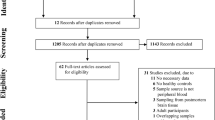
Abstract
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) plays an important role in activity-dependent synaptic plasticity. Altered blood BDNF levels have been frequently identified in people with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). There are however wide discrepancies in the evidence. Therefore, we performed the present systematic review and meta-analysis aimed at qualitative and quantitative synthesis of studies that measured blood BDNF levels in ASD and control subjects. Observational studies were identified through electronic database searching and also hand-searching of reference lists of relevant articles. A total of 183 papers were initially identified for review and eventually twenty studies were included in the meta-analysis. A meta-analysis of blood BDNF in 887 patients with ASD and 901 control subjects demonstrated significantly higher BDNF levels in ASD compared to controls with the SMD of 0.47 (95% CI 0.07–0.86, p = 0.02). In addition subgroup meta-analyses were performed based on the BDNF specimen. The present meta-analysis study led to conclusion that BDNF might play role in autism initiation/ propagation and therefore it can be considered as a possible biomarker of ASD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah, M. W., Mortensen, E. L., Greaves-Lord, K., Larsen, N., Bonefeld-Jorgensen, E. C., Norgaard-Pedersen, B., & Grove, J. (2013). Neonatal levels of neurotrophic factors and risk of autism spectrum disorders. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 128(1), 61–69. doi:10.1111/acps.12020.
Abdallah, M. W., Pearce, B. D., Larsen, N., Greaves-Lord, K., Norgaard-Pedersen, B., Hougaard, D. M., & Grove, J. (2012). Amniotic fluid MMP-9 and neurotrophins in autism spectrum disorders: an exploratory study. Autism Research, 5(6), 428–433. doi:10.1002/aur.1254.
Al-Ayadhi, L. Y. (2012). Relationship between sonic hedgehog protein, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and oxidative stress in autism spectrum disorders. Neurochemical Research, 37(2), 394–400. doi:10.1007/s11064-011-0624-x.
Autry, A. E., & Monteggia, L. M. (2012). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacological Reviews, 64(2), 238–258.
Bailey, A. R., Giunta, B. N., Obregon, D., Nikolic, W. V., Tian, J., Sanberg, C. D., & Tan, J. (2008). Peripheral biomarkers in Autism: Secreted amyloid precursor protein-alpha as a probable key player in early diagnosis. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 1(4), 338–344.
Baio, J. (2012). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders: Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 14 sites, United States, 2008. Morbidity and mortality weekly report. Surveillance summaries (Vol. 61). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Baron-Cohen, S., Leslie, A. M., & Frith, U. (1985). Does the autistic child have a “theory of mind”? Cognition, 21(1), 37–46.
Bauman, M. L., & Kemper, T. L. (2005). Neuroanatomic observations of the brain in autism: A review and future directions. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 23(2), 183–187.
Bryn, V., Halvorsen, B., Ueland, T., Isaksen, J., Kolkova, K., Ravn, K., & Skjeldal, O. H. (2015). Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in childhood. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology, 19(4), 411–414. doi:10.1016/j.ejpn.2015.03.005.
Businaro, R., Corsi, M., Azzara, G., Di Raimo, T., Laviola, G., Romano, E., Ricci, S (2016). Interleukin-18 modulation in autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 13(1), 2. doi:10.1186/s12974-015-0466-6.
Coghlan, S., Horder, J., Inkster, B., Mendez, M. A., Murphy, D. G., & Nutt, D. J. (2012). GABA system dysfunction in autism and related disorders: From synapse to symptoms. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(9), 2044–2055.
Connolly, A. M., Chez, M., Streif, E. M., Keeling, R. M., Golumbek, P. T., Kwon, J. M., & Deuel, R. M. (2006). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and autoantibodies to neural antigens in sera of children with autistic spectrum disorders, Landau–Kleffner syndrome, and epilepsy. Biological Psychiatry, 59(4), 354–363. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.07.004.
Correia, C. T., Coutinho, A. M., Sequeira, A. F., Sousa, I. G., Lourenco Venda, L., Almeida, J. P., & Vicente, A. M. (2010). Increased BDNF levels and NTRK2 gene association suggest a disruption of BDNF/TrkB signaling in autism. The Journal of Neuroscience, 9(7), 841–848. doi: 10.1111/j1601183X.2010.00627.x.
Croen, L. A., Goines, P., Braunschweig, D., Yolken, R., Yoshida, C. K., Grether, J. K., & Van de Water, J. (2008). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and autism: Maternal and infant peripheral blood levels in the early markers for autism (EMA) study. Autism Research, 1(2), 130–137. doi:10.1002/aur.14.
De Rubeis, S., He, X., Goldberg, A. P., Poultney, C. S., Samocha, K., Cicek, A. E., & Walker, S. (2014). Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature, 515(7526), 209–215.
Enstrom, A., Onore, C., Tarver, A., Hertz-Picciotto, I., Hansen, R., Croen, L., & Ashwood, P. (2008). Peripheral blood leukocyte production of BDNF following mitogen stimulation in early onset and regressive autism. American Journal of Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 4(2), 121–129.
Ernfors, P., Lee, K. -F., & Jaenisch, R. (1994). Mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor develop with sensory deficits. Nature, 368, 147–150.
Garcia, K. L., Yu, G., Nicolini, C., Michalski, B., Garzon, D. J., Chiu, V. S., & Fahnestock, M. (2012). Altered balance of proteolytic isoforms of pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor in autism. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 71(4), 289–297. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e31824b27e4.
Gómez-Pinilla, F., Ying, Z., Roy, R. R., Molteni, R., & Edgerton, V. R. (2002). Voluntary exercise induces a BDNF-mediated mechanism that promotes neuroplasticity. Journal of Neurophysiology, 88(5), 2187–2195.
Halepoto, D. M., Bashir, S., & Al-Ayadhi, L. (2014). Possible role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in autism spectrum disorder: Current status. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan, 24(4), 274–278.
Halepoto, D. M., Bashir, S., Zeina, R., & Al-Ayadhi, L. Y. (2015). Correlation between hedgehog (Hh) protein family and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan, 25(12), 882–885.
Han, J. C., Thurm, A., Golden Williams, C., Joseph, L. A., Zein, W. M., Brooks, B. P., & Swedo, S. E. (2013). Association of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) haploinsufficiency with lower adaptive behaviour and reduced cognitive functioning in WAGR/11p13 deletion syndrome. Cortex, 49(10), 2700–2710. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2013.02.009.
Happe, F., Ehlers, S., Fletcher, P., Frith, U., Johansson, M., Gillberg, C., & Frith, C. (1996). Theory of mind in the brain. Evidence from a PET scan study of Asperger syndrome. Neuroreport, 8(1), 197–201.
Hashimoto, K., Iwata, Y., Nakamura, K., Tsujii, M., Tsuchiya, K. J., Sekine, Y., & Mori, N. (2006). Reduced serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in adult male patients with autism. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 30(8), 1529–1531. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2006.06.018.
Hatton, D. D., Sideris, J., Skinner, M., Mankowski, J., Bailey, D. B., Roberts, J., & Mirrett, P. (2006). Autistic behavior in children with fragile X syndrome: prevalence, stability, and the impact of FMRP. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 140(17), 1804–1813.
Kasarpalkar, N. J., Kothari, S. T., & Dave, U. P. (2014). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in children with autism spectrum disorder. Annals of Neurosciences, 21(4), 129–133. doi:10.5214/ans.0972.7531.210403.
Katoh-Semba, R., Wakako, R., Komori, T., Shigemi, H., Miyazaki, N., Ito, H., & Nakayama, A. (2007). Age-related changes in BDNF protein levels in human serum: Differences between autism cases and normal controls. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 25(6), 367–372. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2007.07.002.
Kazim, S. F., Cardenas-Aguayo Mdel, C., Arif, M., Blanchard, J., Fayyaz, F., Grundke-Iqbal, I., & Iqbal, K. (2015). Sera from children with autism induce autistic features which can be rescued with a CNTF small peptide mimetic in rats. PLoS ONE, 10(3), e0118627. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0118627.
Kelleher, R. J., & Bear, M. F. (2008). The autistic neuron: Troubled translation? Cell, 135(3), 401–406.
Kim, J. A., Szatmari, P., Bryson, S. E., Streiner, D. L., & Wilson, F. J. (2000). The prevalence of anxiety and mood problems among children with autism and Asperger syndrome. Autism: The International Journal of Research and Practice, 4(2), 117–132.
Korte, M., Carroll, P., Wolf, E., Brem, G., Thoenen, H., & Bonhoeffer, T. (1995). Hippocampal long-term potentiation is impaired in mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 92(19), 8856–8860.
Lavelle, T. A., Weinstein, M. C., Newhouse, J. P., Munir, K., Kuhlthau, K. A., & Prosser, L. A. (2014). Economic burden of childhood autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics, 133(3), e520–e529.
Lee, L.-C., Harrington, R. A., Louie, B. B., & Newschaffer, C. J. (2008). Children with autism: Quality of life and parental concerns. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(6), 1147–1160.
Leibrock, J., Lottspeich, F., Hohn, A., Hofer, M., Hengerer, B., Masiakowski, P., Barde, Y. -A. (1989). Molecular cloning and expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature, 341, 149–152.
Lu, B. (2003). BDNF and activity-dependent synaptic modulation. Learning & Memory, 10(2), 86–98.
Martinowich, K., Hattori, D., Wu, H., Fouse, S., He, F., Hu, Y., & Sun, Y. E. (2003). DNA methylation-related chromatin remodeling in activity-dependent BDNF gene regulation. Science, 302(5646), 890–893.
Meng, W. D., Sun, S. J., Yang, J., Chu, R. X., Tu, W., & Liu, Q. (2016). Elevated serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) but not BDNF gene Val66Met polymorphism is associated with autism spectrum disorders. Molecular Neurobiology. doi:10.1007/s12035-016-9721-9.
Miyazaki, K., Narita, N., Sakuta, R., Miyahara, T., Naruse, H., Okado, N., & Narita, M. (2004). Serum neurotrophin concentrations in autism and mental retardation: A pilot study. Brain & Development, 26(5), 292–295. doi:10.1016/s0387-7604(03)00168-2.
Nagahara, A. H., Merrill, D. A., Coppola, G., Tsukada, S., Schroeder, B. E., Shaked, G. M., & Conner, J. M. (2009). Neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rodent and primate models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Medicine, 15(3), 331–337.
Nelson, K. B., Grether, J. K., Croen, L. A., Dambrosia, J. M., Dickens, B. F., Jelliffe, L. L., & Phillips, T. M. (2001). Neuropeptides and neurotrophins in neonatal blood of children with autism or mental retardation. Annals of Neurology, 49(5), 597–606.
Nelson, P. G., Kuddo, T., Song, E. Y., Dambrosia, J. M., Kohler, S., Satyanarayana, G., & Nelson, K. B. (2006). Selected neurotrophins, neuropeptides, and cytokines: Developmental trajectory and concentrations in neonatal blood of children with autism or Down syndrome. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 24(1), 73–80. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2005.10.003.
Nishimura, K., Nakamura, K., Anitha, A., Yamada, K., Tsujii, M., Iwayama, Y., & Mori, N. (2007). Genetic analyses of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene in autism. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 356(1), 200–206. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.02.135.
Pardo, C. A., Buckley, A., Thurm, A., Lee, L. C., Azhagiri, A., Neville, D. M., & Swedo, S. E. (2013). A pilot open-label trial of minocycline in patients with autism and regressive features. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 5(1), 9. doi:10.1186/1866-1955-5-9.
Perry, E. K., Lee, M. L., Martin-Ruiz, C. M., Court, J. A., Volsen, S. G., Merrit, J., & Wenk, G. L. (2001). Cholinergic activity in autism: Abnormalities in the cerebral cortex and basal forebrain. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 158(7), 1058–1066. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.158.7.1058.
Ray, B., Long, J. M., Sokol, D. K., & Lahiri, D. K. (2011). Increased secreted amyloid precursor protein-alpha (sAPPalpha) in severe autism: Proposal of a specific, anabolic pathway and putative biomarker. PLoS ONE, 6(6), e20405. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020405.
Ricci, S., Businaro, R., Ippoliti, F., Lo Vasco, V. R., Massoni, F., Onofri, E., Archer, T. (2013). Altered cytokine and BDNF levels in autism spectrum disorder. Neurotoxicity Research, 24(4), 491–501. doi:10.1007/s12640-013-9393-4.
Rodrigues, D. H., Rocha, N. P., Sousa, L. F., Barbosa, I. G., Kummer, A., & Teixeira, A. L. (2014). Circulating levels of neurotrophic factors in autism spectrum disorders. Neuro Endocrinology Letters, 35(5), 380–384.
Sajdel-Sulkowska, E. M., Xu, M., McGinnis, W., & Koibuchi, N. (2011). Brain region-specific changes in oxidative stress and neurotrophin levels in autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Cerebellum, 10(1), 43–48. doi:10.1007/s12311-010-0223-4.
Segura, M., Pedreno, C., Obiols, J., Taurines, R., Pamias, M., Grunblatt, E., & Gella, A. (2015). Neurotrophin blood-based gene expression and social cognition analysis in patients with autism spectrum disorder. Neurogenetics, 16(2), 123–131. doi:10.1007/s10048-014-0434-9.
Sheikh, A. M., Li, X., Wen, G., Tauqeer, Z., Brown, W. T., & Malik, M. (2010). Cathepsin D and apoptosis related proteins are elevated in the brain of autistic subjects. Neuroscience, 165(2), 363–370. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.10.035.
Sheikh, A. M., Malik, M., Wen, G., Chauhan, A., Chauhan, V., Gong, C. X., & Li, X. (2010). BDNF-Akt-Bcl2 antiapoptotic signaling pathway is compromised in the brain of autistic subjects. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 88(12), 2641–2647. doi:10.1002/jnr.22416.
Shirayama, Y., Chen, A. C. H., Nakagawa, S., Russell, D. S., & Duman, R. S. (2002). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor produces antidepressant effects in behavioral models of depression. The Journal of Neuroscience, 22(8), 3251–3261.
Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Charman, T., Chandler, S., Loucas, T., & Baird, G. (2008). Psychiatric disorders in children with autism spectrum disorders: Prevalence, comorbidity, and associated factors in a population-derived sample. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 47(8), 921–929.
Siuciak, J. A., Lewis, D. R., Wiegand, S. J., & Lindsay, R. M. (1997). Antidepressant-like effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 56(1), 131–137.
Sokol, D. K., Chen, D., Farlow, M. R., Dunn, D. W., Maloney, B., Zimmer, J. A., & Lahiri, D. K. (2006). High levels of Alzheimer beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP) in children with severely autistic behavior and aggression. Journal of Child Neurology, 21(6), 444–449.
Spratt, E. G., Granholm, A. C., Carpenter, L. A., Boger, H. A., Papa, C. E., Logan, S., & Brady, K. T. (2015). Pilot study and review: Physiological differences in BDNF, a potential biomarker in males and females with autistic disorder. International Neuropsychiatric Disease Journal, 3(1), 19–26. doi:10.9734/indj/2015/12118.
Stahlberg, O., Soderstrom, H., Rastam, M., & Gillberg, C. (2004). Bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and other psychotic disorders in adults with childhood onset AD/HD and/or autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Neural Transmission, 111(7), 891–902. doi:10.1007/s00702-004-0115-1.
Taurines, R., Segura, M., Schecklmann, M., Albantakis, L., Grunblatt, E., Walitza, S., & Gerlach, M. (2014). Altered peripheral BDNF mRNA expression and BDNF protein concentrations in blood of children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Neural Transmission, 121(9), 1117–1128. doi:10.1007/s00702-014-1162-x.
Tuchman, R., & Rapin, I. (2002). Epilepsy in autism. The Lancet Neurology, 1(6), 352–358.
Vaynman, S., Ying, Z., & Gomez-Pinilla, F. (2004). Hippocampal BDNF mediates the efficacy of exercise on synaptic plasticity and cognition. European Journal of Neuroscience, 20(10), 2580–2590.
Wang, M., Chen, H., Yu, T., Cui, G., Jiao, A., & Liang, H. (2015). Increased serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in autism spectrum disorder. Neuroreport, 26(11), 638–641. doi:10.1097/wnr.0000000000000404.
Wang, Y., Zhao, X., Ju, W., Flory, M., Zhong, J., Jiang, S., & Zhong, N. (2015). Genome-wide differential expression of synaptic long noncoding RNAs in autism spectrum disorder. Translational Psychiatry, 5, e660. doi:10.1038/tp.2015.144.
Wells, G. A., Shea, B., O’connell, D., Peterson, J. E., Welch, V., Losos, M., & Tugwell, P. (2000). The Newcastle–Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses.
White, S. W., Oswald, D., Ollendick, T., & Scahill, L. (2009). Anxiety in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Clinical Psychology Review, 29(3), 216–229.
Wink, L. K., Fitzpatrick, S., Shaffer, R., Melnyk, S., Begtrup, A. H., Fox, E., & Erickson, C. A. (2015). The neurobehavioral and molecular phenotype of Angelman syndrome. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 167(11), 2623–2628. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.37254.
Zhang, Q. B., Jiang, L. F., Kong, L. Y., & Lu, Y. J. (2014). Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in Chinese children with autism spectrum disorders: A pilot study. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 37, 65–68. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2014.06.013.
Zoghbi, H. Y. (2003). Postnatal neurodevelopmental disorders: Meeting at the synapse? Science, 302(5646), 826–830.
Zuccato, C., & Cattaneo, E. (2009). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature Reviews Neurology, 5(6), 311–322.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by a Grant from Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 32828).
Author Contributions
AS developed the concept and designed study, collected and analyzed data, and wrote the original draft of paper; AS and NR critically revised the paper; NR supervised the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human and animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saghazadeh, A., Rezaei, N. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Autism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Autism Dev Disord 47, 1018–1029 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-016-3024-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-016-3024-x