Abstract
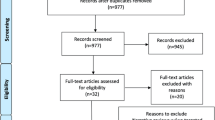
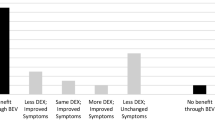
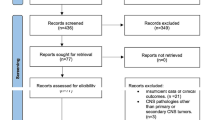
Radiation necrosis is a devastating complication following radiation to the central nervous system. The purpose of this study was to perform a comprehensive analysis of cases in the literature using bevacizumab, a monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor, as treatment for radiation necrosis. A MEDLINE/PubMed search of articles about the use of bevacizumab for radionecrosis treatment yielded 16 studies published between 2007 and 2012. Data was summarized according to patient characteristics, treatment received and outcomes measured. A total of 71 unique cases were identified that met the inclusion criteria. The median age at the time of treatment with bevacizumab was 47 years. The most common tumors treated were glioblastoma (31 %), anaplastic glioma (14 %), and metastatic brain tumors (15 %). The median time from ending radiotherapy to starting treatment with bevacizumab was 11 months and the median follow up time after bevacizumab treatment was 8 months. The median number of cycles of bevacizumab was administered was 4, and the median dosage of bevacizumab was 7.5 mg/kg. The median time elapsed between cycles of bevacizumab was 2 weeks. Overall, pre and post treatment imaging revealed a median decrease in T1 contrast enhancement of 63 %, and a 59 % median decrease in T2/FLAIR signal abnormality. Treatment with bevacizumab resulted in a significant radiographic response for patients with radionecrosis. The median dosage of bevacizumab of 7.5 mg/kg for four cycles every 2 weeks should be considered as a treatment option in this patient population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levin VA, Bidaut L, Hou P, Kumar AJ, Wefel JS, Bekele BN, Grewal J, Prabhu S, Loghin M, Gilbert MR et al (2011) Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of bevacizumab therapy for radiation necrosis of the central nervous system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79:1487–1495. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.12.061
Furuse M, Nonoguchi N, Kawabata S, Yoritsune E, Takahashi M, Inomata T, Kuroiwa T, Miyatake S (2013) Bevacizumab treatment for symptomatic radiation necrosis diagnosed by amino acid PET. Jpn J Clin Oncol 43:337–341. doi:10.1093/jjco/hys231
Giglio P, Gilbert MR (2003) Cerebral radiation necrosis. Neurologist 9:180–188. doi:10.1097/01.nrl.0000080951.78533.c4
Li YQ, Chen P, Jain V, Reilly RM, Wong CS (2004) Early radiation-induced endothelial cell loss and blood-spinal cord barrier breakdown in the rat spinal cord. Radiat Res 161:143–152
Nordal RA, Nagy A, Pintilie M, Wong CS (2004) Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 target genes in central nervous system radiation injury: a role for vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 10:3342–3353. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0426
Nonoguchi N, Miyatake S, Fukumoto M, Furuse M, Hiramatsu R, Kawabata S, Kuroiwa T, Tsuji M, Fukumoto M, Ono K (2011) The distribution of vascular endothelial growth factor-producing cells in clinical radiation necrosis of the brain: pathological consideration of their potential roles. J Neurooncol 105:423–431. doi:10.1007/s11060-011-0610-9
Baker DG, Krochak RJ (1989) The response of the microvascular system to radiation: a review. Cancer Investig 7:287–294
Remler MP, Marcussen WH, Tiller-Borsich J (1986) The late effects of radiation on the blood brain barrier. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 12:1965–1969
Rahmathulla G, Marko NF, Weil RJ (2013) Cerebral radiation necrosis: a review of the pathobiology, diagnosis and management considerations. J Clin Neurosci 20:485–502. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2012.09.011
Gonzalez J, Kumar AJ, Ca Conrad, Va Levin (2007) Effect of bevacizumab on radiation necrosis of the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67:323–326. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.10.010
Wong ET, Huberman M, Lu X, Mahadevan A (2008) Bevacizumab reverses cerebral radiation necrosis. J Clin Oncol 26:5649–5650. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.19.1866
Liu AK, Macy ME, Foreman NK (2009) Bevacizumab as therapy for radiation necrosis in four children with pontine gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75:1148–1154. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.12.032
Torcuator R, Zuniga R, Mohan YS, Rock J, Doyle T, Anderson J, Gutierrez J, Ryu S, Jain R, Rosenblum M et al (2009) Initial experience with bevacizumab treatment for biopsy confirmed cerebral radiation necrosis. J Neurooncol 94:63–68. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-9801-z
Jeyaretna DS, Curry WT, Batchelor TT, Stemmer-Rachamimov A, Plotkin SR (2011) Exacerbation of cerebral radiation necrosis by bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol 29:e159–e162. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.31.4815
Benoit A, Ducray F, Cartalat-Carel S, Psimaras D, Ricard D, Honnorat J (2011) Favorable outcome with bevacizumab after poor outcome with steroids in a patient with temporal lobe and brainstem radiation necrosis. J Neurol 258:328–329. doi:10.1007/s00415-010-5747-5
Matuschek C, Bölke E, Nawatny J, Hoffmann TK, Peiper M, Orth K, Gerber PA, Rusnak E, Lammering G, Budach W (2011) Bevacizumab as a treatment option for radiation-induced cerebral necrosis. Strahlenther Onkol 187:135–139. doi:10.1007/s00066-010-2184-4
Sanborn MR, Danish SF, Rosenfeld MR, O’Rourke D, Lee JYK (2011) Treatment of steroid refractory, Gamma Knife related radiation necrosis with bevacizumab: case report and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113:798–802. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2011.08.007
Arratibel-Echarren I, Albright K, Dalmau J, Rosenfeld MR (2011) Use of bevacizumab for neurological complications during initial treatment of malignant gliomas. Neurologia 26:74–80. doi:10.1016/S2173-5808(11)70017-7
DeSalvo MN (2012) Radiation necrosis of the pons after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: diagnosis and treatment. J Radiol Case Rep 6:9–16. doi:10.3941/jrcr.v6i7.1108
Wang Y, Pan L, Sheng X, Mao Y, Yao Y, Wang E, Zhang N, Dai J (2012) Reversal of cerebral radiation necrosis with bevacizumab treatment in 17 Chinese patients. Eur J Med Res 17:25. doi:10.1186/2047-783X-17-25
Gronier S, Bourg V, Frenay M, Cohen M, Mondot L, Thomas P, Lebrun C (2011) Bevacizumab for the treatment of cerebral radionecrosis. Rev Neurol 167:331–336. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2010.10.012
McPherson CM, Warnick RE (2004) Results of contemporary surgical management of radiation necrosis using frameless stereotaxis and intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurooncol 68:41–47
Williamson R, Kondziolka D, Kanaan H, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC (2008) Adverse radiation effects after radiosurgery may benefit from oral vitamin E and pentoxifylline therapy: a pilot study. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 86:359–366. doi:10.1159/000163557
Rizzoli HV, Pagnanelli DM (1984) Treatment of delayed radiation necrosis of the brain. A clinical observation. J Neurosurg 60:589–594. doi:10.3171/jns.1984.60.3.0589
Leber KA, Eder HG, Kovac H, Anegg U, Pendl G (1998) Treatment of cerebral radionecrosis by hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 70(Suppl 1):229–236
Perez-Espejo MA, Garcia-Fernandez R, Tobarra-Gonzalez BM, Palma-Copete JD, Gonzalez-Lopez A, De la Fuente-Munoz I, Salinas-Ramos J, Felipe-Murcia M, Martinez-Lage JF, Fernandez-Perez J et al (2009) Usefulness of hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of radionecrosis and symptomatic brain edema after LINAC radiosurgery. Neurocirugia 20:449–453
Kang KB, Wang TT, Woon CT, Cheah ES, Moore XL, Zhu C, Wong MC (2007) Enhancement of glioblastoma radioresponse by a selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib: inhibition of tumor angiogenesis with extensive tumor necrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67:888–896. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.09.055
Tsao MN, Li YQ, Lu G, Xu Y, Wong CS (1999) Upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with radiation-induced blood-spinal cord barrier breakdown. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:1051–1060
Gerstner ER, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Ryg PA, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Ivy P, Jain RK, Batchelor TT (2009) VEGF inhibitors in the treatment of cerebral edema in patients with brain cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6:229–236. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.14
Cheung MC, Chan AS, Law SC, Chan JH, Tse VK (2003) Impact of radionecrosis on cognitive dysfunction in patients after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 97:2019–2026. doi:10.1002/cncr.11295
Jain RK (2001) Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med 7:987–989. doi:10.1038/nm0901-987
Dai F, Shu L, Bian Y, Wang Z, Yang Z, Chu W, Gao S (2013) Safety of bevacizumab in treating metastatic colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of all randomized clinical trials. Clin Drug Investig 33:779–788. doi:10.1007/s40261-013-0125-6
Merkenschlager A, Hirsch W, Syrbe S, Bernhard M, Wurm R (2011) Successful bevacizumab therapy for CNS radiation necrosis after stereotactic radiotherapy of an arteriovenous malformation. Neuropediatrics 42:P046
Conflict of interest
The authors’ report that Dr. Kelly Nicholas is a consultant for Genentech.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tye, K., Engelhard, H.H., Slavin, K.V. et al. An analysis of radiation necrosis of the central nervous system treated with bevacizumab. J Neurooncol 117, 321–327 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1391-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1391-8