Abstract
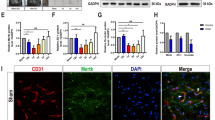
FK-506 (Tacrolimus) is a very commonly used immunomodulatory agent that plays important roles in modulating the calcium-dependent phosphoserine–phosphothreonine protein phosphatase calcineurin and thus inhibits calcineurin-mediated secondary neuronal damage. The biological function of FK-506 in the spinal cord has not been fully elucidated. To clarify the anti-inflammatory action of FK-506 in spinal cord injury (SCI), we performed an acute spinal cord contusion injury model in adult rats and hypoxia-treated primary spinal cord microglia cultures. This work studied the activation of NF-κB and proinflammatory cytokine (TNF-a, IL-1b, and IL-6) expression. ELISA and q-PCR analysis revealed that TNF-a, IL-1b, and IL-6 levels significantly increased 3 days after spinal cord contusion and decreased after 14 days, accompanied by the increased activation of NF-κB. This increase was reversed by an FK-506 treatment. Double immunofluorescence labeling suggested that NF-κB activation was especially prominent in microglia. Immunohistochemistry confirmed no alteration in the number of microglia. Moreover, the results in hypoxia-treated primary spinal cord microglia confirmed the effect of FK-506 on TNF-a, IL-1b, and IL-6 expression and NF-κB activation. These findings suggest that FK-506 may be involved in microglial activation after SCI.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira S, Hirano T, Taga T, Kishimoto T (1990) Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J 4:2860–2867
Bareyre FM, Schwab ME (2003) Inflammation, degeneration and regeneration in the injured spinal cord: insights from DNA microarrays. Trends Neurosci 26:555–563
Barnes PJ, Karin M (1997) Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 336:1066–1071
Bartholdi D, Schwab ME (1997) Expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine mRNA upon experimental spinal cord injury in mouse: an in situ hybridization study. Eur J Neurosci 9:1422–1438
Baskar Jesudasan SJ, Todd KG, Winship IR (2014) Reduced inflammatory phenotype in microglia derived from neonatal rat spinal cord versus brain. PLoS One 9:e99443
Bethea JR, Dietrich WD (2002) Targeting the host inflammatory response in traumatic spinal cord injury. Curr Opin Neurol 15:355–360
Bethea JR, Castro M, Keane RW, Lee TT, Dietrich WD, Yezierski RP (1998) Traumatic spinal cord injury induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation. J Neurosci 18:3251–3260
Carlson GD, Gorden C (2002) Current developments in spinal cord injury research. Spine J 2:116–128
Chengke L, Weiwei L, Xiyang W, Ping W, Xiaoyang P, Zhengquan X, Hao Z, Penghui Z, Wei P (2013) Effect of infliximab combined with methylprednisolone on expressions of NF-κB, TRADD, and FADD in rat acute spinal cord injury. Spine 3814:E861–E869
Diaz-Ruiz A, Vergara P, Perez-Severiano F, Segovia J, Guizar-Sahagun G, Ibarra A, Rios C (2005) Cyclosporin-A inhibits constitutive nitric oxide synthase activity and neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthase expressions after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurochem Res 30:245–251
Du S, Hiramatsu N, Hayakawa K, Kasai A, Okamura M, Huang T, Yao J, Takeda M, Araki I, Sawada N, Paton AW, Paton JC, Kitamura M (2009) Suppression of NF-kappaB by cyclosporin a and tacrolimus (FK506) via induction of the C/EBP family: implication for unfolded protein response. J Immunol 182:7201–7211
Farina C, Aloisi F, Meinl E (2007) Astrocytes are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends Immunol 28:138–145
Goldshmit Y, Frisca F, Pinto AR, Pébay A, Tang JK, Siegel AL, Kaslin J, Currie PD (2014) Fgf2 improves functional recovery-decreasing gliosis and increasing radial glia and neural progenitor cells after spinal cord injury. Brain Behav 4:187–200
Green HF, Nolan YM (2012) GSK-3 mediates the release of IL-1beta, TNFalpha and IL-10 from cortical glia. Neurochem Int 61:666–671
Hu JZ, Huang JH, Xiao ZM, Li JH, Li XM, Lu HB (2013) Tetramethylpyrazine accelerates the function recovery of traumatic spinal cord in rat model by attenuating inflammation. J Neurol Sci 324:94–99
Hua K, Schindler MK, McQuail JA, Forbes ME, Riddle DR (2012) Regionally distinct responses of microglia and glial progenitor cells to whole brain irradiation in adult and aging rats. PLoS One 7:e52728
Kettenmann H, Hanisch UK, Noda M, Verkhratsky A (2011) Physiology of microglia. Physiol Rev 91:461–553
Lai AY, Todd KG (2006) Hypoxia-activated microglial mediators of neuronal survival are differentially regulated by tetracyclines. Glia 53:809–816
Lai AY, Todd KG (2008) Differential regulation of trophic and proinflammatory microglial effectors is dependent on severity of neuronal injury. Glia 56:259–270
Lambertsen KL, Clausen BH, Babcock AA, Gregersen R, Fenger C, Nielsen HH, Haugaard LS, Wirenfeldt M, Nielsen M, Dagnaes-Hansen F, Bluethmann H, Faergeman NJ, Meldgaard M, Deierborg T, Finsen B (2009) Microglia protect neurons against ischemia by synthesis of tumor necrosis factor. J Neurosci 29:131913–131930
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2:725–734
Liberto CM, Albrecht PJ, Herx LM, Yong VW, Levison SW (2004) Pro-regenerative properties of cytokine-activated astrocytes. J Neurochem 89:1092–1100
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Ni B, Cao Z, Liu Y (2013) Glycyrrhizin protects spinal cord and reduces inflammation in spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Neurosci 123:745–751
Nikodemova M, Watters JJ (2012) Efficient isolation of live microglia with preserved phenotypes from adult mouse brain. J Neuroinflammation 9:147
Pan F, Chen A, Guo F, Zhu C, Tao F (2008) Effect of FK506 on expression of hepatocyte growth factor in murine spinal cord following peripheral nerve injury. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 28:159–162
Profyris C, Cheema SS, Zang D, Azari MF, Boyle K, Petratos S (2004) Degenerative and regenerative mechanisms governing spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis 15:415–436
Saganová K, Gálik J, Blaško J, Korimová A, Račeková E, Vanický I (2012) Immunosuppressant FK506: focusing on neuroprotective effects following brain and spinal cord injury. Life Sci 91:77–82
Smith PD, Puskas F, Meng X, Lee JH, Cleveland JC Jr, Weyant MJ, Fullerton DA, Reece TB (2012) The evolution of chemokine release supports a bimodal mechanism of spinal cord ischemia and reperfusion injury. Circulation 126(11 Suppl 1):S110–S117
Sofroniew MV (2009) Molecular dissection of reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation. Trends Neurosci 32:638–647
Sticozzi C, Belmonte G, Meini A, Carbotti P, Grasso G, Palmi M (2013) IL-1β induces GFAP expression in vitro and in vivo and protects neurons from traumatic injury-associated apoptosis in rat brain striatum via NFκB/Ca2+-calmodulin/ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Neuroscience 252:367–383
Su L, Ji J, Bian J, Fu Y, Ge Y, Yuan Z (2012) Tacrolimus (FK506) prevents early retinal neovascularization in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Int Immunopharmacol 14:606–612
Thuret S, Moon LD, Gage FH (2006) Therapeutic interventions after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:628–643
Vafadari R, Kraaijeveld R, Weimar W, Baan CC (2013) Tacrolimus inhibits NF-κB activation in peripheral human T cells. PLoS One. 8(4):e60784
Wang YF, Zu JN, Li J, Chen C, Xi CY, Yan JL (2014) Curcumin promotes the spinal cord repair via inhibition of glial scar formation and inflammation. Neurosci Lett 560:51–56
Wei HY, Ma X (2014) Tamoxifen reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells, apoptosis and inhibits IKK/NF-κB pathway after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurol Sci 35(11):1763–1768. doi:10.1007/s10072-014-1828-z
Werry EL, Liu GJ, Lovelace MD, Nagarajah R, Hickie IB, Bennett MR (2011) Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated interleukin-10 release from neonatal spinal cord microglia is potentiated by glutamate. Neuroscience 175:93–103
Yang L, Jones NR, Blumbergs PC, Van Den Heuvel C, Moore EJ, Manavis J, Sarvestani GT, Ghabriel MN (2005) Severity-dependent expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in traumatic spinal cord injury in the rat. J Clin Neurosci 12:276–284
Yang Z, Zhao TZ, Zou YJ, Zhang JH, Feng H (2014) Hypoxia induces autophagic cell death through hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in microglia. PLoS One 9:e96509
Yenari MA, Kauppinen TM, Swanson RA (2010) Microglial activation in stroke: therapeutic targets. Neurother J Am Soc Exp Neuro Ther 7:378–391
Yin X, Yin Y, Cao FL, Chen YF, Peng Y, Hou WG, Sun SK, Luo ZJ (2012) Tanshinone IIA attenuates the inflammatory response and apoptosis after traumatic injury of the spinal cord in adult rats. PLoS One 7:e38381
Young W (1993) Secondary injury mechanisms in acute spinal cord injury. J Emerg Med 11(Suppl 1):13–22
Yousuf S, Atif F, Kesherwani V, Agrawal SK (2011) Neuroprotective effects of Tacrolimus (FK-506) and Cyclosporin (CsA) in oxidative injury. Brain Behav 1:87–94
Zawadzka M, Kaminska B (2005) A novel mechanism of FK506-mediated neuroprotection: downregulation of cytokine expression in glial cells. Glia 49:36–51
Zhang Z, Krebs CJ, Guth L (1997) Experimental analysis of progressive necrosis after spinal cord trauma in the rat: etiological role of the inflammatory response. Exp Neurol 143:141–152
Zhang J, Zhang A, Sun Y, Cao X, Zhang N (2009) Treatment with immunosuppressants FTY720 and tacrolimus promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. Tohoku J Exp Med 219:295–302
Zhang X, Zeng L, Yu T, Xu Y, Pu S, Du D, Jiang W (2014) Positive feedback loop of autocrine BDNF from microglia causes prolonged microglia activation. Cell Physiol Biochem 34:715–723
Zhou N, Fu Y, Wang Y, Chen P, Meng H, Guo S, Zhang M, Yang Z, Ge Y (2014) p27 kip1 haplo-insufficiency improves cardiac function in early-stages of myocardial infarction by protecting myocardium and increasing angiogenesis by promoting IKK activation. Sci Rep 7(4):5978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Fan, G., Guo, G. et al. FK506 Attenuates the Inflammation in Rat Spinal Cord Injury by Inhibiting the Activation of NF-κB in Microglia Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37, 843–855 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0422-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0422-8