Abstract
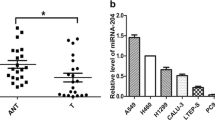
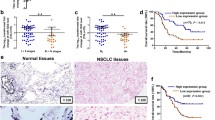
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that have important roles in cancer. The altered expressions of miRNAs and their target genes are frequently detected in various tumors. In this study, downregulation of miR-15a-16 in nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) was found to be inversely correlated with Cripto. Results from the Luciferase reporter assay and Western blot analysis also confirmed that Cripto is a direct target of miR-15a-16. In addition, transfection of miR-15a-16 expression plasmid inhibited the invasion ability and promoted the apoptosis of NCI-H23 and NCI-H358 cells. Moreover, miR-15a-16 overexpression suppressed tumor growth in vivo. These findings clearly suggest that the downregulation of miR-15a-16 with Cripto amplification may be involved in the development of NSCLC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach PB (2011) Inconsistencies in findings from the early lung cancer action project studies of lung cancer screening. J Natl Cancer Inst 103(13):1002–1006
Van’t Westeinde SC, van Klaveren RJ (2011) Screening and early detection of lung cancer. Cancer J 17(1):3–10
Brivanlou AH et al (2003) Stem cells. Setting standards for human embryonic stem cells. Science 300(5621):913–916
Ciardiello F et al (1994) Inhibition of CRIPTO expression and tumorigenicity in human colon cancer cells by antisense RNA and oligodeoxynucleotides. Oncogene 9(1):291–298
Xing PX et al (2004) Cripto: a novel target for antibody-based cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Res 64(11):4018–4023
Normanno N et al (2004) Cripto-1 overexpression leads to enhanced invasiveness and resistance to anoikis in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 198(1):31–39
Bianco C et al (2006) Identification of cripto-1 as a novel serologic marker for breast and colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12(17):5158–5164
Bianco C et al (2013) Regulation of human Cripto-1 expression by nuclear receptors and DNA promoter methylation in human embryonal and breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 228(6):1174–1188
Soria-Valles C et al (2013) The anti-metastatic activity of collagenase-2 in breast cancer cells is mediated by a signaling pathway involving decorin and miR-21. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.267
Kang HW et al (2012) miR-20a promotes migration and invasion by regulating TNKS2 in human cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett 586(6):897–904
Ma L (2010) Role of miR-10b in breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res 12(5):210
Takakura S et al (2008) Oncogenic role of miR-17-92 cluster in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. Cancer Sci 99(6):1147–1154
Wu H, Zhu S, Mo YY (2009) Suppression of cell growth and invasion by miR-205 in breast cancer. Cell Res 19(4):439–448
Selcuklu SD et al (2012) MicroRNA-9 inhibition of cell proliferation and identification of novel miR-9 targets by transcriptome profiling in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 287(35):29516–29528
Hermeking H (2010) The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 17(2):193–199
Liu C et al (2012) Distinct microRNA expression profiles in prostate cancer stem/progenitor cells and tumor-suppressive functions of let-7. Cancer Res 72(13):3393–3404
Bonci D et al (2008) The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med 14(11):1271–1277
Bhattacharya R et al (2009) MiR-15a and MiR-16 control Bmi-1 expression in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 69(23):9090–9095
Luo Q et al (2013) MiR-15a is underexpressed and inhibits the cell cycle by targeting CCNE1 in breast cancer. Int J Oncol 43(4):1212–1218
Dai L et al (2012) Vector-based miR-15a/16-1 plasmid inhibits colon cancer growth in vivo. Cell Biol Int 36(8):765–770
Bandi N et al (2009) miR-15a and miR-16 are implicated in cell cycle regulation in a Rb-dependent manner and are frequently deleted or down-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 69(13):5553–5559
Bandi N, Vassella E (2011) miR-34a and miR-15a/16 are co-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer and control cell cycle progression in a synergistic and Rb-dependent manner. Mol Cancer 10:55
Jusufovic E et al (2012) let-7b and miR-126 are down-regulated in tumor tissue and correlate with microvessel density and survival outcomes in non–small–cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 7(9):e45577
Yang M et al (2013) High expression of miR-21 and miR-155 predicts recurrence and unfavourable survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer 49(3):604–615
Zhang JG et al (2010) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin Chim Acta 411(11–12):846–852
Yuxia M, Zhennan T, Wei Z (2012) Circulating miR-125b is a novel biomarker for screening non-small-cell lung cancer and predicts poor prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138(12):2045–2050
Aqeilan RI, Calin GA, Croce CM (2010) miR-15a and miR-16-1 in cancer: discovery, function and future perspectives. Cell Death Differ 17(2):215–220
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Feng Chen and Shi-ke Hou contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Hou, Sk., Fan, Hj. et al. MiR-15a-16 represses Cripto and inhibits NSCLC cell progression. Mol Cell Biochem 391, 11–19 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-1981-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-1981-y