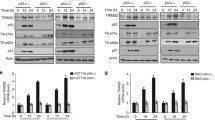
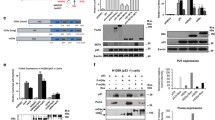
Abstract
MDM2, Pirh2 and COP1 are important E3 ubiquitin ligases, which directly interact with p53 and target p53 for proteasome-mediated degradation. MDMX, the MDM2 homologous protein, inhibits p53-mediated transcription activity. The interplay between MDM2, MDMX, Pirh2 and COP1 has not been reported, except the interaction between MDM2 and MDMX. Here, we reported that there were interactions between these four proteins independently of p53. The protein levels of MDM2, MDMX, Pirh2 and COP1 changed when any two of them were co-transfected. Our data also showed that the integrity of MDM2 RING finger domain was crucial for its ability to elevate the protein levels of COP1 and Pirh2. Any two of these four proteins could inhibit p53-mediated transcriptional activity synergistically. Furthermore, COP1 inhibited MDM2 self-ubiquitination and interfered with MDMX ubiquitination by MDM2. Our results suggest that MDM2, MDMX, Pirh2 and COP1 might inhibit p53 activity synergistically in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vousden KH, Lu X (2002) Live or let die: the cell’s response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer 2:594–604
Wu M, Mao C, Chen Q, Cu X-W, Zhang W.S (2010) Serum p53 protein and anti-p53 antibodies are associated with increased cancer risk: a case-control study of 569 patients and 879 healthy controls. Mol Biol Rep 37:339–343
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M (1997) Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 387:296–299
Honda R, Tanaka H, Yasuda H (1997) Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase E3 for tumor suppressor p53. FEBS Lett 420:25–27
Fang SY, Jensen JP, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH, Weissman AM (2000) Mdm2 is a RING finger-dependent ubiquitin protein ligase for itself and p53. J Biol Chem 275:8945–8951
Honda R, Yasuda H (2000) Activity of MDM2, a ubiquitin Ligase, toward p53 or itself is dependent on the RING finger domain of the ligase. Oncogene 19:1473–1476
Kruse JP, Gu W (2009) Modes of p53 regulation. Cell 137:609–622
Tanimura S, Ohtsuka S, Mitsui K, Shirouzu K, Yoshimura A, Ohtsubo M (1999) MDM2 interacts with MDMX through their RING finger domains. FEBS Lett 447:5–9
Shvarts A, Steegenga WT, Riteco N, vanLaar T, Dekker P, Bazuine M, vanHam RCA, vanOordt WV, Hateboer G, vanderEb AJ, ochemsen AG (1996) MDMX: a novel p53-binding protein with some functional properties of MDM2. EMBO J 15:5349–5357
Shvarts A, Bazuine M, Dekker P, Ramos YFM, Steegenga WT, Merckx G, van Ham RCA, van der Houven van Oordt W, van der Eb AJ, Jochemsen AG (1997) Isolation and identification of the human homolog of a new p53-binding protein, Mdmx. Genomics 43:34–42
de Graaf P, Little NA, Ramos YFM, Meulmeester E, Letteboer SJF, Jochemsen AG (2003) Hdmx protein stability is regulated by the ubiquitin ligase activity of Mdm2. J Biol Chem 278:38315–38324
Pan Y, Chen JD (2003) MDM2 promotes ubiquitination and degradation of MDMX. Mol Cell Biol 23:5113–5121
Jackson MW, Berberich SJ (2000) MdmX protects p53 from Mdm2-mediated degradation. Mol Cell Biol 20:1001–1007
Stad R, Ramos YFM, Little N, Grivell S, Attema J, van der Eb AJ, Jochemsen AG (2000) Hdmx stabilizes Mdm2 and p53. J Biol Chem 275:28039–28044
Stad R, Little NA, Xirodimas DP, Frenk R, van der Eb AJ, Lane DP, Saville MK, Jochemsen AG (2001) Mdmx stabilizes p53 and Mdm2 via two distinct mechanisms. EMBO Rep 2:1029–1034
Leng RP, Lin YP, Ma WL, Wu H, Lemmers B, Chung S, Parant JM, Lozano G, Hakem R, Benchimol S (2003) Pirh2, a p53-induced ubiquitin-protein ligase, promotes p53 degradation. Cell 112:779–791
Dornan D, Wertz I, Shimizu H, Arnott D, Frantz GD, Dowd P, O’ Rourke K, Koeppen H, Dixit VM (2004) The ubiquitin ligase COP1 is a critical negative regulator of p53. Nature 429:86–92
Barak Y, Juven T, Haffner R, Oren M (1993) Mdm2 expression is induced by wild type-P53 activity. EMBO J 12:461–468
Xian L, Zhao J, Wang J, Fang Z, Peng B, Wang W, Ji X, Yu L (2009) p53 Promotes proteasome-dependent degradation of oncogenic protein HBx by transcription of MDM2. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9855-1
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ (1992) The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell 69:1237–1245
Chen J, Lin J, Levine AJ (1995) Regulation of transcription functions of the p53 tumor suppressor by the mdm-2 oncogene. Mol Med 1:142–152
Marine JC, Jochemsen AG (2004) Mdmx and Mdm2—brothers in arms? Cell Cycle 3:900–904
Gilkes DM, Pan Y, Coppola D, Yeatman T, Reuther GW, Chen JD (2008) Regulation of MDMX expression by mitogenic signaling. Mol Cell Biol 28:1999–2010
Strachan GD, Rallapalli R, Pucci B, Lafond TP, Hall DJ (2001) A transcriptionally inactive E2F-1 targets the MDM family of proteins for proteolytic degradation. J Biol Chem 276:45677–45685
Gentiletti F, Mancini F, D’Angelo M, Sacchi A, Pontecorvi A, Jochemsen AG, Moretti F (2002) MDMX stability is regulated by p53-induced caspase cleavage in NIH3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Oncogene 21:867–877
Meulmeester E, Maurice MM, Boutell C, Teunisse A, Ovaa H, Abraham TE, Dirks RW, Jochemsen AG (2005) Loss of HAUSP-mediated deubiquitination contributes to DNA damage-induced destabilization of Hdmx and Hdm2. Mol Cell 18:565–576
Logan IR, Sapountzi V, Gaughan L, Neal DE, Robson CN (2004) Control of human PIRH2 protein stability—involvement of TIP60 and the proteasome. J Biol Chem 279:11696–11704
Zheng G, Ning JY, Yang YC (2007) PLAGL2 controls the stability of Pirh2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase for p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 364:344–350
Dornan D, Shimizu H, Mah A, Dudhela T, Eby M, O’Rourke K, Seshagiri S, Dixit VM (2006) ATM engages autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 after DNA damage. Science 313:1122–1126
Wade M, Wahl GM (2009) Targeting Mdm2 and Mdmx in cancer therapy: better living through medicinal chemistry? Mol Cancer Res 7:1–11
Duan WR, Gao L, Druhan LJ, Zhu WG, Morrison C, Otterson GA, Villalona-Calero MA (2004) Expression of Pirh2, a newly identified ubiquitin protein ligase, in lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:1718–1721
Dornan D, Bheddah S, Newton K, Ince W, Frantz GD, Dowd P, Koeppen H, Dixit VM, French DM (2004) COP1, the negative regulator of p53, is overexpressed in breast and ovarian adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 64:7226–7230
Acknowledgements
We thank Chenji Wang for supply of COP1 expression vector, Qian Wang for discussions and Zhen Zhang from University of Wisconsin for proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11033_2010_99_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 1 (A) 4 × 105 H1299 cells in six-well plate were transfected with myc-MDM2 (300ng), myc-MDM2-C464A (300 ng), myc-Pirh2 (100 ng), HA-MDMX (500 ng) and FLAG-Ub (1 μg) expression vectors as indicated. (B) 4 × 105 H1299 cells in six-well plate were transfected with myc-MDM2 (1 μg), myc-MDM2-C464A (1μg), myc-MDMX (300 ng), HA-Pirh2 (200 ng) and FLAG-Ub (1 μg) expression vectors as indicated. (C) 4 × 105 H1299 cells in six-well plate were transfected with myc-Pirh2 (400 ng), FLAG-COP1 (600 ng) and HA-Ub (1 μg) expression vectors as indicated. (D) 4 × 105 H1299 cells in six-well plate were transfected with myc-MDM2 (300 ng), myc-MDM2-C464A (300 ng), myc-MDMX (300 ng), myc-Pirh2 (100 ng), FLAG-COP1 (1 μg) and HA-Ub (1 μg) expression vectors as indicated. (E) 4 × 105 H1299 cells in six-well plate were transfected with myc-MDM2 (1 μg), myc-MDM2-C464A (1 μg), HA-MDMX (300 ng), HA-Pirh2 (200 ng), and FLAG-Ub (1μg) expression vectors as indicated. Cells were treated with 20 μM MG132 for 8h before harvested. Whole cell lysates (WCL) were analyzed by direct immunoblotting (IB) and detected using indicated antibodies in each figure. In figure (A) and (B), immunoprecipitations (IP) were performed using anti-HA antibody. The precipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting and detected using anti-FLAG antibody. In figure (C) and (D), immunoprecipitations were performed using anti-myc and anti-FLAG antibody, respectively. The precipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting and detected using anti-HA antibody. In figure (E), immunoprecipitations were performed using anti-myc antibody. The precipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting and detected using anti-FLAG antibody. (TIFF 33404 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., He, G., Zhang, P. et al. Interplay between MDM2, MDMX, Pirh2 and COP1: the negative regulators of p53. Mol Biol Rep 38, 229–236 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0099-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0099-x