Abstract
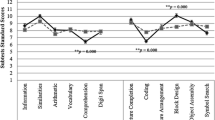
Changes in the Wechsler Intelligence Scales for Children-IV (WISC-IV) may affect the IQ profile characteristic of autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Moreover, the association of particular component cognitive abilities (unlike overall IQ) with symptomatology and adaptive functioning in ASD remains unclear. This archival study characterizes the WISC-IV IQ profile among 56 high-functioning (IQ > 70) children with ASD and correlates WISC-IV performance with ASD and ADHD symptomatology and adaptive functioning. The ASD WISC-IV profile included strengths on Matrix Reasoning and Similarities, weaknesses on Comprehension (which correlated negatively with social symptoms) and the subtests comprising the Processing Speed Index (Coding, Symbol Search). Processing speed task performance correlated negatively with communication symptoms and positively with communication abilities, indicating its importance to functional outcomes in ASD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M. H., Lincoln, A. J., & Kaufman, A. S. (1991). Sequential and simultaneous processing abilities of high-functioning autistic and language-impaired children. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 21, 483–502.
Asarnow, R. F., Tanguay, P. E., Bott, L., & Freeman, B. J. (1987). Patterns of intellectual functioning in non-retarded autistic and schizophrenic children. Journal Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 28, 273–280.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B (Methodological), 57, 289–300.
Billstedt, E., Gillberg, I. C., & Gillberg, C. (2007). Autism in adults: Symptom patterns and early childhood predictors. Use of the DISCO in a community sample followed from childhood. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48, 1102–1110.
Black, D. O., Wallace, G. L., Sokoloff, J. L., & Kenworthy, L. (2009). Brief report: IQ split predicts social symptoms and communication abilities in high-functioning children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39, 1613–1619.
Bolte, S., & Poustka, F. (2002). The relation between general cognitive level and adaptive behavior domains in individuals with autism with and without co-morbid mental retardation. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 33, 165–172.
Calhoun, S. L., & Mayes, S. D. (2005). Processing speed in children with clinical disorders. Psychology in the Schools, 42, 333–343.
Carter, A. S., Volkmar, F. R., Sparrow, S. S., Wang, J., Lord, C., Dawson, G., et al. (1998). The Vineland adaptive behavior scales: Supplementary norms for individuals with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 28, 287–302.
Chhabildas, N., Pennington, B. F., & Willcutt, E. G. (2001). A comparison of the neuropsychological profiles of the DSM-IV subtypes of ADHD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 29, 529–540.
Dawson, M., Soulieres, I., Gernsbacher, M. A., & Mottron, L. (2007). Research report: The level and nature of autistic intelligence. Psychological Science, 18, 657–662.
Dennis, M., Lockyer, L., Lazenby, A. L., Donnelly, R. E., Wilkinson, M., & Schoonheyt, W. (1999). Intelligence patterns among children with high-functioning autism, phenylketonuria, and childhood head injury. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29, 5–17.
Donders, J., & Jenke, K. (2008). Criterion validity of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Fourth Edition after pediatric traumatic brain injury. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 14, 651–655.
DuPaul, G. J., Power, T. J., Anastopoulos, A. D., & Reid, R. (1998). ADHD rating scale- IV: Checklists, norms, and clinical interpretation. New York: The Guilford Press.
Elliott, C. D. (1990). The differential ability scales. Lutz, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc.
Fiorello, C. A., Hale, J. B., McGrath, M., Ryan, K., & Quinn, S. (2001). IQ interpretation for children with flat and variable test profiles. Learning and Individual Differences, 13, 115–125.
Freeman, B. J., Chapman, L. J., Forness, S. R., & Ritvo, E. R. (1985). Cognitive processing of high functioning autistic children: Comparing the K-ABC and the WISC-R. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 4, 357–362.
Freeman, B. J., Del’Homme, M., Guthrie, D., & Zhang, F. (1999). Vineland adaptive behavior scale scores as a function of age and initial IQ in 210 autistic children. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29, 379–384.
Goldstein, G., Allen, D. N., Minshew, N. J., Williams, D. L., Volkmar, F., Klin, A., et al. (2008). The structure of intelligence in children and adults with high functioning autism. Neuropsychology, 22, 301–312.
Goldstein, S., & Schwebach, A. J. (2004). The comorbidity of pervasive developmental disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Results of a retrospective chard review. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34, 329–339.
Happé, F. G. (1994). Wechsler IQ profile and theory of mind in autism: A research note. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 35, 1461–1471.
Hollingshead, A. B. (1975). Four factor index of social status. New Haven: Yale University.
Joseph, R. M., Tager-Flusberg, H., & Lord, C. (2002). Cognitive profiles and social communicative functioning in children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 46, 807–821.
Kenworthy, L. E., Black, D. O., Wallace, G. L., Ahluvalia, T., Wagner, A. E., & Sirian, L. M. (2005). Disorganization: The forgotten executive dysfunction in high-functioning autism (HFA) spectrum disorders. Developmental Neuropsychology, 28, 809–827.
Kenworthy, L., Case, L., Harms, M. B., Martin, A., & Wallace, G. L. (2010). Adaptive behavior ratings correlate with symptomatology and IQ among individual with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40, 416–423.
Klin, A., Saulnier, C. A., Sparrow, S. S., Cicchetti, D. V., Volkmar, F. R., & Lord, C. (2007). Social and communication abilities and disabilities in higher functioning individuals with autism spectrum disorders: The Vineland and the ADOS. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 748–759.
Koegel, L. K., Koegel, R. L., & Smith, A. (1997). Variables related to differences in standardized test outcomes for children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 27, 233–244.
Koyama, T., Tachimori, H., Osada, H., & Kurita, H. (2006). Cognitive and symptom profiles in high functioning pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36, 373–380.
Koyama, T., Tachimori, H., Osada, H., Takeda, T., & Kurita, H. (2007). Cognitive and symptom profiles in Asperger’s syndrome and high functioning autism. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 61, 99–104.
Lainhart, J. E., Bigler, E. D., Bocian, M., Coon, H., Dinh, E., Dawson, G., et al. (2006). Head circumference and height in autism: A study by the collaborative program of excellence in autism. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 140, 2257–2274.
Le Couteur, A., Rutter, M., Lord, C., Rios, P., Robertson, S., Holdgrafer, M., et al. (1989). Autism diagnostic interview: A standardized investigator-based instrument. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 19, 363–387.
Leyfer, O. T., Folstein, S. E., Bacalman, S., Davis, N. O., Dinh, E., Morgan, J., et al. (2006). Comorbid psychiatric disorders in children with autism: Interview development and rates of disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36, 849–861.
Lincoln, A. J., Courchesne, E., Kilman, B. A., Elmasian, R., & Allen, M. (1988). A study of intellectual abilities in high-functioning people with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 18, 505–524.
Liss, M., Harel, B., Fein, D., Allen, D., Dunn, M., Feinstein, C., et al. (2001). Predictors and correlates of adaptive functioning in children with developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31, 219–230.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., DiLavore, P. C., & Risi, S. (1999). Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule–WPS (ADOS-WPS). Los Angeles, CA: Western Psychological Services.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., & Le Couteur, A. (1994). Autism diagnostic interview-revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers and individuals with possible developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 24, 659–685.
Mayes, S. D., & Calhoun, S. L. (2003). Analysis of WISC-III, Stanford-Binet: IV, and academic achievement test scores in children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 33, 329–341.
Mayes, S. D., & Calhoun, S. L. (2004). Similarities and differences in Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Third Edition (WISC-III) profiles: Support for subtest analysis in clinical referrals. Clinical Neuropsychologist, 18, 559–572.
Mayes, S. D., & Calhoun, S. L. (2006). WISC-III and WISC-IV profiles in children with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 9, 486–493.
Mayes, S. D., & Calhoun, S. L. (2008). WISC-IV and WIAT-II profiles in children with high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 428–439.
McAuley, T., Chen, S., Goos, L., Schachar, R., & Crosbie, J. (2010). Is the behavior rating inventory of executive function more strongly associated with measures of impairment or executive function? Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 16, 495–505.
Nyden, A., Billstedt, E., Hjelmquist, E., & Gillberg, C. (2001). Neurocognitive stability in Asperger syndrome, ADHD, and reading and writing disorder: A pilot study. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 43, 65–171.
Pfeiffer, S., Reddy, L., Kletzel, J., Schmelzler, E., & Boyer, L. (2000). The practitioner’s view of IQ testing and profile analysis. School Psychology Quarterly, 15, 376–385.
Power, T. J., Doherty, B. J., Panichelli-Mindel, S. M., Karustis, J. L., Eiraldi, R. B., Anastopoulos, A. D., et al. (1998). The predictive validity of parent and teacher reports of ADHD symptoms. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 20, 57–81.
Scheuffgen, K., Happé, F., Anderson, M., & Frith, U. (2000). High ‘‘intelligence’’, low ‘‘IQ’’? Speed of processing and measured IQ in children with autism. Development and Psychopathology, 12, 83–90.
Siegel, D. J., Minshew, N. J., & Goldstein, G. (1996). Wechsler IQ profiles in diagnosis of high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 26, 389–406.
Sinzig, J., Morsch, D., Bruning, N., Schmidt, M. H., & Lehmkuhl, G. (2008). Inhibition, flexibility, working memory and planning in autism spectrum disorders with and without comorbid ADHD-symptoms. Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health, 2, 4.
Sparrow, S. S., Cicchetti, D. V., & Balla, D. A. (2005). Vineland adaptive behavior scales: Second edition (Vineland II), survey interview form/caregiver rating form. Livonia, MN: Pearson Assessments.
Tallal, P. (2004). Opinion–improving language and literacy is a matter of time. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 5, 721–728.
Tillman, C., Eninger, L., Forssman, L., & Bohlin, G. (2011). The relation between working memory components and ADHD symptoms from a developmental perspective. Developmental Neuropsychology, 36, 181–198.
Venter, A., Lord, C., & Schopler, E. (1992). A follow-up-study of high-functioning autistic children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 33, 489–507.
Volkmar, F. R., Sparrow, S. S., Goudreau, D., Cicchetti, D. V., Paul, R., & Cohen, D. J. (1987). Social deficits in autism: An operational approach using the Vineland-adaptive behavior scales. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 26, 156–161.
Wallace, G. L., Anderson, M., & Happé, F. (2009a). Brief report: Information processing speed is intact in autism but not correlated with measured intelligence. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39, 809–814.
Wallace, G. L., Happé, F., & Giedd, J. N. (2009b). A case study of a multiply-talented savant with an autism spectrum disorder: Neuropsychological functioning and brain morphometry. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society: Section B: Biological Sciences, 364, 1425–1432.
Wechsler, D. (2003). Wechsler intelligence scale for children-fourth edition (WISC-IV). San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
Yerys, B. E., Wallace, G. L., Sokoloff, J. L., Shook, D. A., James, J. D., & Kenworthy, L. (2009). Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms moderate cognition and behavior in children with autism spectrum disorders. Autism Research, 2, 322–333.
Yoshida, Y., & Uchiyama, T. (2004). The clinical necessity for assessing attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (AD/HD) symptoms in children with high functioning pervasive developmental disorder (PDD). European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 13, 307–314.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Institute of Mental Health. We would like to thank the children and families who so kindly gave their time and energy to assist in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveras-Rentas, R.E., Kenworthy, L., Roberson, R.B. et al. WISC-IV Profile in High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorders: Impaired Processing Speed is Associated with Increased Autism Communication Symptoms and Decreased Adaptive Communication Abilities. J Autism Dev Disord 42, 655–664 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-011-1289-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-011-1289-7