Abstract
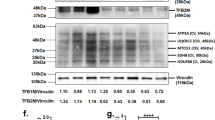
This study evaluated the effects of aldosterone upon Na+/H+ exchange (NHE) activity in immortalized proximal tubular epithelial (PTE) cells from the spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) and the normotensive controls (Wistar Kyoto rat; WKY). Increases in NHE activity after exposure to aldosterone occurred in time- and concentration-dependent manner in SHR PTE cells, but not in WKY PTE cells. The aldosterone-induced increases in NHE activity were prevented by spironolactone, but not by the glucocorticoid receptor antagonist Ru 38486. The presence of the mineralocorticoid receptor transcript was confirmed by PCR and NHE1, NHE2, and NHE3 proteins were detected by immunoblot analysis. Cariporide and EIPA, but not S3226, inhibited the aldosterone-induced increase in NHE activity, indicating that NHE1 is the most likely involved NHE isoform. Pretreatment of SHR PTE cells with actinomycin D attenuated the aldosterone-induced increases in NHE activity. The SHR PTE cells had an increased rate of H2O2 production when compared with WKY PTE cells. Treatment of cells with apocynin, a NADPH oxidase inhibitor, markedly reduced the rate of H2O2 production. The aldosterone-induced increase in NHE activity SHR PTE cells was completely prevented by apocynin. In conclusion, the aldosterone-induced stimulation of NHE1 activity is a genomic event unique in SHR PTE cells, which involves the activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor, but ultimately requires the availability of H2O2 in excess.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Booth RE, Johnson JP, Stockand JD (2002) Aldosterone. Adv Physiol Educ 26:8–20
Eaton DC, Malik B, Saxena NC, Al-Khalili OK, Yue G (2001) Mechanisms of aldosterone’s action on epithelial Na+ transport. J Membr Biol 184:313–319
Verrey F (1999) Early aldosterone action: toward filling the gap between transcription and transport. Am J Physiol 277:F319–F327
Pearce D, Verrey F, Chen SY, Mastroberardino L, Meijer OC, Wang J, Bhargava A (2000) Role of SGK in mineralocorticoid-regulated sodium transport. Kidney Int 57:1283–1289
Krug AW, Grossmann C, Schuster C, Freudinger R, Mildenberger S, Govindan MV, Gekle M (2003) Aldosterone stimulates epidermal growth factor receptor expression. J Biol Chem 278:43060–43066
Boldyreff B, Wehling M (2003) Non-genomic actions of aldosterone: mechanisms and consequences in kidney cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:1693–1695
Gekle M, Freudinger R, Mildenberger S, Silbernagl S (2002) Aldosterone interaction with epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282: F669–F679
Gekle M, Freudinger R, Mildenberger S, Schenk K, Marschitz I, Schramek H (2001) Rapid activation of Na+/H+-exchange in MDCK cells by aldosterone involves MAP-kinase ERK1/2. Pflugers Arch 441:781–786
Krug AW, Papavassiliou F, Hopfer U, Ullrich KJ, Gekle M (2003) Aldosterone stimulates surface expression of NHE3 in renal proximal brush borders. Pflugers Arch 446:492–496
Drumm K, Kress TR, Gassner B, Krug AW, Gekle M (2006) Aldosterone stimulates activity and surface expression of NHE3 in human primary proximal tubule epithelial cells (RPTEC). Cell Physiol Biochem 17:21–28
Masereel B, Pochet L, Laeckmann D (2003) An overview of inhibitors of Na+/H+ exchanger. Eur J Med Chem 38:547–554
Putney LK, Denker SP, Barber DL (2002) The changing face of the Na+/H+ exchanger, NHE1: structure, regulation, and cellular actions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 42:527–552
Good DW (2007) Nongenomic actions of aldosterone on the renal tubule. Hypertension 49:728–739
Lifton RP, Gharavi AG, Geller DS (2001) Molecular mechanisms of human hypertension. Cell 104:545–556
Suzuki H, Swei A, Zweifach BW, Schmid-Schonbein GW (1995) In vivo evidence for microvascular oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hydroethidine microfluorography. Hypertension 25:1083–1089
Beswick RA, Zhang H, Marable D, Catravas JD, Hill WD, Webb RC (2001) Long-term antioxidant administration attenuates mineralocorticoid hypertension and renal inflammatory response. Hypertension 37:781–786
Park YM, Park MY, Suh YL, Park JB (2004) NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitor prevents blood pressure elevation and cardiovascular hypertrophy in aldosterone-infused rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:812–817
Miyata K, Rahman M, Shokoji T, Nagai Y, Zhang GX, Sun GP, Kimura S, Yukimura T, Kiyomoto H, Kohno M, Abe Y, Nishiyama A (2005) Aldosterone stimulates reactive oxygen species production through activation of NADPH oxidase in rat mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:2906–2912
Beswick RA, Dorrance AM, Leite R, Webb RC (2001) NADH/NADPH oxidase and enhanced superoxide production in the mineralocorticoid hypertensive rat. Hypertension 38:1107–1111
Woost PG, Orosz DE, Jin W, Frisa PS, Jacobberger JW, Douglas JG, Hopfer U (1996) Immortalization and characterization of proximal tubule cells derived from kidneys of spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive rats. Kidney Int 50:125–134
Gomes P, Soares-da-Silva P (2002) Na+/H+ exchanger activity and dopamine D1-like receptor function in two opossum kidney cell clonal sublines. Cell Physiol Biochem 12:259–268
Gomes P, Vieira-Coelho MA, Soares-da-Silva P (2001) Ouabain-insensitive acidification by dopamine in renal OK cells: primary control of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 281:R10–R18
Roos A, Boron WF (1981) Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev 61:296–434
Xu J, Li XX, Albrecht FE, Hopfer U, Carey RM, Jose PA (2000) Dopamine1 receptor, Gsalpha, and Na+–H+ exchanger interactions in the kidney in hypertension. Hypertension 36:395–399
Yingst DR, Massey KJ, Rossi NF, Mohanty MJ, Mattingly RR (2004) Angiotensin II directly stimulates activity and alters the phosphorylation of Na-K-ATPase in rat proximal tubule with a rapid time course. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F713–F721
Ebata S, Muto S, Okada K, Nemoto J, Amemiya M, Saito T, Asano Y (1999) Aldosterone activates Na+/H+ exchange in vascular smooth muscle cells by nongenomic and genomic mechanisms. Kidney Int 56:1400–1412
Stolk J, Hiltermann TJ, Dijkman JH, Verhoeven AJ (1994) Characteristics of the inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation in neutrophils by apocynin, a methoxy-substituted catechol. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 11:95–102
Kelly MP, Quinn PA, Davies JE, Ng LL (1997) Activity and expression of Na+–H+ exchanger isoforms 1 and 3 in kidney proximal tubules of hypertensive rats. Circ Res 80:853–860
Pedrosa R, Gomes P, Zeng C, Hopfer U, Jose PA, Soares-da-Silva P (2004) Dopamine D3 receptor-mediated inhibition of Na+/H+ exchanger activity in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rat proximal tubular epithelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 142:1343–1353
Carraro-Lacroix LR, Ramirez MA, Zorn TM, Reboucas NA, Malnic G (2006) Increased NHE1 expression is associated with serum deprivation-induced differentiation in immortalized rat proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F129–F139
Rosskopf D, Fromter E, Siffert W (1993) Hypertensive sodium–proton exchanger phenotype persists in immortalized lymphoblasts from essential hypertensive patients. A cell culture model for human hypertension. J Clin Invest 92:2553–2559
Lehoux S, Abe J, Florian JA, Berk BC (2001) 14–3-3 Binding to Na+/H+ exchanger isoform-1 is associated with serum-dependent activation of Na+/H+ exchange. J Biol Chem 276:15794–15800
Yamamuro M, Yoshimura M, Nakayama M, Abe K, Shono M, Suzuki S, Sakamoto T, Saito Y, Nakao K, Yasue H, Ogawa H (2006) Direct effects of aldosterone on cardiomyocytes in the presence of normal and elevated extracellular sodium. Endocrinology 147:1314–1321
Acknowledgments
Supported by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, POCI, FEDER and Programa Comunitário de Apoio (POCI/SAU-OBS/57916/2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1009-9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinto, V., Pinho, M.J., Hopfer, U. et al. Oxidative stress and the genomic regulation of aldosterone-stimulated NHE1 activity in SHR renal proximal tubular cells. Mol Cell Biochem 310, 191–201 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9680-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9680-6