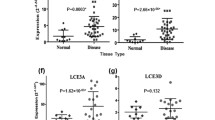
Abstract
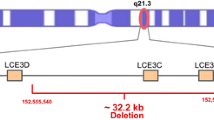
A deletion of two genes from the late cornified envelope (LCE), LCE3B and LCE3C within epidermal differentiation complex on chromosome 1 was shown to be associated with both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in several populations. To assess whether this deletion may contribute to the genetic predisposition to PsA in Tunisia, a total of 73 patients with PsA and 120 healthy matched controls were screened for the deletion, LCE3C_LCE3B-del, and its tag SNP, rs4112788. We also evaluated a possible relationship between PSORS1 and LCE3C_LCE3B-del through genotyping two proxy markers to HLA-C (rs12191877 and rs2073048). Our results did not provide evidence for association between the LCE3C_LCE3B-del nor the rs4112788 and the PsA. Similarly, no significant epistatic effect was observed. Our data suggest that The LCE deletion, previously identified in patients with psoriasis, is not of a major importance in the development of PsA in Tunisian patients supporting the current perception that different genetic risk factors contribute to skin and joint disease. However, these results need to be confirmed by additional large-scale studies of Tunisian PsA patients and controls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H (2006) Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum 54:2665–2673
Nograles KE, Brasington RD, Bowcock AM (2009) New insights into the pathogenesis and genetics of psoriatic arthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 5:83–91
Gelfand JM, Gladman DD, Mease PJ, Smith N, Margolis DJ, Nijsten T et al (2005) Epidemiology of psoriatic arthritis in the population of the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol 53:573
Gladman DD (2009) Psoriatic arthritis from Wright’s era until today. J Rheumatol Suppl 83:4–8
Kleinert S, Feuchtenberger M, Kneitz C, Tony HP (2007) Psoriatic arthritis: clinical spectrum and diagnostic procedures. Clin Dermatol 25:519–523
Chandran V, Raychaudhuri SP (2010) Geoepidemiology and environmental factors of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Autoimmun 34:J314–J321
Taylor WJ (2002) Epidemiology of psoriatic arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 14:98–103
Ammar M, Bouchlaka-Souissi C, Rebaï A, Doss N, Sioud A, Zaraa I et al (2009) Linkage analysis of three genetic loci for disease susceptibility in Tunisian Psoriatic families. J Dermatol Sci 54:137–139
Chandran V, Schentag CT, Brockbank JE, Pellett FJ, Shanmugarajah S, Toloza SM et al (2009) Familial aggregation of psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:664–667
Moll JM, Wright V (1973) Familial occurrence of psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 32:181–201
Myers A, Kay LJ, Lynch SA, Walker DJ (2005) Recurrence risk for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis within sibships. Rheumatology 44:773–776
Pedersen OB, Svendsen AJ, Ejstrup L, Skytthe A, Junker P (2008) On the heritability of psoriatic arthritis. Disease concordance among monozygotic and dizygotic twins. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1417–1421
Duffin KC, Chandran V, Gladman DD, Krueger GG, Elder JT, Rahman P (2008) Genetics of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: update and future discussion. J Rheumatol 35:1449–1453
Rahman P, Elder JT (2005) Genetic epidemiology of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64(Suppl 2):37–41 ii
Gladman DD, Cheung C, Ng CM, Wade JA (1999) HLA-C locus alleles in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Hum Immunol 60:259–261
Ho PY, Barton A, Worthington J, Plant D, Griffiths CE, Young HS et al (2008) Investigating the role of the HLACw*06 and HLA-DRB1 genes in susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis: comparison with psoriasis and undifferentiated inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:677–682
Filer C, Ho P, Smith RL, Griffiths C, Young HS, Worthington J et al (2008) Investigation of association of the IL12B and IL23R genes with psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:3705–3709
Hüffmeier U, Lascorz J, Böhm B, Lohmann J, Wendler J, Mössner R et al (2009) Genetic variants of the IL-23R pathway: association with psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis vulgaris, but no specific risk factor for arthritis. J Invest Dermatol 129:355–358
Filer CE, Ho P, Bruce IN, Worthington J, Barton A (2009) Investigation of association of genes NAT9, SLC9A3R1 and RAPTOR on chromosome 17q25 with psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:292–293
Liu Y, Helms C, Liao W, Zaba LC, Duan S, Gardner J et al (2008) A genome-wide association study of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis identifies new disease loci. PLoS Genet 4:e1000041
Nair RP, Duffin KC, Helms C, Ding J, Stuart PE, Goldgar D et al (2009) Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-kappaB pathways. Nat Genet 41:199–204
Rahman P, Inman RD, Maksymowych WP, Reeve JP, Peddle L, Gladman DD (2009) Association of interleukin 23 receptor variants with psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol 36:137–140
Bowes J, Orozco G, Flynn E, Ho P, Brier R, Marzo-Ortega H et al (2011) Confirmation of TNIP1 and IL23A as susceptibility loci for psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1641–1644
de Cid R, Riveira-Munoz E, Zeeuwen PL, Robarge J, Liao W, Dannhauser EN et al (2009) Deletion of the late cornified envelope LCE3B and LCE3C genes as a susceptibility factor for psoriasis. Nat Genet 41:211–215
Zhang XJ, Huang W, Yang S, Sun LD, Zhang FY, Zhu QX et al (2009) Psoriasis genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility variants within LCE gene cluster at 1q21. Nat Genet 41:205–210
Hüffmeier U, Bergboer JG, Becker T, Armour JA, Traupe H, Estivill X et al (2010) Replication of LCE3C-LCE3B CNV as a Risk Factor for Psoriasis and Analysis of Interaction with Other Genetic Risk Factors. J Invest Dermatol 130:979–984
Coto E, Santos Juanes J, Coto Segura P, Díaz M, Soto J, Queiro R et al (2010) Mutation analysis of the LCE3B/LCE3C genes in psoriasis. BMC Med Genet 11:45
Li M, Wu Y, Chen G, Yang Y, Zhou D, Zhang Z et al (2011) Deletion of the late cornified envelope genes LCE3C and LCE3B is associated with psoriasis in a Chinese population. J Invest Dermatol 131:1639–1643
Xu L, Li Y, Zhang X, Sun H, Sun D, Jia X et al (2011) Deletion of LCE3C and LCE3B genes is associated with psoriasis in a northern Chinese population. Br J Dermatol 165:882–887
Riveira-Munoz E, He SM, Escaramís G, Stuart PE, Hüffmeier U, Lee C et al (2011) Meta-analysis confirms the LCE3C_LCE3B deletion as a risk factor for psoriasis in several ethnic groups and finds interaction with HLA-Cw6. J Invest Dermatol 131:1105–1109
Ammar M, Bouazizi F, Bouhaha R, Zaraa I, Kouidhi S, Ourheni S et al (2012) Association analysis of LCE3C-LCE3B deletion in Tunisian psoriatic population. Arch Dermatol Res 304:733–738
Bowes J, Flynn E, Ho P, Aly B, Morgan AW, Marzo-Ortega H et al (2010) Variants in linkage disequilibrium with the late cornified envelope gene cluster deletion are associated with susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:2199–2203
Docampo E, Giardina E, Riveira-Muñoz E, de Cid R, Escaramís G, Perricone C et al (2011) Deletion of LCE3C and LCE3B is a susceptibility factor for psoriatic arthritis: a study in Spanish and Italian populations and meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum 6:1860–1865
Hüffmeier U, Estivill X, Riveira-Munoz E, Traupe H, Wendler J, Lohmann J et al (2010) Deletion of LCE3C and LCE3B genes at PSORS4 does not contribute to susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis in German patients. Ann Rheum Dis 69:876–878
Feng BJ, Sun LD, Soltani-Arabshahi R, Bowcock AM, Nair RP, Stuart P et al (2009) Multiple loci within the major histocompatibility complex confer risk of psoriasis. PLoS Genet 5(8):e1000606
Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H et al (2006) Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum 54:2665–2673
Gauderman WJ (2002) Sample size requirements for association studies of gene–gene interaction. Am J Epidemiol 155:478–484
Romdhane L, Kefi R, Azaiez H, Ben Halim N, Dellagi K, Abdelhak S (2012) Founder mutations in Tunisia: implications for diagnosis in North Africa and Middle East. Orphanet J Rare Dis 7:52
Bowes J, Barton A (2010) The genetics of psoriatic arthritis: lessons from genome-wide association studies. Discov Med 10:177–183
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients and family members. This work was supported by the Tunisian Ministry of Scientific and Technological Research and, Development of Competencies (Laboratory of Genetics, Immunology and Human Pathologies).
Conflict of interest
We state that we have no commercial affiliations, consultancies, stock or equity interests and patent-licensing arrangements that could be considered to pose a conflict of interest regarding the submitted article. We state that this work has been approved by the local Research Ethics Committee of la Rabta Hospital of Tunis. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiraz, B.S., Myriam, A., Ines, Z. et al. Deletion of late cornified envelope genes, LCE3C_LCE3B-del, is not associated with psoriatic arthritis in Tunisian patients. Mol Biol Rep 41, 4141–4146 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3285-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3285-4