Abstract
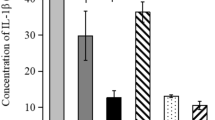
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 infections cause serious public health problems worldwide. The translocation intimin receptor (Tir) is responsible for adhesion and attaching and effacing lesions. In the current study, we used a mitomycin-treated mouse model to evaluate the efficacy of subcutaneous vs intranasal administration of the recombinant Tir as vaccine. Following immunization, mice were infected with E. coli O157:H7 and faces were monitored for shedding. Mice immunized intrasally with purified Tir proteins produced higher IgG and IgA titers in serum and feces, resulting in significant reductions in fecal shedding of EHEC O157 and higher a survival rate (92.9%), compared with subcutaneous or control immunizations. These results demonstrate the potential for the use of Tir proteins in mucosal vaccine formulations to prevent colonization and shedding of E. coli O157:H7. Therefore, purified Tir protects mice against EHEC challenge after intranasal immunization and is worth further clinical development as a vaccine candidate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karmali MA, Petric M, Louie S, Cheung R (1986) Antigenic heterogeneity of Escherichia coli verotoxins. Lancet 1:164–165
Sjogren R, Neill R, Rachmilewitz D, Fritz D, Newland J, Sharpnack D, Colleton C (1994) Role of Shiga-like toxin I in bacterial enteritis: comparison between isogenic Escherichia coli strains induced in rabbits. Gastroenterology 106:306–317
Takeda T (1993) Hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with entero-hemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Nippon Rinsho 51:198–203
Gianviti A, Rosmini F, Caprioli A, Corona R, Matteucci MC, Principato F, Luzzi I, Rizzoni G (1994) Haemolytic-uraemic syndrome in childhood: surveillance and case-control studies in Italy. Italian HUS Study Group. Pediatr Nephrol 8:705–709
Zhao X, Li Y, Wang L, You L, Xu Z, Li L, He X, Liu Y, Wang J, Yang L (2010) Development and application of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method on rapid detection Escherichia coli O157 strains from food samples. Mol Biol Rep 37:2183–2188
Safdar N, Said A, Gangnon RE, Maki DG (2002) Risk of hemolytic uremic syndrome after antibiotic treatment of Escherichia coli O157:H7 enteritis. JAMA 288(8):996–1001
Wong CS, Jelacic S, Habeeb RL, Watkins SL, Tarr PI (2000) The risk of the hemolytic-uremic syndrome after antibiotic treatment of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. N Engl J Med 342:1930–1936
Besser RE, Griffin PM, Slutsker L (1999) Escherichia coli O157:H7 gastroenteritis and the hemolytic uremic syndrome: an emerging infectious disease. Annu Rev Med 50:355–367
Acheson DW, Levine MM, Kaper JB, Keusch GT (1996) Protective immunity to Shiga-like toxin I following oral immunization with Shiga-like toxin I B-subunit-producing Vibrio cholerae CVD 103-HgR. Infect Immun 64:355–357
Butterton JR, Ryan ET, Acheson DW, Calderwood SB (1997) Co-expression of the B subunit of Shiga toxin 1 and EaeA from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in Vibrio cholerae vaccine strain. Infect Immun 65:2127–2135
Konadu EY, Parke JC, Tran HT, Bryla DA, Robbins JB, Szu SC (1998) Investigational vaccine for Escherichia coli O157 phase 1 study of O157 O-specific polysaccharide Pseudomonas aeruginosa recombinant exoprotein A conjugates in adults. J Infect Dis 177:383–387
Judge NA, Mason HS, O’Brien AD (2004) Plant cell-based intimin vaccine given orally to mice primed with intimin reduces time of Escherichia coli O157:H7 shedding in feces. Infect Immun 72:168–175
Potter AA, Klashinsky S, Li Y, Frey E, Townsend H, Rogan D (2004) Decreased shedding of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by cattle following vaccination with type III secreted proteins. Vaccine 22:362–369
Mayr UB, Haller C, Haidinger W, Atrasheuskaya A, Bukin E, Lubitz W, Ignatyev G (2005) Bacterial ghosts as an Oral vaccine: a single dose of Escherichia coli O157:H7 bacterial ghosts protects mice against lethal challenge. Infect Immun 73:4810–4817
Donkersgoed JV, Hancock D, Rogean D, Potter AA (2005) Escherichia coli O157:H7 vaccine field trial in 9 feedlots in Albeta and Saskatchewan. Can Vet J 46:724–728
Zhang Q, Ma Q, Li Q, Yao W, Wang C (2010) Enhanced protection against nasopharyngeal carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae elicited by oral multiantigen DNA vaccines delivered in attenuated Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0219-7
Zhang J, Zhang X, Zhang W, Guo Y, Guo G, Mao X, Zou Q (2010) Fusion expression and immunogenicity of Bordetella pertussis PTS1-FHA protein: implications for the vaccine development. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0317-6
Seyyed ME, Majid T, Khosrow A, Hassan N, Ali M (2010) Prokaryotic expression and characterization of avian influenza A virus M2 gene as a candidate for universal recombinant vaccine against influenza A subtypes; specially H5N1 and H9N2. Mol Biol Rep 37:2909–2914
Seyyed ME, Majid T (2010) Heterologous expression, purification and characterization of the influenza A virus M2e gene fused to Mycobacterium tuberculosis HSP70359–610 in prokaryotic system as a fusion protein. Mol Biol Rep 37:2877–2883
Donnenberg MS, Kaper JB, Finlay BB (1997) Interactions between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and host epithelial cells. Trends Microbiol 5:109–114
Frankel G, Phillips AD, Rosenshine I, Dougan G, Kaper JB, Knutton S (1998) Enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli: more subversive elements. Mol Microbiol 30:911–921
Hueck CJ (1998) Type III protein secretion systems in bacterial pathogens of animals and plants. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:379–433
Knutton S, Rosenshine I, Pallen MJ, Nisan I, Neves BC, Bain C, Wolff C, Dougan G, Frankel G (1998) A novel EspA-associated surface organelle of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli involved in protein translocation into epithelial cells. EMBO J 17:2166–2176
Wolff C, Nisan I, Hanski E, Frankel G, Rosenshine I (1998) Protein translocation into host epithelial cells by infecting enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 28:143–155
Kenny B, Devinney R, Stein M, Reinscheid DJ, Frey EA, Finlay BB (1997) Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) transfers its receptor for intimate adherence into mammalian cells. Cell 91:511–520
Junkal G, Gad F, Valerie FC (2005) Enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli infections: translocation, translocation, translocation. Infect Immun 73:2573–2585
Deng W, Li Y, Hardwidge PR (2005) Regulation of type III secretion hierarchy of translocators and effectors in attaching and effacing bacterial pathogens. Infect Immun 73:2135–2146
Vlisidou I, Dziva F, La Ragione RM, Best A, Garmendia J, Hawes P (2006) Role of intimin-tir interactions and the tir-cytoskeleton coupling protein in the colonization of calves and lambs by Escherichia coli O157:H7. Infect Immun 74:758–764
Sinclair JF, Dean-Nystrom EA, Alison DO (2006) The established intimin receptor Tir and the putative eucaryotic intimin receptors nucleolin and β1 integrin localize at or near the site of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence to enterocytes in vivo. Infect Immun 74:1255–1265
Nathan TR, Benjamin LM (2007) Characterization of the binding surface of the translocated intimin receptor, an essential protein for EPEC and EHEC cell adhesion. Protein Sci 16:2677–2683
Wang L, Long BG, Fan HY, Luo J (2009) Bioinformatics analysis of the Tir gene of Enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7. Chn J Trop Med 9:506–509
Sanches MI, Keller R (2000) Human colostrum and serum contain antibodies reactive to the intimin-binding region of the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli translocated intimin receptor. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 30(1):73–77
Babiuk S, Asper DJ, Rogan D, Mutwiri GK, Potter AA (2008) Subcutaneous and intranasal immunization with type III secreted proteins can prevent colonization and shedding of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in mice. Microb Pathogenesis 45:7–11
Zhang Y, Lu SQ, Zhang YZ (2004) The study for the immuno-protection of E. coli O157:H7 outer membrane protein. Natl Med J China 84:58–62
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Dean of the School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, Southern Medical University (no. GW200801-039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hong-ying Fan and Ling Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Hy., Wang, L., Luo, J. et al. Protection against Escherichia coli O157:H7 challenge by immunization of mice with purified Tir proteins. Mol Biol Rep 39, 989–997 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0824-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0824-0