Abstract
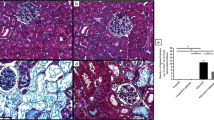
Myoglobinuric acute renal failure (ARF) is a uremic syndrome caused by traumatic or non-traumatic skeletal muscle breakdown and intracellular elements that are released into the bloodstream. We hypothesized that hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy could be beneficial in the treatment of myoglobinuric ARF caused by rhabdomyolysis. A total of 32 rats were used in the study. The rats were divided into four groups: control, control+hyperbaric oxygen (control+HBO), ARF, and ARF+hyperbaric oxygen (ARF+HBO). Glycerol (8 ml/kg) was injected into the hind legs of each of the rats in ARF and ARF+HBO groups. 2.5 atmospheric absolute HBO was applied to the rats in the control+HBO and ARF+HBO groups for 90 min on two consecutive days. Plasma urea, creatinine, sodium, potassium, calcium, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, lactic dehydrogenase, creatinine kinase and urine creatinine and sodium were examined. Creatinine clearance and fractional sodium excretion could then be calculated. Superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were assessed in renal tissue. Tissue samples were evaluated by Hematoxylin-eosin, PCNA and TUNEL staining histopathologically. MDA levels were found to be significantly decreased whereas SOD and CAT were twofold higher in the ARF+HBO group compared to the ARF group. Renal function tests were ameliorated by HBO therapy. Semiquantitative evaluation of histopathological findings indicated that necrosis and cast formation was decreased by HBO therapy and TUNEL staining showed that apoptosis was inhibited. PCNA staining showed that HBO therapy did not increase regeneration. Ultimately, we conclude that, in accordance with our hypothesis, HBO could be beneficial in the treatment of myoglobinuric ARF.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abassi ZA, Hoffman A, Better OS (1998) Acute renal failure complicating muscle crush injury. Semin Nephrol 18(5):558–565
Abul-Ezz SR, Walker PD, Shah SV (1991) Role of glutathione in an animal model of myoglobinuric acute renal failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(21):9833–9837
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Atasoyu EM, Yildiz S, Bilgi O, Cermik H, Evrenkaya R, Aktas S, Gültepe M, Kandemir EG (2005) Investigation of the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Arch Toxicol 79(5):289–293
Ay H, Uzun G, Onem Y, Aydinoz S, Yildiz S, Bilgi O, Topal T, Atasoyu EM (2007) Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Ren Fail 29(4):495–501
Aydogdu N, Atmaca G, Yalcin O, Taskiran R, Tastekin E, Kaymak K (2006) Protective effects of L-carnitine on myoglobinuric acute renal failure in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 33(1–2):119–124
Baliga R, Ueda N, Walker PD, Shah SV (1997) Oxidant mechanisms in toxic acute renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis 29(3):465–477
Bamri-Ezzine S, Ao ZJ, Londoño I, Gingras D, Bendayan M (2003) Apoptosis of tubular epithelial cells in glycogen nephrosis during diabetes. Lab Invest 83(7):1069–1080
Beetham R (2000) Biochemical investigation of suspected rhabdomyolysis. Ann Clin Biochem 37(Pt 5):581–587
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Bonegio R, Lieberthal W (2002) Role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of acute renal failure. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 11(3):301–308
Bouachour G, Cronier P, Gouello JP, Toulemonde JL, Talha A, Alquier P (1996) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in the management of crush injuries: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Trauma 41(2):333–339
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Chan RK, Austen WG Jr, Ibrahim S, Ding GY, Verna N, Hechtman HB, Moore FD Jr (2004) Reperfusion injury to skeletal muscle affects primarily type II muscle fibers. J Surg Res 122(1):54–60
Cohn GH (1986) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Promoting healing in difficult cases. Postgrad Med 79(2):89–92
Emerit J, Beaumont C, Trivin F (2001) Iron metabolism, free radicals, and oxidative injury. Biomed Pharmacother 55(6):333–339
Fitzpatrick DT, Murphy PT, Bryce M (1998) Adjunctive treatment of compartment syndrome with hyperbaric oxygen. Mil Med 163(8):577–579
Freeman BA, Crapo JD (1982) Biology of disease: free radicals and tissue injury. Lab Invest 47(5):412–426
Gonzalez D (2005) Crush syndrome. Crit Care Med 33(1 Suppl):34–41
Holt SG, Moore KP (2001) Pathogenesis and treatment of renal dysfunction in rhabdomyolysis. Intensive Care Med 27(5):803–811
Homsi E, Janino P, de Faria JB (2006) Role of caspases on cell death, inflammation, and cell cycle in glycerol-induced acute renal failure. Kidney Int 69(8):1385–1392
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of Avidin–Biotin–Peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Ijichi H, Taketomi A, Yoshizumi T, Uchiyama H, Yonemura Y, Soejima Y, Shimada M, Maehara Y (2006) Hyperbaric oxygen induces vascular endothelial growth factor and reduces liver injury in regenerating rat liver after partial hepatectomy. J Hepatol 45(1):28–34
Ishizuka S, Yano T, Hagiwara K, Sone M, Nihei H, Ozasa H, Horikawa S (1999) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase mediates renal regeneration in rats with myoglobinuric acute renal injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 254(1):88–92
Kannan K, Jain SK (2000) Oxidative stress and apoptosis. Pathophysiology 7(3):153–163
Kim YS, Jung MH, Choi MY, Kim YH, Sheverdin V, Kim JH, Ha HJ, Park DJ, Kang SS, Cho GJ, Choi WS, Chang SH (2009) Glutamine attenuates tubular cell apoptosis in acute kidney injury via inhibition of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylation of 14-3-3. Crit Care Med 37(6):2033–2044
Knochel JP (1998) Rhabdomyolisis and acute renal failure. In: Glossock RJ (ed) Current therapy in nephrology and hypertension, 4th edn. Mosby, St. Louis, pp 262–265
MacLean JG, Barrett DS (1993) Rhabdomyolysis: a neglected priority in the early management of severe limb trauma. Injury 24(3):205–207
Malinoski DJ, Slater MS, Mullins RJ (2004) Crush injury and rhabdomyolysis. Crit Care Clin 20(1):171–192
Mink RB, Dutka AJ (1995) Hyperbaric oxygen after global cerebral ischemia in rabbits reduces brain vascular permeability and blood flow. Stroke 26(12):2307–2312
Miwa S, Muller FL, Beckman KB (2008) Oxidative stress in aging: from model systems to human diseases. Springer, New York
Myers RA (2000) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for trauma: crush injury, compartment syndrome, and other acute traumatic peripheral ischemias. Int Anesthesiol Clin 38(1):139–151
Nylander G, Lewis D, Nordström H, Larsson J (1985) Reduction of postischemic edema with hyperbaric oxygen. Plast Reconstr Surg 76(4):596–603
Odeh M (1991) The role of reperfusion-induced injury in the pathogenesis of the crush syndrome. N Engl J Med 324(20):1417–1422
Ozden TA, Uzun H, Bohloli M, Toklu AS, Paksoy M, Simsek G, Durak H, Issever H, Ipek T (2004) The effects of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on oxidant and antioxidants levels during liver regeneration in rats. Tohoku J Exp Med 203(4):253–265
Paller MS (1988) Hemoglobin- and myoglobin-induced acute renal failure in rats: role of iron in nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol 255(3 Pt 2):F539–F544
Paller MS, Hedlund BE (1988) Role of iron in postischemic renal injury in the rat. Kidney Int 34(4):474–480
Reitan JA, Kien ND, Thorup S, Corkill G (1990) Hyperbaric oxygen increases survival following carotid ligation in gerbils. Stroke 21(1):119–123
Rubinstein I, Abassi Z, Milman F, Ovcharenko E, Coleman R, Winaver J, Better OS (2009) Hyperbaric oxygen treatment improves GFR in rats with ischaemia/reperfusion renal injury: a possible role for the antioxidant/oxidant balance in the ischaemic kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24(2):428–436
Shah SV (1988) Evidence suggesting a role for hydroxyl radical in passive Heymann nephritis in rats. Am J Physiol 254(3 Pt 2):F337–F344
Shah SV, Walker PD (1988) Evidence suggesting a role for hydroxyl radical in glycerol-induced acute renal failure. Am J Physiol 255(3 Pt 2):438–443
Skyhar MJ, Hargens AR, Strauss MB, Gershuni DH, Hart GB, Akeson WH (1996) Hyperbaric oxygen reduces edema and necrosis of skeletal muscle in compartment syndromes associated with hemorrhagic hypotension. J Bone Joint Surg Am 68(8):1218–1224
Smith J, Greaves I (2003) Crush injury and crush syndrome: a review. J Trauma 54(5 Suppl):226–230
Solmazgul E, Uzun G, Cermik H, Atasoyu EM, Aydinoz S, Yildiz S (2007) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Urol Int 78(1):82–85
Strauss MB, Hargens AR, Gershuni DH, Greenberg DA, Crenshaw AG, Hart GB, Akeson WH (1983) Reduction of skeletal muscle necrosis using intermittent hyperbaric oxygen in a model compartment syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65(5):656–662
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Vanholder R, Sever MS, Erek E, Lameire N (2000a) Acute renal failure related to the crush syndrome: towards an era of seismo-nephrology? Nephrol Dial Transplant 15(10):1517–1521
Vanholder R, Sever MS, Erek E, Lameire N (2000b) Rhabdomyolysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 11(8):1553–1561
Warren JD, Blumbergs PC, Thompson PD (2002) Rhabdomyolysis: a review. Muscle Nerve 25(3):332–347
Wong VY, Keller PM, Nuttall ME, Kikly K, DeWolf WE Jr, Lee D, Ali SM, Nadeau DP, Grygielko ET, Laping NJ, Brooks DP (2001) Role of caspases in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol 433(2–3):135–140
Zager RA (1989) Studies of mechanisms and protective maneuvers in myoglobinuric acute renal injury. Lab Invest 60(5):619–629
Zager RA (1996) Rhabdomyolysis and myohemoglobinuric acute renal failure. Kidney Int 49(2):314–326
Acknowledgments
This study was supported as Project TUBAB 2011-41 by Trakya University Research Center, Edirne, Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayvaz, S., Aksu, B., Kanter, M. et al. Preventive effects of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on glycerol-induced myoglobinuric acute renal failure in rats. J Mol Hist 43, 161–170 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9391-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9391-5