Abstract
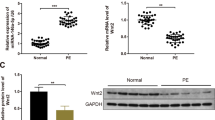
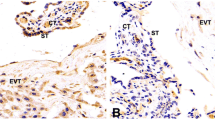
Preeclampsia complicates 5–10 % of pregnancies and is a leading cause of maternal/fetal morbidity and mortality. Although the cause is unknown, the reduced migration/invasion of extravillous trophoblasts is generally regarded as a key feature of preeclampsia genesis. The present study examined the expression of activator protein-2α (AP-2α), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 (TIMP-2), matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and E-cadherin in severe preeclamptic placentas and normal placentas using real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. The expression levels of AP-2α, TIMP-2, and E-cadherin were elevated, while MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels were decreased in severe preeclamptic placentas when compared with normal placentas. To explore the underlying molecular mechanisms, BeWo cells were transfected with an AP-2α-expression construct as well as a siRNA against AP-2α. The over-expression of AP-2α decreased the invasive abilities of BeWo cells. AP-2α induction was followed by the induction of TIMP-2 and E-cadherin and a significant reduction of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Whereas in AP-2α-silencing BeWo cells, we observed the decreased expression of TIMP-2 and E-cadherin and the increased expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9. We presume that AP-2α may suppress trophoblast invasion by repression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and up-regulation of E-cadherin, thus leading to shallow placentation in severe preeclampsia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Redman CW, Sargent IL (2005) Latest advances in understanding preeclampsia. Science 308:1592–1594
Sibai B, Dekker G, Kupferminc M (2005) Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 365:785–799
Nishizawa H, Ota S, Suzuki M, Kato T, Sekiya T et al (2011) Comparative gene expression profiling of placentas from patients with severe pre-eclampsia and unexplained fetal growth restriction. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 9:107
Keelan JA, Mitchell MD (2007) Placental cytokines and preeclampsia. Front Biosci 2007(12):2706–2727
Wang W, Lv L, Pan K, Zhang Y, Zhao JJ et al (2011) Reduced expression of transcription factor AP-2alpha is associated with gastric adenocarcinoma prognosis. PLoS One 6:e24897
Mitchell PJ, Wang C, Tjian R (1987) Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell 50:847–861
Morales A, Alvarez A, Arvelo F, Suarez AI, Compagnone RS et al (2011) The natural diterpene ent-16beta-17alpha-dihydroxykaurane down-regulates Bcl-2 by disruption of the Ap-2alpha/Rb transcription activating complex and induces E2F1 up-regulation in MCF-7 cells. Apoptosis 16:1245–1252
Gershenwald JE, Sumner W, Calderone T, Wang Z, Huang S et al (2001) Dominant-negative transcription factor AP-2 augments SB-2 melanoma tumor growth in vivo. Oncogene 20:3363–3375
Kotani T, Iwase A, Ino K, Sumigama S, Yamamoto E et al (2009) Activator protein-2 impairs the invasion of a human extravillous trophoblast cell line. Endocrinology 150:4376–4385
Harris LK, Keogh RJ, Wareing M, Baker PN, Cartwright JE et al (2007) BeWo cells stimulate smooth muscle cell apoptosis and elastin breakdown in a model of spiral artery transformation. Hum Reprod 22:2834–2841
Bilban M, Tauber S, Haslinger P, Pollheimer J, Saleh L, Pehamberger H et al (2010) Trophoblast invasion: assessment of cellular models using gene expression signatures. Placenta 31:989–996
Ye’sica PG, Maymo’ JL et al (2010) 17Βeta-Estradiol enhances leptin expression in human placental cells through genomic and nongenomic actions. Biol Reprod 83:42–51
AlNasiry S, Geusens N, Hanssens M, Luyten C, Pijnenborg R (2007) The use of Alamar Blue assay forquantitative analysis of viability, migration and invasion of choriocarcinoma cells. Hum Reprod 22(5):1304–1309
Madeja Z, Yadi H, Apps R, Boulenouar S, Roper SJ et al (2011) Paternal MHC expression on mouse trophoblast affects uterine vascularization and fetal growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:4012–4017
Lockwood CJ, Yen CF, Basar M, Kayisli UA, Martel M et al (2008) Preeclampsia-related inflammatory cytokines regulate interleukin-6 expression in human decidual cells. Am J Pathol 172:1571–1579
Wagner PK, Otomo A, Christians JK (2011) Regulation of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A2 (PAPPA2) in a human placental trophoblast cell line (BeWo). Reprod Biol Endocrinol 9:48
Hunt MA, Currie MJ, Robinson BA, Dachs GU (2010) Optimizing transfection of primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells using commercially available chemical transfection reagents. J Biomol Tech 21:66–72
Yamamoto E, Ito T, Abe A, Sido F, Ino K et al (2005) Ikaros is expressed in human extravillous trophoblasts and involved in their migration and invasion. Mol Hum Reprod 11:825–831
Zhang L, Jia L, Cui S, Shi Y, Chang A et al (2012) AP-2α-dependent regulation of Bcl-2/Bax expression affects apoptosis in the trophoblast. J Mol Histol 43:681–689
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Merchant SJ, Crocker IP, Baker PN, Tansinda D, Davidge ST et al (2004) Matrix metalloproteinase release from placental explants of pregnancies complicated by intrauterine growth restriction. J Soc Gynecol Investig 11:97–103
Zhao HB, Wang C, Li RX, Tang CL, Li MQ et al (2010) E-cadherin, as a negative regulator of invasive behavior of human trophoblast cells, is down-regulated by cyclosporin A via epidermal growth factor/extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase signaling pathway. Biol Reprod 83:370–376
Zhou WH, Du MR, Dong L, Zhu XY, Yang JY et al (2007) Cyclosporin A increases expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 and 2 and invasiveness in vitro of the first-trimester human trophoblast cells via the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Hum Reprod 22:2743–2750
Du MR, Zhou WH, Dong L, Zhu XY, He YY et al (2008) Cyclosporin A promotes growth and invasiveness in vitro of human first-trimester trophoblast cells via MAPK3/MAPK1-mediated AP1 and Ca2+/calcineurin/NFAT signaling pathways. Biol Reprod 78:1102–1110
Haider S, Knöfler M (2009) Human tumour necrosis factor: physiological and pathological roles in placenta and endometrium. Placenta 30:111–123
Brasch J, Harrison OJ, Honig B, Shapiro L (2012) Thinking outside the cell: how cadherins drive adhesion. Trends Cell Biol 22:299–310
Williams PJ, Bulmer JN, Innes BA, Pipkin FB (2011) Possible roles for folic acid in the regulation of trophoblast invasion and placental development in normal early human pregnancy. Bio Reprod 84:1148–1153
Naruse K, Lash GE, Innes BA, Otun HA et al (2009) Localization of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9 and tissue inhibitors for MMPs (TIMPs) in uterine natural killer cells in early human pregnancy. Hum Reprod 24:553–561
Staun-Ram E, Goldman S, Shalev E (2009) p53 mediates epidermal growth factor (EGF) induction of MMP-2 transcription and trophoblast invasion. Placenta 30:1029–1036
Kugler A (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Anticancer Res 19:1589–1592
Luo J, Qiao F, Yin X (2011) Hypoxia induces FGF2 production by vascular endothelial cells and alters MMP9 and TIMP1 expression in extravillous trophoblasts and their invasiveness in a cocultured model. J. Reprod Dev 57:84–91
Schwartz B, Melnikova VO, Tellez C, Mourad-Zeidan A, Blehm K et al (2007) Loss of AP-2alpha results in deregulation of E-cadherin and MMP-9 and an increase in tumorigenicity of colon cancer cells in vivo. Oncogene 26:4049–4058
Nawrocki-Raby B, Gilles C, Polette M, Martinella-Catusse C, Bonnet N et al (2003) E-Cadherin mediates MMP down-regulation in highly invasive bronchial tumor cells. Am J Pathol 163:653–661
Weiss JM, Ridnour LA, Back T, Hussain SP, He P et al (2010) Macrophage-dependent nitric oxide expression regulates tumor cell detachment and metastasis after IL-2/anti-CD40 immunotherapy. J Exp Med 207:2455–2467
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Key Laboratory of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University in China. The authors gratefully acknowledge the faculty of Obstetric Institute and Department of Pathology for their technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Zhang, L., Jia, L. et al. AP-2α suppresses invasion in BeWo cells by repression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and up-regulation of E-cadherin. Mol Cell Biochem 381, 31–39 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1685-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1685-8