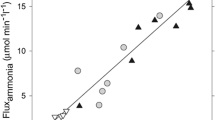
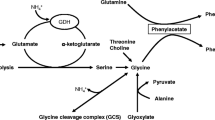
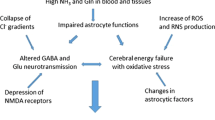
Abstract
Hyperammonemia is necessary for development of the cerebral complications to liver disease including hepatic encephalopathy and cerebral edema but the mechanisms are unclear. Ammonia is taken up by the brain in proportion to its arterial concentration. The flux into the brain is most likely by both diffusion of NH3 and mediated transport of NH4 + . Astrocytic detoxification of ammonia involves formation of glutamine at concentrations high enough to produce cellular edema, but compensatory mechanisms reduce this effect. Glutamine can be taken up by astrocytic mitochondria and initiate the mitochondrial permeability transition but the clinical relevance is uncertain. Elevated astrocytic glutamine interferes with neurotransmission. Thus, animal studies show enhanced glutamatergic neurotransmission via the NMDA receptor which may be related to the acute cerebral complications to liver failure, while impairment of the NMDA activated glutamate-NO-cGMP pathway could relate to the behavioural changes seen in hepatic encephalopathy. Elevated glutamine also increases GABA-ergic tone, an effect which is aggravated by mitochondrial production of neurosteroids; this may relate to decreased neurotransmission and precipitation of encephalopathy by GABA targeting drugs. Hyperammonemia may compromise cerebral energy metabolism as elevated cerebral lactate is generally reported. Hypoxia is unlikely since cerebral oxygen:glucose utilisation and lactate:pyruvate ratio are both normal in clinical studies. Ammonia inhibits α-ketoglutaratedehydrogenase in isolated mitochondria, but the clinical relevance is dubious due to the observed normal cerebral oxygen:glucose utilization. Recent studies suggest that ammonia stimulates glycolysis in excess of TCA cycle activity, a hypothesis that may warrant further testing, in being in accordance with the limited clinical observations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams SL, Younathan ES (1971) Modulation of the kinetic properties of phosphofructokinase by ammonium ions. J Biol Chem 246(8):2464–2467
Ahboucha S, Araqi F, Layrargues GP, Butterworth RF (2005) Differential effects of ammonia on the benzodiazepine modulatory site on the GABA-A receptor complex of human brain. Neurochem Int 47(1–2):58–63. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2005.04.007
Ahl B, Weissenborn K, van den Hoff J, Fischer-Wasels D, Kostler H, Hecker H, Burchert W (2004) Regional differences in cerebral blood flow and cerebral ammonia metabolism in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 40(1):73–79. doi:10.1002/hep.20290
Albrecht J, Norenberg MD (2006) Glutamine: a Trojan horse in ammonia neurotoxicity. Hepatology 44(4):788–794. doi:10.1002/hep.21357
Bak LK, Iversen P, Sorensen M, Keiding S, Vilstrup H, Ott P, Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A (2009) Metabolic fate of isoleucine in a rat model of hepatic encephalopathy and in cultured neural cells exposed to ammonia. Metab Brain Dis 24(1):135–145. doi:10.1007/s11011-008-9123-4
Belanger M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ (2011) Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab 14(6):724–738. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.08.016
Bernal W, Hall C, Karvellas CJ, Auzinger G, Sizer E, Wendon J (2007) Arterial ammonia and clinical risk factors for encephalopathy and intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure. Hepatology 46(6):1844–1852. doi:10.1002/hep.21838
Bessman SP, Bessman AN (1955) The cerebral and peripheral uptake of ammonia in liver disease with an hypothesis for the mechanism of hepatic coma. J Clin Investig 34(4):622–628. doi:10.1172/JCI103111
Bjerring PN, Hauerberg J, Frederiksen HJ, Jorgensen L, Hansen BA, Tofteng F, Larsen FS (2008) Cerebral glutamine concentration and lactate-pyruvate ratio in patients with acute liver failure. Neurocrit Care 9(1):3–7. doi:10.1007/s12028-008-9060-4
Bjerring PN, Hauerberg J, Jorgensen L, Frederiksen HJ, Tofteng F, Hansen BA, Larsen FS (2010) Brain hypoxanthine concentration correlates to lactate/pyruvate ratio but not intracranial pressure in patients with acute liver failure. J Hepatol 53(6):1054–1058. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2010.05.032
Bosoi CR, Rose CF (2013) Oxidative stress: a systemic factor implicated in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 28(2):175–178. doi:10.1007/s11011-012-9351-5
Butterworth RF (2010) Altered glial-neuronal crosstalk: cornerstone in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Int 57(4):383–388. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2010.03.012
Canales JJ, Elayadi A, Errami M, Llansola M, Cauli O, Felipo V (2003) Chronic hyperammonemia alters motor and neurochemical responses to activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens in rats in vivo. Neurobiol Dis 14(3):380–390
Cauli O, Llansola M, Erceg S, Felipo V (2006) Hypolocomotion in rats with chronic liver failure is due to increased glutamate and activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors in substantia nigra. J Hepatol 45(5):654–661. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2006.06.019
Cauli O, Rodrigo R, Piedrafita B, Boix J, Felipo V (2007) Inflammation and hepatic encephalopathy: ibuprofen restores learning ability in rats with portacaval shunts. Hepatology 46(2):514–519. doi:10.1002/hep.21734
Cauli O, Mansouri MT, Agusti A, Felipo V (2009a) Hyperammonemia increases GABAergic tone in the cerebellum but decreases it in the rat cortex. Gastroenterology 136(4):1359–1367. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.12.057, e1351-1352
Cauli O, Rodrigo R, Llansola M, Montoliu C, Monfort P, Piedrafita B, El Mlili N, Boix J, Agusti A, Felipo V (2009b) Glutamatergic and gabaergic neurotransmission and neuronal circuits in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 24(1):69–80. doi:10.1007/s11011-008-9115-4
Cauli O, Rodrigo R, Piedrafita B, Llansola M, Mansouri MT, Felipo V (2009c) Neuroinflammation contributes to hypokinesia in rats with hepatic encephalopathy: ibuprofen restores its motor activity. J Neurosci Res 87(6):1369–1374. doi:10.1002/jnr.21947
Chan H, Butterworth RF (2003) Cell-selective effects of ammonia on glutamate transporter and receptor function in the mammalian brain. Neurochem Int 43(4–5):525–532
Clemmesen JO, Gerbes AL, Gulberg V, Hansen BA, Larsen FS, Skak C, Tygstrup N, Ott P (1999a) Hepatic blood flow and splanchnic oxygen consumption in patients with liver failure. Effect of high-volume plasmapheresis. Hepatology 29(2):347–355. doi:10.1002/hep.510290206
Clemmesen JO, Larsen FS, Kondrup J, Hansen BA, Ott P (1999b) Cerebral herniation in patients with acute liver failure is correlated with arterial ammonia concentration. Hepatology 29(3):648–653. doi:10.1002/hep.510290309
Clemmesen JO, Hoy CE, Kondrup J, Ott P (2000) Splanchnic metabolism of fuel substrates in acute liver failure. J Hepatol 33(6):941–948
Clemmesen O, Ott P, Larsen FS (2004) Splanchnic metabolism in acute liver failure and sepsis. Curr Opin Crit Care 10(2):152–155
Cooper AJ, Plum F (1987) Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia. Physiol Rev 67(2):440–519
Cordoba J, Gottstein J, Blei AT (1996) Glutamine, myo-inositol, and organic brain osmolytes after portocaval anastomosis in the rat: implications for ammonia-induced brain edema. Hepatology 24(4):919–923. doi:10.1002/hep.510240427
Cordoba J, Crespin J, Gottstein J, Blei AT (1999) Mild hypothermia modifies ammonia-induced brain edema in rats after portacaval anastomosis. Gastroenterology 116(3):686–693
Dam G, Keiding S, Munk OL, Ott P, Vilstrup H, Bak LK, Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A, Sorensen M (2013) Hepatic encephalopathy is associated with decreased cerebral oxygen metabolism and blood flow, not increased ammonia uptake. Hepatology 57(1):258–265. doi:10.1002/hep.25995
Desjardins P, Butterworth RF (2002) The “peripheral-type” benzodiazepine (omega 3) receptor in hyperammonemic disorders. Neurochem Int 41(2–3):109–114
Erceg S, Monfort P, Hernandez-Viadel M, Rodrigo R, Montoliu C, Felipo V (2005) Oral administration of sildenafil restores learning ability in rats with hyperammonemia and with portacaval shunts. Hepatology 41(2):299–306. doi:10.1002/hep.20565
Gjedde A, Keiding S, Vilstrup H, Iversen P (2010) No oxygen delivery limitation in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 25(1):57–63. doi:10.1007/s11011-010-9179-9
Goldbecker A, Buchert R, Berding G, Bokemeyer M, Lichtinghagen R, Wilke F, Ahl B, Weissenborn K (2010) Blood–brain barrier permeability for ammonia in patients with different grades of liver fibrosis is not different from healthy controls. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(7):1384–1393. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2010.22
Gore DC, Jahoor F, Hibbert JM, DeMaria EJ (1996) Lactic acidosis during sepsis is related to increased pyruvate production, not deficits in tissue oxygen availability. Ann Surg 224(1):97–102
Goulenok C, Bernard B, Cadranel JF, Thabut D, Di Martino V, Opolon P, Poynard T (2002) Flumazenil vs. placebo in hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16(3):361–372
Hawkins RA, O’Kane RL, Simpson IA, Vina JR (2006) Structure of the blood–brain barrier and its role in the transport of amino acids. J Nutr 136(1 Suppl):218S–226S
Iversen P, Sorensen M, Bak LK, Waagepetersen HS, Vafaee MS, Borghammer P, Mouridsen K, Jensen SB, Vilstrup H, Schousboe A, Ott P, Gjedde A, Keiding S (2009) Low cerebral oxygen consumption and blood flow in patients with cirrhosis and an acute episode of hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 136(3):863–871. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.10.057
Jayakumar AR, Rama Rao KV, Schousboe A, Norenberg MD (2004) Glutamine-induced free radical production in cultured astrocytes. Glia 46(3):296–301. doi:10.1002/glia.20003
Johansen ML, Bak LK, Schousboe A, Iversen P, Sorensen M, Keiding S, Vilstrup H, Gjedde A, Ott P, Waagepetersen HS (2007) The metabolic role of isoleucine in detoxification of ammonia in cultured mouse neurons and astrocytes. Neurochem Int 50(7–8):1042–1051. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2007.01.009
Kanamatsu T, Tsukada Y (1999) Effects of ammonia on the anaplerotic pathway and amino acid metabolism in the brain: an ex vivo 13C NMR spectroscopic study of rats after administering [2-13C]] glucose with or without ammonium acetate. Brain Res 841(1–2):11–19
Keiding S, Sorensen M, Bender D, Munk OL, Ott P, Vilstrup H (2006) Brain metabolism of 13N-ammonia during acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis measured by positron emission tomography. Hepatology 43(1):42–50. doi:10.1002/hep.21001
Keiding S, Sorensen M, Munk OL, Bender D (2010) Human (13)N-ammonia PET studies: the importance of measuring (13)N-ammonia metabolites in blood. Metab Brain Dis 25(1):49–56. doi:10.1007/s11011-010-9181-2
Kosenko E, Kaminsky Y, Grau E, Minana MD, Marcaida G, Grisolia S, Felipo V (1994) Brain ATP depletion induced by acute ammonia intoxication in rats is mediated by activation of the NMDA receptor and Na+, K(+)-ATPase. J Neurochem 63(6):2172–2178
Lai JC, Cooper AJ (1986) Brain alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: kinetic properties, regional distribution, and effects of inhibitors. J Neurochem 47(5):1376–1386
Larsen RH, Kjaer MS, Eefsen M, Larsen FS, Bjerring PN (2013) Ciclosporin does not attenuate intracranial hypertension in rats with acute hyperammonaemia. World J Hepatol 5(9):513–520. doi:10.4254/wjh.v5.i9.513
Leke R, Bak LK, Anker M, Melo TM, Sorensen M, Keiding S, Vilstrup H, Ott P, Portela LV, Sonnewald U, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2011a) Detoxification of ammonia in mouse cortical GABAergic cell cultures increases neuronal oxidative metabolism and reveals an emerging role for release of glucose-derived alanine. Neurotoxicity Res 19(3):496–510. doi:10.1007/s12640-010-9198-7
Leke R, Bak LK, Iversen P, Sorensen M, Keiding S, Vilstrup H, Ott P, Portela LV, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2011b) Synthesis of neurotransmitter GABA via the neuronal tricarboxylic acid cycle is elevated in rats with liver cirrhosis consistent with a high GABAergic tone in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. J Neurochem 117(5):824–832. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07244.x
Llansola M, Montoliu C, Cauli O, Hernandez-Rabaza V, Agusti A, Cabrera-Pastor A, Gimenez-Garzo C, Gonzalez-Usano A, Felipo V (2013) Chronic hyperammonemia, glutamatergic neurotransmission and neurological alterations. Metab Brain Dis 28(2):151–154. doi:10.1007/s11011-012-9337-3
Lockwood AH, Yap EW, Wong WH (1991) Cerebral ammonia metabolism in patients with severe liver disease and minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11(2):337–341. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1991.67
Marcaida G, Felipo V, Hermenegildo C, Minana MD, Grisolia S (1992) Acute ammonia toxicity is mediated by the NMDA type of glutamate receptors. FEBS Lett 296(1):67–68
Marcaida G, Minana MD, Burgal M, Grisolia S, Felipo V (1995) Ammonia prevents activation of NMDA receptors by glutamate in rat cerebellar neuronal cultures. Eur J NeuroSci 7(12):2389–2396
Marcaida G, Kosenko E, Minana MD, Grisolia S, Felipo V (1996) Glutamate induces a calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation of Na+, K(+)-ATPase that results in its activation in cerebellar neurons in culture. J Neurochem 66(1):99–104
Marini AM, Matassi G, Raynal V, Andre B, Cartron JP, Cherif-Zahar B (2000) The human Rhesus-associated RhAG protein and a kidney homologue promote ammonium transport in yeast. Nat Genet 26(3):341–344. doi:10.1038/81656
Master S, Gottstein J, Blei AT (1999) Cerebral blood flow and the development of ammonia-induced brain edema in rats after portacaval anastomosis. Hepatology 30(4):876–880. doi:10.1002/hep.510300428
Mohr M, Rasmussen P, Drust B, Nielsen B, Nybo L (2006) Environmental heat stress, hyperammonemia and nucleotide metabolism during intermittent exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 97(1):89–95. doi:10.1007/s00421-006-0152-6
Nagaraja TN, Brookes N (1998) Intracellular acidification induced by passive and active transport of ammonium ions in astrocytes. Am J Physiol 274(4 Pt 1):C883–C891
Norenberg MD, Martinez-Hernandez A (1979) Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res 161(2):303–310
O’Kane RL, Hawkins RA (2003) Na + -dependent transport of large neutral amino acids occurs at the abluminal membrane of the blood–brain barrier. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285(6):E1167–E1173. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00193.2003
Ong JP, Aggarwal A, Krieger D, Easley KA, Karafa MT, Van Lente F, Arroliga AC, Mullen KD (2003) Correlation between ammonia levels and the severity of hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Med 114(3):188–193
Ott P, Larsen FS (2004) Blood–brain barrier permeability to ammonia in liver failure: a critical reappraisal. Neurochem Int 44(4):185–198
Ott P, Clemmesen O, Larsen FS (2005) Cerebral metabolic disturbances in the brain during acute liver failure: from hyperammonemia to energy failure and proteolysis. Neurochem Int 47(1–2):13–18. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2005.04.002
Pellerin L, Magistretti PJ (2012) Sweet sixteen for ANLS. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32(7):1152–1166. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2011.149
Quentin F, Eladari D, Cheval L, Lopez C, Goossens D, Colin Y, Cartron JP, Paillard M, Chambrey R (2003) RhBG and RhCG, the putative ammonia transporters, are expressed in the same cells in the distal nephron. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 14(3):545–554
Quero JC, Hartmann IJ, Meulstee J, Hop WC, Schalm SW (1996) The diagnosis of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis using neuropsychological tests and automated electroencephalogram analysis. Hepatology 24(3):556–560. doi:10.1002/hep.510240316
Rama Rao KV, Norenberg MD (2012) Brain energy metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction in acute and chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Int 60(7):697–706. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2011.09.007
Rama Rao KV, Chen M, Simard JM, Norenberg MD (2003) Suppression of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling by cyclosporin A. J Neurosci Res 74(6):891–897. doi:10.1002/jnr.10755
Rama Rao KV, Jayakumar AR, Tong X, Curtis KM, Norenberg MD (2010) Brain aquaporin-4 in experimental acute liver failure. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69(9):869–879. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181ebe581
Ratnakumari L, Murthy CR (1992) In vitro and in vivo effects of ammonia on glucose metabolism in the astrocytes of rat cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett 148(1–2):85–88
Ratnakumari L, Murthy CR (1993) Response of rat cerebral glycolytic enzymes to hyperammonemic states. Neurosci Lett 161(1):37–40
Ratnakumari L, Qureshi IA, Butterworth RF (1992) Effects of congenital hyperammonemia on the cerebral and hepatic levels of the intermediates of energy metabolism in spf mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 184(2):746–751
Rose CF (2010) Increase brain lactate in hepatic encephalopathy: cause or consequence? Neurochem Int 57(4):389–394. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2010.06.012
Rose C, Michalak A, Pannunzio M, Chatauret N, Rambaldi A, Butterworth RF (2000) Mild hypothermia delays the onset of coma and prevents brain edema and extracellular brain glutamate accumulation in rats with acute liver failure. Hepatology 31(4):872–877. doi:10.1053/he.2000.5923
Routsi C, Bardouniotou H, Delivoria-Ioannidou V, Kazi D, Roussos C, Zakynthinos S (1999) Pulmonary lactate release in patients with acute lung injury is not attributable to lung tissue hypoxia. Crit Care Med 27(11):2469–2473
Schliess F, Gorg B, Haussinger D (2006) Pathogenetic interplay between osmotic and oxidative stress: the hepatic encephalopathy paradigm. Biol Chem 387(10–11):1363–1370. doi:10.1515/BC.2006.171
Schmidt LE, Tofteng F, Strauss GI, Larsen FS (2004) Effect of treatment with the Molecular Adsorbents Recirculating System on arterial amino acid levels and cerebral amino acid metabolism in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Scand J Gastroenterol 39(10):974–980. doi:10.1080/00365520410003227
Schousboe A, Bak LK, Waagepetersen HS (2013) Astrocytic control of biosynthesis and turnover of the neurotransmitters glutamate and GABA. Front Endocrinol 4:102. doi:10.3389/fendo.2013.00102
Shawcross D, Jalan R (2005) The pathophysiologic basis of hepatic encephalopathy: central role for ammonia and inflammation. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 62(19–20):2295–2304. doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5089-0
Shen J, Petersen KF, Behar KL, Brown P, Nixon TW, Mason GF, Petroff OA, Shulman GI, Shulman RG, Rothman DL (1999) Determination of the rate of the glutamate/glutamine cycle in the human brain by in vivo 13C NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(14):8235–8240
Sibson NR, Mason GF, Shen J, Cline GW, Herskovits AZ, Wall JE, Behar KL, Rothman DL, Shulman RG (2001) In vivo (13)C NMR measurement of neurotransmitter glutamate cycling, anaplerosis and TCA cycle flux in rat brain during. J Neurochem 76(4):975–989
Sorensen M (2013) Update on cerebral uptake of blood ammonia. Metab Brain Dis 28(2):155–159. doi:10.1007/s11011-013-9395-1
Sorensen M, Keiding S (2007) New findings on cerebral ammonia uptake in HE using functional (13)N-ammonia PET. Metab Brain Dis 22(3–4):277–284. doi:10.1007/s11011-007-9066-1
Sorensen M, Munk OL, Keiding S (2009) Backflux of ammonia from brain to blood in human subjects with and without hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 24(1):237–242. doi:10.1007/s11011-008-9126-1
Stephan J, Haack N, Kafitz KW, Durry S, Koch D, Hochstrate P, Seifert G, Steinhauser C, Rose CR (2012) Kir4.1 channels mediate a depolarization of hippocampal astrocytes under hyperammonemic conditions in situ. Glia 60(6):965–978. doi:10.1002/glia.22328
Strauss GI, Moller K, Larsen FS, Kondrup J, Knudsen GM (2003) Cerebral glucose and oxygen metabolism in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Liver Transplant Off Publ Am Assoc Study Liver Dis Int Liver Transplant Soc 9(12):1244–1252. doi:10.1016/j.lts.2003.09.020
Tofteng F, Jorgensen L, Hansen BA, Ott P, Kondrup J, Larsen FS (2002) Cerebral microdialysis in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology 36(6):1333–1340. doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.36944
Verlander JW, Miller RT, Frank AE, Royaux IE, Kim YH, Weiner ID (2003) Localization of the ammonium transporter proteins RhBG and RhCG in mouse kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284(2):F323–F337. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00050.2002
Weiner ID, Verlander JW (2003) Renal and hepatic expression of the ammonium transporter proteins, Rh B glycoprotein and Rh C glycoprotein. Acta Physiol Scand 179(4):331–338. doi:10.1046/j.0001-6772.2003.01210.x
Weiner ID, Miller RT, Verlander JW (2003) Localization of the ammonium transporters, Rh B glycoprotein and Rh C glycoprotein, in the mouse liver. Gastroenterology 124(5):1432–1440
Weissenborn K, Ahl B, Fischer-Wasels D, van den Hoff J, Hecker H, Burchert W, Kostler H (2007) Correlations between magnetic resonance spectroscopy alterations and cerebral ammonia and glucose metabolism in cirrhotic patients with and without hepatic encephalopathy. Gut 56(12):1736–1742. doi:10.1136/gut.2006.110569
Wilkinson DJ, Smeeton NJ, Castle PC, Watt PW (2011) Absence of neuropsychological impairment in hyperammonaemia in healthy young adults; possible synergism in development of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) symptoms? Metab Brain Dis 26(3):203–212. doi:10.1007/s11011-011-9251-0
Yao H, Sadoshima S, Fujii K, Kusuda K, Ishitsuka T, Tamaki K, Fujishima M (1987) Cerebrospinal fluid lactate in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Eur Neurol 27(3):182–187
Zwingmann C, Chatauret N, Leibfritz D, Butterworth RF (2003) Selective increase of brain lactate synthesis in experimental acute liver failure: results of a [H-C] nuclear magnetic resonance study. Hepatology 37(2):420–428. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50052
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ott, P., Vilstrup, H. Cerebral effects of ammonia in liver disease: current hypotheses. Metab Brain Dis 29, 901–911 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9494-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9494-7