Abstract
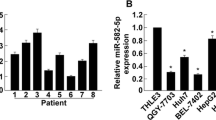
Dysregulation of miR-452 has been observed in many tumors, but its biological function in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is still unknown. Our results showed that miR-452 expression is significantly increased in HCC tissues and HCC cell lines. We also found that overexpression of miR-452 dramatically accelerated proliferation, induced cell cycle from G1 to S transition, and blocked apoptosis of HCC cells. Migration and matrigel invasion assays indicated that miR-452 significantly promotes HepG2 and QGY-7703 cells migration and invasion in vitro. Further studies showed that miR-452 directly targets the 3′-untranslated region of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (CDKN1B), ectopic miR-452 expression suppressed CDKN1B expression on mRNA and protein level. Silencing CDKN1B by small interfering RNA resembled the phenotype resulting from ectopic miR-452 expression. This study provides new insights into the potential molecular mechanisms that miRNA-452 contributed to HCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Hou J, Lin L, Zhou W et al (2011) Identification of miRNomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 19:232–243
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O’Donnell KA et al (2009) Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 137:1005–1017
Aravalli RN, Cressman EN, Steer CJ (2013) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Arch Toxicol 87:227–247
Zhi Q, Zhu J, Guo X et al (2013) Metastasis-related miR-185 is a potential prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma in early stage. Biomed Pharmacother 67:393–398
Selbach M, Schwanhausser B, Thierfelder N, Fang Z, Khanin R, Rajewsky N (2008) Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 455:58–63
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Baek D, Villen J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP (2008) The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 455:64–71
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK (2009) MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:369–378
Whittaker S, Marais R, Zhu AX (2010) The role of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 29:4989–5005
Sun J, Lu H, Wang X, Jin H (2013) MicroRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: regulation, function, and clinical implications. ScientificWorldJournal 2013:924206
Gu H, Guo X, Zou L, Zhu H, Zhang J (2013) Upregulation of microRNA-372 associates with tumor progression and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 375:23–30
Zhang L, Yang L, Liu X et al (2013) MicroRNA-657 promotes tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting transducin-like enhancer protein 1 through nuclear factor kappa B pathways. Hepatology 57:1919–1930
Yau WL, Lam CS, Ng L et al (2013) Over-expression of miR-106b promotes cell migration and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition process. PLoS ONE 8:e57882
Yang X, Liang L, Zhang XF et al (2013) MicroRNA-26a suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting IL-6-Stat3 pathway. Hepatology 58:158–170
Dang Y, Luo D, Rong M, Chen G (2013) Underexpression of miR-34a in hepatocellular carcinoma and its contribution towards enhancement of proliferating inhibitory effects of agents targeting c-MET. PLoS ONE 8:e61054
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2007) microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol 302:1–12
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT et al (2005) A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 435:828–833
Liu L, Chen K, Wu J et al (2013) Downregulation of miR-452 promotes stem-like traits and tumorigenicity of gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 19:3429–3438
Cobrinik D (2005) Pocket proteins and cell cycle control. Oncogene 24:2796–2809
van den Heuvel S, Dyson NJ (2008) Conserved functions of the pRB and E2F families. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:713–724
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Ferracin M et al (2008) MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 27:5651–5661
Tannapfel A, Grund D, Katalinic A et al (2000) Decreased expression of p27 protein is associated with advanced tumor stage in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 89:350–355
Sherr CJ (1994) G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell 79:551–555
Sherr CJ (1996) Cancer cell cycles. Science 274:1672–1677
Sandhu C, Slingerland J (2000) Deregulation of the cell cycle in cancer. Cancer Detect Prev 24:107–118
Morishita A, Masaki T, Yoshiji H et al (2004) Reduced expression of cell cycle regulator p18(INK4C) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 40:677–686
Harper JW, Elledge SJ (1996) Cdk inhibitors in development and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 6:56–64
Fischer PM, Gianella-Borradori A (2003) CDK inhibitors in clinical development for the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 12:955–970
Morishita A, Gong J, Deguchi A et al (2011) Frequent loss of p19INK4D expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: relationship to tumor differentiation and patient survival. Oncol Rep 26:1363–1368
Trang P, Wiggins JF, Daige CL et al (2011) Systemic delivery of tumor suppressor microRNA mimics using a neutral lipid emulsion inhibits lung tumors in mice. Mol Ther 19:1116–1122
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31300718 and 31200974), Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation (No. Y204499), and Universities of Zhejiang the most important Biology Subject (a) Foundation.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Q., Sheng, Q., Jiang, C. et al. MicroRNA-452 promotes tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B. Mol Cell Biochem 389, 187–195 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1940-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1940-z