Abstract
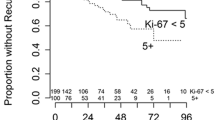
The expression and role of periostin in meningiomas remains unknown. Tissue specimens of 175 convexity meningiomas were immunohistochemically examined with antibodies against periostin and Ki67. The expression levels of periostin and Ki67 were compared among different WHO groups. The role of periostin and Ki67 in postoperative prognosis of meningiomas was also analyzed. Negative (−) expression of Ki67 was observed in 101 (57.7 %) cases of all the surgical tissue samples. The Ki67 expressions differed significantly among the WHO groups (P < 0.001) and correlated positively with the WHO grade (r = 0.673, P < 0.001). Low/negative staining of periostin was observed in 116 (66.3 %) cases. The periostin expressions differed significantly among the WHO groups (P < 0.001). Periostin expression correlated positively with the WHO grade (r = 0.742, P < 0.001). There was a positive correlation between Ki67 expression and periostin (r = 0.513, P < 0.001). Both Ki67 expression and periostin expression was found statistically different between brain invasion tumor and non-invasion tumor (p < 0.001). The recurrence rate and PFS rate in both varied Ki67 expression groups and periostin expression groups was statistically different (P < 0.001). The survival time and PFS time in both varied Ki67 expression groups and periostin expression groups was also statistically different (P < 0.001). Periostin was expressed in tumor stroma of meningiomas. Both periostin and Ki67 may behave as a maker in predicting the grade and prognosis in meningiomas. Drugs that targets periostin aims at reducing invasion of meningioma patients should be further researched.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bondy M, Ligon BL (1996) Epidemiology and etiology of intracranial meningiomas: a review. J Neurooncol 29:197–205
Fuller GN, Scheithauer BW (2007) The 2007 revised World Health Organization (WHO) classification of tumours of the central nervous system: newly codified entities. Brain Pathol 17:304–307
Durand A, Labrousse F, Jouvet A, Bauchet L, Kalamarides M, Menei P, Deruty R, Moreau JJ, Fevre-Montange M, Guyotat J (2009) WHO grade II and III meningiomas: a study of prognostic factors. J Neurooncol 95:367–375
Vranic A, Popovic M, Cor A, Prestor B, Pizem J (2010) Mitotic count, brain invasion, and location are independent predictors of recurrence-free survival in primary atypical and malignant meningiomas: a study of 86 patients. Neurosurgery 67:1124–1132
Weber DC, Lovblad KO, Rogers L (2010) New pathology classification, imagery techniques and prospective trials for meningiomas: the future looks bright. Curr Opin Neurol 23:563–570
Ohba S, Kobayashi M, Horiguchi T, Onozuka S, Yoshida K, Ohira T, Kawase T (2011) Long-term surgical outcome and biological prognostic factors in patients with skull base meningiomas. J Neurosurg 114:1278–1287
Nakasu S, Fukami T, Jito J, Nozaki K (2009) Recurrence and regrowth of benign meningiomas. Brain Tumor Pathol 26:69–72
Takeshita S, Kikuno R, Tezuka K, Amann E (1993) Osteoblast-specific factor 2: cloning of a putative bone adhesion protein with homology with the insect protein fasciclin I. Biochem J 294(Pt 1):271–278
Ruan K, Bao S, Ouyang G (2009) The multifaceted role of periostin in tumorigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:2219–2230
Bao S, Ouyang G, Bai X, Huang Z, Ma C, Liu M, Shao R, Anderson RM, Rich JN, Wang XF (2004) Periostin potently promotes metastatic growth of colon cancer by augmenting cell survival via the Akt/PKB pathway. Cancer Cell 5:329–339
Baril P, Gangeswaran R, Mahon PC, Caulee K, Kocher HM, Harada T, Zhu M, Kalthoff H, Crnogorac-Jurcevic T, Lemoine NR (2007) Periostin promotes invasiveness and resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to hypoxia-induced cell death: role of the beta4 integrin and the PI3k pathway. Oncogene 26:2082–2094
Gunia S, Jain A, Koch S, Denzinger S, Gotz S, Niessl N, May M (2013) Periostin expression correlates with pT-stage, grading and tumour size, and independently predicts cancer-specific survival in surgically treated penile squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Pathol 66:297–301
Kim CJ, Sakamoto K, Tambe Y, Inoue H (2011) Opposite regulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cell invasiveness by periostin between prostate and bladder cancer cells. Int J Oncol 38:1759–1766
Kudo Y, Ogawa I, Kitajima S, Kitagawa M, Kawai H, Gaffney PM, Miyauchi M, Takata T (2006) Periostin promotes invasion and anchorage-independent growth in the metastatic process of head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 66:6928–6935
Nuzzo PV, Rubagotti A, Zinoli L, Ricci F, Salvi S, Boccardo S, Boccardo F (2012) Prognostic value of stromal and epithelial periostin expression in human prostate cancer: correlation with clinical pathological features and the risk of biochemical relapse or death. BMC Cancer 12:625
Shao R, Bao S, Bai X, Blanchette C, Anderson RM, Dang T, Gishizky ML, Marks JR, Wang XF (2004) Acquired expression of periostin by human breast cancers promotes tumor angiogenesis through up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression. Mol Cell Biol 24:3992–4003
Siriwardena BS, Kudo Y, Ogawa I, Kitagawa M, Kitajima S, Hatano H, Tilakaratne WM, Miyauchi M, Takata T (2006) Periostin is frequently overexpressed and enhances invasion and angiogenesis in oral cancer. Br J Cancer 95:1396–1403
Sun C, Zhao X, Xu K, Gong J, Liu W, Ding W, Gou Y, Xia G, Ding Q (2011) Periostin: a promising target of therapeutical intervention for prostate cancer. J Transl Med 9:99
Takanami I, Abiko T, Koizumi S (2008) Expression of periostin in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: correlation with angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Int J Biol Markers 23:182–186
Tischler V, Fritzsche FR, Wild PJ, Stephan C, Seifert HH, Riener MO, Hermanns T, Mortezavi A, Gerhardt J, Schraml P, Jung K, Moch H, Soltermann A, Kristiansen G (2010) Periostin is up-regulated in high grade and high stage prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 10:273
Tsunoda T, Furusato B, Takashima Y, Ravulapalli S, Dobi A, Srivastava S, McLeod DG, Sesterhenn IA, Ornstein DK, Shirasawa S (2009) The increased expression of periostin during early stages of prostate cancer and advanced stages of cancer stroma. Prostate 69:1398–1403
Hasseleid BF, Meling TR, Ronning P, Scheie D, Helseth E (2012) Surgery for convexity meningioma: simpson Grade I resection as the goal: clinical article. J Neurosurg 117:999–1006
Qi ST, Liu Y, Pan J, Chotai S, Fang LX (2012) A radiopathological classification of dural tail sign of meningiomas. J Neurosurg 117:645–653
Jensen R, Lee J (2012) Predicting outcomes of patients with intracranial meningiomas using molecular markers of hypoxia, vascularity, and proliferation. Neurosurgery 71:146–156
Morra L, Moch H (2011) Periostin expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: a review and an update. Virchows Arch 459:465–475
Yan W, Shao R (2006) Transduction of a mesenchyme-specific gene periostin into 293T cells induces cell invasive activity through epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. J Biol Chem 281:19700–19708
Gillan L, Matei D, Fishman DA, Gerbin CS, Karlan BY, Chang DD (2002) Periostin secreted by epithelial ovarian carcinoma is a ligand for alpha(V)beta(3) and alpha(V)beta(5) integrins and promotes cell motility. Cancer Res 62:5358–5364
Wilisch-Neumann A, Kliese N, Pachow D, Schneider T, Warnke JP, Braunsdorf WE, Bohmer FD, Hass P, Pasemann D, Helbing C, Kirches E, Mawrin C (2013) The integrin inhibitor cilengitide affects meningioma cell motility and invasion. Clin Cancer Res 19:5402–5412
Abry E, Thomassen IO, Salvesen OO, Torp SH (2010) The significance of Ki-67/MIB-1 labeling index in human meningiomas: a literature study. Pathol Res Pract 206:810–815
Rezanko T, Akkalp AK, Tunakan M, Sari AA (2008) MIB-1 counting methods in meningiomas and agreement among pathologists. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 30:47–52
Taddei GL, Caldarella A, Raspollini MR, Taddei A, Buccoliero AM (2002) Estrogen and progesterone receptors in meningiomas: immunohistochemical (Mib-1, p53) and clinico-morphological correlations. Pathologica 94:10–15
Kim Y, Stolarska MA, Othmer HG (2011) The role of the microenvironment in tumor growth and invasion. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 106:353–379
Koontongkaew S (2013) The tumor microenvironment contribution to development, growth, invasion and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Cancer 4:66–83
Ng YZ, South AP (2014) Tissue engineering of tumor stromal microenvironment with application to cancer cell invasion. J Vis Exp. doi:10.3791/51321
Li M, Li C, Li D, Xie Y, Shi J, Li G, Guan Y, Li M, Zhang P, Peng F, Xiao Z, Chen Z (2012) Periostin, a stroma-associated protein, correlates with tumor invasiveness and progression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 29:865–877
Hong LZ, Wei XW, Chen JF, Shi Y (2013) Overexpression of periostin predicts poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett 6:1595–1603
Utispan K, Sonongbua J, Thuwajit P, Chau-In S, Pairojkul C, Wongkham S, Thuwajit C (2012) Periostin activates integrin alpha5beta1 through a PI3K/AKTdependent pathway in invasion of cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Oncol 41:1110–1118
Conflict of interest
All the authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yi Liu, Jin Shi and Ming Chen are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Shi, J., Chen, M. et al. Periostin: a novel prognostic predictor for meningiomas. J Neurooncol 121, 505–512 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1678-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1678-9