Abstract
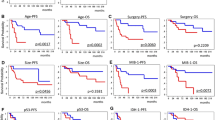
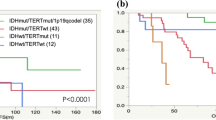
The objective of this study was to evaluate, in a series of 43 pediatric high-grade gliomas (21 anaplastic astrocytoma WHO grade III and 22 glioblastoma WHO grade IV), the prognostic value of histological grading and expression of p53 and YKL-40. Moreover, mutational screening for TP53 and IDH1 was performed in 27 of 43 cases. The prognostic stratification for histological grading showed no difference in overall (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) between glioblastomas and anaplastic astrocytomas. Overexpression of YKL40 was detected in 25 of 43 (58%) cases, but YKL-40 expression was not prognostic in terms of OS and PFS. p53 protein expression was observed in 13 of 43 (31%) cases but was not prognostic. TP53 mutations were detected in five of 27 (18%) cases (four glioblastomas and one anaplastic astrocytoma). Patients with TP53 mutation had a shorter median OS (9 months) and PFS (8 months) than those without mutations (OS, 17 months; PFS, 16 months), although this trend did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.07). IDH1 mutations were not detected in any of the cases analyzed. Our results suggest that in pediatric high-grade gliomas: (i) histological grading does not have strong prognostic significance, (ii) YKL-40 overexpression is less frequent than adult high-grade gliomas and does not correlate with a more aggressive behavior, (iii) TP53 mutations but not p53 expression may correlate with a more aggressive behavior, and (iv) IDH1 mutations are absent. These observations support the concept that, despite identical histological features, the biology of high-grade gliomas in children differs from that in adults, and therefore different prognostic factors are needed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaatsch P, Rickert CH, Kühl J, Schüz J, Michaelis J (2001) Population-based epidemiologic data on brain tumors in German children. Cancer. Dec 15:3155–3164
Kim TS, Halliday AL, Hedley-Whyte ET, Convery K (1991) Correlates of survival and the Daumas–Duport grading system for astrocytomas. J Neurosurg 74:27–37
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavanee WK (eds) (2007) WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. IARC, Lyon
Ohgaki H, Dessen P, Jourde B, Horstmann S, Nishikawa T, Di Patre PL, Burkhard C, Schüler D, Probst-Hensch NM, Maiorka PC, Baeza N, Pisani P, Yonekawa Y, Yasargil MG, Lütolf UM, Kleihues P (2004) Genetic pathways to glioblastoma: a population-based study. Cancer Res 1:6892–6899
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2007) Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol 170:1445–1453
Nobusawa S, Watanabe T, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H (2009) IDH1 mutations as molecular signature and predictive factor of secondary glioblastomas. Clin Cancer Res 15:6002–6007
Pollack IF, Finkelstein SD, Woods J, Burnham J, Holmes EJ, Hamilton RL, Yates AJ, Boyett JM, Finlay JL, Sposto R (2002) Expression of p53 and prognosis in children with malignant gliomas. N Engl J Med 346:420–427
Rood BR, Macdonald TJ (2005) Pediatric high grade glioma: molecular genetics clues for innovative therapeutic approaches. J Neurooncol 75:267–272
Rickert CH, Sträter R, Kaatsch P, Wassmann H, Jürgens H, Dockhorn-Dworniczak B, Paulus W (2001) Pediatric high-grade astrocytomas show chromosomal imbalances distinct from adult cases. Am J Pathol 158:1525–1532
Faury D, Nantel A, Dunn SE, Guiot MC, Haque T, Hauser P, Garami M, Bognár L, Hanzély Z, Liberski PP, Lopez-Aguilar E, Valera ET, Tone LG, Carret AS, Del Maestro RF, Gleave M, Montes JL, Pietsch T, Albrecht S, Jabado N (2007) Molecular profiling identifies prognostic subgroups of pediatric glioblastoma and shows increased YB-1 expression in tumors. J Clin Oncol 25:1196–1207
Haque T, Faury D, Albrecht S, Lopez-Aguilar E, Hauser P, Garami M, Hanzély Z, Bognár L, Del Maestro RF, Atkinson J, Nantel A, Jabado N (2007) Gene expression profiling from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumors of pediatric glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:6284–6292
Johnson R, Wright KD, Gilbertson RJ (2009) Molecular profiling of pediatric brain tumors: insight into biology and treatment. Curr Oncol Rep 11:68–72
Rivera AL, Pelloski CE, Sulman E, Aldape K (2008) Prognostic and predictive markers in glioma and other neuroepithelial tumors. Curr Probl Cancer 32:97–123
Pelloski CE, Mahajan A, Maor M, Chang EL, Woo S, Gilbert M, Colman H, Yang H, Ledoux A, Blair H, Passe S, Jenkins RB, Aldape KD (2005) YKL-40 expression is associated with poorer response to radiation and shorter overall survival in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 1:3326–3334
Cunningham JM, Kimmel DW, Scheithauer BW, O’Fallon JR, Novotny PJ, Jenkins RB (1997) Analysis of proliferation markers and p53 expression in gliomas of associated origin: relationship and prognostic value. J Neurosurg 86:121–130
Danks RA, Chopra G, Gonzales MF, Orian JM, Kaye AH (1995) Aberrant p53 expression does not correlate with the prognosis in anaplastic astrocytoma. Neurosurgery 37:246–254
Yan H, Parsons DW, Jin G, McLendon R, Rasheed BA, Yuan W, Kos I, Batinic-Haberle I, Jones S, Riggins GJ, Friedman H, Friedman A, Reardon D, Herndon J, Kinzler KW, Velculescu VE, Vogelstein B, Bigner DD (2009) IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. N Engl J Med 360:765–773
De Carli E, Wang X, Puget (2009) IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in glioma. N Engl J Med 360:2248–2249
Recklies AD, White C, Ling H (2002) The chitinase 3-like protein human cartilage glycoprotein 39 (HC-gp39) stimulates proliferation of human connective-tissue cells and activates both extracellular signal-regulated kinase- and protein kinase B-mediated signalling pathways. Biochem J 1:119–126
Pelloski CE, Lin E, Zhang L, Yung WK, Colman H, Liu JL, Woo SY, Heimberger AB, Suki D, Prados M, Chang S, Barker FG 3rd, Fuller GN, Aldape KD (2006) Prognostic associations of activated mitogen-activated protein kinase and Akt pathways in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 1:3935–3941
Malinda KM, Ponce L, Kleinman HK, Shackelton LM, Millis AJ (1999) Gp38 k, a protein synthesized by vascular smooth muscle cells, stimulates directional migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 250:168–173
Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD, Misra A, Nigro JM, Colman H, Soroceanu L, Williams PM, Modrusan Z, Feuerstein BG, Aldape K (2006) Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 9:157–173
Pfister S, Witt O (2009) Pediatric gliomas. Recent Results Cancer Res 171:67–81
Pollack IF, Finkelstein SD, Burnham J, Holmes EJ, Hamilton RL, Yates AJ, Finlay JL, Sposto R (2001) Age and TP53 mutation frequency in childhood malignant gliomas: results in a multi-institutional cohort. Cancer Res 15:7404–7407
Cheng Y, Ng HK, Zhang SF, Ding M, Pang JC, Zheng J, Poon WS (1999) Genetic alterations in pediatric high-grade astrocytomas. Hum Pathol 30:1284–1290
Suri V, Das P, Jain A, Sharma MC, Borkar SA, Suri A, Gupta D, Sarkar C (2009) Pediatric glioblastomas: a histopathological and molecular genetic study. Neuro Oncol 11:274–280
Okamoto Y, Di Patre PL, Burkhard C, Horstmann S, Jourde B, Fahey M, Schüler D, Probst-Hensch NM, Yasargil MG, Yonekawa Y, Lütolf UM, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H (2004) Population-based study on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations of low-grade diffuse astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas. Acta Neuropathol 108:49–56
Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, Lin JC, Leary RJ, Angenendt P, Mankoo P, Carter H, Siu IM, Gallia GL, Olivi A, McLendon R, Rasheed BA, Keir S, Nikolskaya T, Nikolsky Y, Busam DA, Tekleab H, Diaz LA Jr, Hartigan J, Smith DR, Strausberg RL, Marie SK, Shinjo SM, Yan H, Riggins GJ, Bigner DD, Karchin R, Papadopoulos N, Parmigiani G, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE, Kinzler KW (2008) An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science 26(321):1807–1812
Balss J, Meyer J, Mueller W, Korshunov A, Hartmann C, von Deimling A (2008) Analysis of the IDH1 codon 132 mutation in brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol 116:597–602
Ichimura K, Pearson DM, Kocialkowski S, Bäcklund LM, Chan R, Jones DT, Collins VP (2009) IDH1 mutations are present in the majority of common adult gliomas but are rare in primary glioblastomas. Neuro Oncol (Epub ahead of print)
Sanson M, Marie Y, Paris S, Idbaih A, Laffaire J, Ducray F, Hallani SE, Boisselier B, Mokhtari K, Hoang-Xuan K, Delattre JY (2009) Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 codon 132 mutation is an important prognostic biomarker in gliomas. J Clin Oncol (Epub ahead of print)
Sanders RP, Kocak M, Burger PC, Merchant TE, Gajjar A, Broniscer A (2007) High-grade astrocytoma in very young children. Pediatr Blood Cancer 49:888–893
Wolff JE, Gnekow AK, Kortmann RD, Pietsch T, Urban C, Graf N, Kühl J (2002) Preradiation chemotherapy for pediatric patients with high-grade glioma. Cancer 94:264–271 2002
Acknowledgments
This study was in part supported by “Il Fondo di Giò Onlus”. Manila Antonelli is supported by a grant from Associazione Italiana per la Lotta al Neuroblastoma. We thank Maura Massimino and Maria Luisa Garrè for their assistance with the clinical information, and Alessandra Angiolosanto and Anne-Marie Camus for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonelli, M., Buttarelli, F.R., Arcella, A. et al. Prognostic significance of histological grading, p53 status, YKL-40 expression, and IDH1 mutations in pediatric high-grade gliomas. J Neurooncol 99, 209–215 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0129-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0129-5