9011-6