Abstract
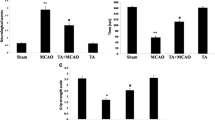
The present study was designed to evaluate the beneficial effects of Withania somnifera (WS) pre-supplementation on middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model of ischemic stroke. Ischemic stroke was induced in the rats by inserting intraluminal suture for 90 min, followed by reperfusion injury for 24 h. The animals were assessed for locomotor functions (by neurological deficit scores, narrow beam walk and rotarod test), cognitive and anxiety-like behavioural functions (by morris water maze and elevated plus maze test). MCAO animals showed significant impairment in locomotor and cognitive functions. Neurobehavioural changes were accompanied by decreased acetylcholinesterase activity, increased oxidative stress in terms of enhanced lipid peroxidation and lowered thiol levels in the MCAO animals. In addition, MCAO animals had cerebral infarcts and the presence of pycnotic nuclei. Single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) of MCAO animals revealed a cerebral infarct as a hypoactive area. On the other hand, pre-supplementation with WS (300 mg/kg body weight) for 30 days to MCAO animals was effective in restoring the acetylcholinesterase activity, lipid peroxidation, thiols and attenuated MCAO induced behavioural deficits. WS significantly reduced the cerebral infarct volume and ameliorated histopathological alterations. Improved blood flow was observed in the SPECT images from the brain regions of ischemic rats pre-treated with WS. The results of the study showed a protective effect of WS supplementation in ischemic stroke and are suggestive of its potential application in stroke management.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AChE:
-
Acetylcholinesterase
- WS :
-
Withania somnifera
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- T-SHs:
-
Total thiols
- LMW-SHs:
-
Low molecular weight thiols
- P-SHs:
-
Protein thiols
- TTC:
-
2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride
References
Adams HP Jr, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, Bhatt DL, Brass L, Furlan A, Grubb RL, Higashida RT, Jauch EC, Kidwell C, Lyden PD, Morgenstern LB, Qureshi AI, Rosenwasser RH, Scott PA, Wijdicks EF (2007) Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Groups: The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke 38:1655–1711
Ahmad A, Khan MM, Hoda MN, Raza SS, Khan MB, Javed H, Ishrat T, Ashafaq M, Ahmad ME, Safhi MM, Islam F (2011) Quercetin protects against oxidative stress associated damages in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Neurochem Res 36:1360–1371
Ahmed ME, Javed H, Khan MM, Vaibhav K, Ahmad A, Khan A, Tabassum R, Islam F, Safhi MM (2013) Attenuation of oxidative damage-associated cognitive decline by Withania somnifera in rat model of streptozotocin-induced cognitive impairment. Protoplasma 250:1067–1078
Albers GW, Amarenco P, Easton JD, Sacco RL, Teal P (2008) Antithrombotic and thrombolytic therapy for ischemic stroke: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (8th Edition). Chest 133:630S–690S
Baitharu I, Jain V, Deep SN, Hota KB, Hota SK, Prasad D, Ilavazhagan G (2013) Withania somnifera root extract ameliorates hypobaric hypoxia induced memory impairment in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 145:431–441
Bharavi K, Reddy AG, Rao GS, Reddy AR, Rao SV (2010) Reversal of cadmium-induced oxidative stress in chicken by herbal adaptogens Withania somnifera and Ocimum sanctum. Toxicol Int 17:59–63
Bhattacharya SK, Satyan KS, Ghosal S (1997) Antioxidant activity of glycowithanolides from Withania somnifera. Indian J Exp Biol 35:236–239
Bhattacharya SK, Bhattacharya A, Sairam K, Ghosal S (2000) Anxiolytic-antidepressant activity of Withania somnifera glycowithanolides: an experimental study. Phytomedicine 7:463–469
Bingham D, Martin SJ, Macrae IM, Carswell HV (2012) Watermaze performance after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat: the role of sensorimotor versus memory impairments. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:989–999
Bouet V, Freret T, Toutain J, Divoux D, Boulouard M, Schumann-Bard P (2007) Sensorimotor and cognitive deficits after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the mouse. Exp Neurol 203:555–567
Braca A, De Tommasi N, Di Bari L, Pizza C, Politi M, Morelli I (2001) Antioxidant principles from Bauhinia tarapotensis. J Nat Prod 64:892–895
Candelario-Jalil E, Gonzalez-Falcon A, Garcia-Cabrera M, Leon OS, Fiebich BL (2007) Post-ischaemic treatment with the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor nimesulide reduces blood-brain barrier disruption and leukocyte infiltration following transient focal cerebral ischaemia in rats. J Neurochem 100:1108–1120
Carmichael ST (2005) Rodent models of focal stroke: size, mechanism, and purpose. NeuroRx 2:396–409
Chaudhary G, Sharma U, Jagannathan NR, Gupta YK (2003) Evaluation of Withania somnifera in a middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30:399–404
Chaurasiya ND, Uniyal GC, Lal P, Misra L, Sangwan NS, Tuli R, Sangwan R (2008) Analysis of withanolides in root and leaf of Withania somnifera by HPLC with photodiode array and evaporative lightscattering detection. Phytochem Anal 19(2):148–154
Cherubini A, Ruggiero C, Polidori MC, Mecocci P (2005) Potential markers of oxidative stress in stroke. Free Radic Biol Med 39:841–852
Dickstein DL, Walsh J, Brautigam H, Stockton SD Jr, Gandy S, Hof PR (2010) Role of vascular risk factors and vascular dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Mt Sinai J Med 77:82–102
DiPasquale R (2014) Effect of ashwagandha on tests of cognitive and psychomotor performance: review of a prospective, double blind, multidose, placebo controlled, crossover study. Nat Med J 6:5
Garnier P, Bertrand N, Demougeot C, Prigent-Tessier A, Marie C, Beley A (2002) Chemical preconditioning with 3-nitropropionic acid: lack of induction of neuronal tolerance in gerbil hippocampus subjected to transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res Bull 58:33–39
Gl Ellman, Courtney KD, Andres VJR, Feather Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Gupta GL, Rana AC (2008) Effect of Withania somnifera Dunal in ethanol-induced anxiolysis and withdrawal anxiety in rats. Indian J Exp Biol 46:470–475
Gupta YK, Briyal S, Gulati A (2010) Therapeutic potential of herbal drugs in cerebral ischemia. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 54:99–122
Hara MR, Snyder SH (2007) Cell signaling and neuronal death. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:117–141
Hattori S, Hashimoto R, Miyakawa T, Yamanaka H, Maeno H, Wada K, Kunugi H (2007) Enriched environments influence depression-related behavior in adult mice and the survival of newborn cells in their hippocampi. Behav Brain Res 180:69–76
Ikeda Y, Young LH, Lefer AM (2002) Attenuation of neutrophil-mediated myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by a calpain inhibitor. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 282:H1421–H1426
Karnick CR (1991) A double blind, placebo controlled clinical studies on the effects of Withania somnifera and Panax ginseng extracts on psychomotor performance in healthy Indian volunteers. Indian Med 3:1–5
Kataria H, Wadhwa R, Kaul SC, Kaur G (2012) Water extract from the leaves of Withania somnifera protect RA differentiated C6 and IMR-32 cells against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. PLoS One 7:e37080
Khodaei M, Jafari M, Noor M (2012) Remedial use of Withanolides from Withania coagulans (Stocks) Dunal. Adv Lif Sci 2:6–19
Kiernan JA (2008) Histological and histochemical methods, 4th edn. Pergamon Press, Oxfordshire
Kumar GP, Khanum F (2012) Neuroprotective potential of phytochemicals. Pharmacogn Rev 6:81–90
Kurapati KR, Atluri VS, Samikkannu T, Nair MP (2013) Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) reverses beta-amyloid1-42 induced toxicity in human neuronal cells: implications in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). PLoS One 8(10):e77624
Lee JD, Kim DI, Ryu YH, Whang GJ, Park CI, Kim DG (1998) Technetium-99m-ECD brain SPECT in cerebral palsy: comparison with MRI. J Nucl Med 39:619–623
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mehrotra A, Sandhir R (2014) Mitochondrial cofactors in experimental Huntington’s disease: behavioral, biochemical and histological evaluation. Behav Brain Res 261:345–355
Mirjalili MH, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Cusido RM, Palazon J (2009) Steroidal lactones from Withania somnifera, an ancient plant for novel medicine. Molecules 14(7):2373–2393
Mishra LC, Singh BB, Dagenais S (2000) Scientific basis for the therapeutic use of Withania somnifera (ashwagandha): a review. Altern Med Rev 5:334–346
Moretti JL, Tamgac F, Weinmann P, Caillat-Vigneron N, Belin CA, Cesaro P, Holman BL, Defer G (1994) Early and delayed brain SPECT with technetium-99m-ECD and iodine-123-IMP in subacute strokes. J Nucl Med 35:1444–1449
Nagashayana N, Sankarankutty P, Nampoothiri MR, Mohan PK, Mohana kumar KP (2000) Association of L-DOPA with recovery following Ayurveda medication in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 176:124–127
Nam E, Lee SM, Koh SE, Joo WS, Maeng S, Im HI (2005) Melatonin protects against neuronal damage induced by 3-nitropropionic acid in rat striatum. Brain Res 1046:90–96
Parihar MS, Chaudhary M, Shetty R, Hemnani T (2004) Susceptibility of hippocampus and cerebral cortex to oxidative damage in streptozotocin treated mice: prevention by extracts of Withania somnifera and Aloe vera. J Clin Neurosci 11:397–402
Pingali U, Pilli R, Fatima N (2014) Effect of standardized aqueous extract of Withania somnifera on tests of cognitive and psychomotor performance in healthy human participants. Pharmacognosy Res 6:12–18
Popp A, Jaenisch N, Witte OW, Frahm C (2009) Identification of ischemic regions in a rat model of stroke. PLoS One 4:e4764
Prabu PC, Panchapakesan S, Raj CD (2013) Acute and sub-acute oral toxicity assessment of the hydroalcoholic extract of Withania somnifera roots in Wistar rats. Phytother Res 27:1169–1178
Prakash J, Chouhan S, Yadav SK, Westfall S, Rai SN, Singh SP (2014) Withania somnifera alleviates parkinsonian phenotypes by inhibiting apoptotic pathways in dopaminergic neurons. Neurochem Res 39(12):2527–2536
Raghavan A, Shah ZA (2015) Withania somnifera: a pre-clinical study on neuroregenerative therapy for stroke. Neural Regen Res 10(2):183–185
Rasool M, Varalakshmi P (2006) Immunomodulatory role of Withania somnifera root powder on experimental induced inflammation: an in vivo and in vitro study. Vascul Pharmacol 44:406–410
Reed DJ (1990) Glutathione: toxicological implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 30:603–631
Rink C, Khanna S (2011) Significance of brain tissue oxygenation and the arachidonic acid cascade in stroke. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:1889–1903
Roberts JC, Francetic DJ (1993) The importance of sample preparation and storage in glutathione analysis. Anal Biochem 211:183–187
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Makuc DM, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, Moy CS, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nichol G, Paynter NP, Soliman EZ, Sorlie PD, Sotoodehnia N, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB (2012) Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics–2012 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 125:188–197
Rogers DC, Hunter AJ (1997) Photothrombotic lesions of the rat cortex impair acquisition of the water maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 56:747–754
Rozas G, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL (1997) An automated rotarod method for quantitative drug-free evaluation of overall motor deficits in rat models of parkinsonism. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 2:75–84
Sakakima H, Khan M, Dhammu TS, Shunmugavel A, Yoshida Y, Singh I, Singh AK (2012) Stimulation of functional recovery via the mechanisms of neurorepair by S-nitrosoglutathione and motor exercise in a rat model of transient cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Restor Neurol Neurosci 30:383–396
Sankar SR, Manivasagam T, Krishnamurti A, Ramanathan M (2007) The neuroprotective effect of Withania somnifera root extract in MPTP-intoxicated mice: an analysis of behavioral and biochemical variables. Cell Mol Biol Lett 12:473–481
Schliebs R, Liebmann A, Bhattacharya SK, Kumar A, Ghosal S, Bigl V (1997) Systemic administration of defined extracts from Withania somnifera (Indian Ginseng) and Shilajit differentially affects cholinergic but not glutamatergic and GABAergic markers in rat brain. Neurochem Int 30(2):181–190
Sedlak J, Hanus L (1982) Changes of glutathione and protein bound SH-groups concentration in rat adrenals under acute and repeated stress. Endocrinol Exp 16:103–109
Sehgal N, Gupta A, Valli RK, Joshi SD, Mills JT, Hamel E, Khanna P, Jain SC, Thakur SS, Ravindranath V (2012) Withania somnifera reverses Alzheimer’s disease pathology by enhancing low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:3510–3515
Senthilnathan P, Padmavathi R, Magesh V, Sakthisekaran D (2006) Stabilization of membrane bound enzyme profiles and lipid peroxidation by Withania somnifera along with paclitaxel on benzo(a)pyrene induced experimental lung cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 292:13–17
Shahriar M. et al. (2012) Membrane stabilizing and anti-thrombolytic activities of four medicinal plants of bangladesh. Experiment 4:265–270
Singh RH, Narsimhamurthy K, Singh G (2008) Neuronutrient impact of Ayurvedic Rasayana therapy in brain aging. Biogerontology 9:369–374
Soman S, Korah PK, Jayanarayanan S, Mathew J, Paulose CS (2012) Oxidative stress induced NMDA receptor alteration leads to spatial memory deficits in temporal lobe epilepsy: ameliorative effects of Withania somnifera and withanolide A. Neurochem Res 37:1915–1927
Soman S, Anju TR, Jayanarayanan S, Antony S, Paulose CS (2013) Impaired motor learning attributed to altered AMPA receptor function in the cerebellum of rats with temporal lobe epilepsy: ameliorating effects of Withania somnifera and withanolide A. Epilepsy Behav 27:484–491
Sun JH, Tan L, Yu JT (2014) Post-stroke cognitive impairment: epidemiology, mechanisms and management. Ann Transl Med 2:80
Thiyagarajan M, Sharma SS (2004) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin in middle cerebral artery occlusion induced focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci 74:969–985
Thrift AG, Cadilhac DA, Thayabaranathan T, Howard G, Howard VJ, Rothwell PM (2014) Global stroke statistics. Int J Stroke 9:6–18
Tohda C, Kuboyama T, Komatsu K (2005) Search for natural products related to regeneration of the neuronal network. Neurosignals 14:34–45
Varga-Szabo D, Braun A, Kleinschnitz C, Bender M, Pleines I, Pham M, Renne T, Stoll G, Nieswandt B (2008) The calcium sensor STIM1 is an essential mediator of arterial thrombosis and ischemic brain infarction. J Exp Med 205:1583–1591
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 1:848–858
Walf AA, Frye CA (2007) The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat Protoc 2:322–328
Walvekar M, Shaikh N, Sarvalkar P (2013) Effects of glycowithanolides on lipid peroxidation and lipofuscinogenesis in male reproductive organs of mice. Iran J Reprod Med 11:711–716
Wills ED (1966) Mechanisms of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues. Biochem J 99:667–676
Yadav CS, Kumar V, Suke SG, Ahmed RS, Mediratta PK, Banerjee BD (2010) Propoxur-induced acetylcholine esterase inhibition and impairment of cognitive function: attenuation by Withania somnifera. Indian J Biochem Biophys 47(2):117–120
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial assistance received from the University Grants Commission (New-Delhi) under Basic Science Research (BSR) scheme-Special Assistance Programme (SAP) and Department of Science and Technology (DST, New-Delhi) under DST-FIST Programme. The authors also acknowledge Dabur India Private Limited (Ghaziabad, India) for providing hydro-alcoholic root extract of WS for research purpose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sood, A., Kumar, A., Dhawan, D.K. et al. Propensity of Withania somnifera to Attenuate Behavioural, Biochemical, and Histological Alterations in Experimental Model of Stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol 36, 1123–1138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0305-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0305-4