Abstract
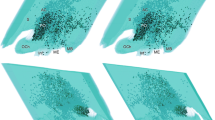
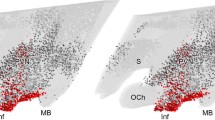
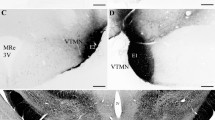
This study reports the distribution of parathyroid hormone 2 receptor (PTH2R)-immunoreactive fibers in the hypothalamus using fluorescent amplification immunocytochemistry. The pattern of immunolabeling is strikingly similar to that of tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues (TIP39), a peptide recently purified from bovine hypothalamus and proposed to be a ligand of the PTH2R based on pharmacological data. To investigate the anatomical basis of suggestions that TIP39 affects the secretion of several hypophysiotropic hormones we performed double-labeling studies and found that only somatostatin fibers contain PTH2R in the median eminence, which suggests that somatostatin release could be directly regulated via the PTH2R. However, several hypothalamic nuclei projecting to the median eminence contain a high density of both TIP39 and PTH2R fibers and terminals. We report here, that the PTH2R terminals also contain vesicular glutamate transporter−2, and suggest that TIP39 terminals are ideally positioned to modulate glutamatergic influences on hypophysiotropic neurons.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palkovits M (1992) Peptidergic neurotransmitters in the endocrine hypothalamus. Ciba Found Symp 168:3–10 discussion 10–15
Usdin TB, Gruber C, Bonner TI (1995) Identification and functional expression of a receptor selectively recognizing parathyroid hormone, the PTH2 receptor. J Biol Chem 270:15455–15458
Harmar AJ (2001) Family-B G-protein-coupled receptors. Genome Biol 2:30131–30110
Usdin TB, Bonner TI, Hoare SR (2002) The parathyroid hormone 2 (PTH2) receptor. Receptors Channels 8:211–218
Wang T, Palkovits M, Rusnak M, Mezey E, Usdin TB (2000) Distribution of parathyroid hormone−2 receptor-like immunoreactivity and messenger RNA in the rat nervous system. Neuroscience 100:629–649
Pang PK, Kaneko T, Harvey S (1988) Immunocytochemical distribution of PTH immunoreactivity in vertebrate brains. Am J Physiol 255:R643–R647
Fraser RA, Kronenberg HM, Pang PK, Harvey S (1990) Parathyroid hormone messenger ribonucleic acid in the rat hypothalamus. Endocrinology 127:2517–2522
Usdin TB (1997) Evidence for a parathyroid hormone−2 receptor selective ligand in the hypothalamus. Endocrinology 138:831–834
Hoare SR, Bonner TI, Usdin TB (1999) Comparison of rat and human parathyroid hormone 2 (PTH2) receptor activation: PTH is a low potency partial agonist at the rat PTH2 receptor. Endocrinology 140:4419–4425
Usdin TB, Hoare SR, Wang T, Mezey E, Kowalak JA (1999) TIP39: a new neuropeptide and PTH2-receptor agonist from hypothalamus. Nat Neurosci 2:941–943
Dobolyi A, Ueda H, Uchida H, Palkovits M, Usdin TB (2002) Anatomical and physiological evidence for involvement of tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues in nociception. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1651–1656
Hansen IA, Jakob O, Wortmann S, Arzberger T, Allolio B, Blind E (2002) Characterization of the human and mouse genes encoding the tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues, a ligand of the parathyroid hormone receptor family. J Endocrinol 174:95–102
John MR, Arai M, Rubin DA, Jonsson KB, Juppner H (2002) Identification and characterization of the murine and human gene encoding the tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues. Endocrinology 143:1047–1057
Usdin TB (2000) The PTH2 receptor and TIP39: a new peptide-receptor system. Trends Pharmacol Sci 21:128–130
Dobolyi A, Palkovits M, Usdin TB (2003) Expression and distribution of tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 455:547–566
Dobolyi A, Palkovits M, Bodnar I, Usdin TB (2003) Neurons containing tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues project to limbic, endocrine, auditory and spinal areas in rat. Neuroscience 122:1093–1105
Ward HL, Small CJ, Murphy KG, Kennedy AR, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (2001) The actions of tuberoinfundibular peptide on the hypothalamo-pituitary axes. Endocrinology 142:3451–3456
Sugimura Y, Murase T, Ishizaki S, Tachikawa K, Arima H, Miura Y, Usdin TB, Oiso Y (2003) Centrally administered tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues inhibits arginine vasopressin release in conscious rats. Endocrinology 144:2791–2796
Usdin TB, Dobolyi A, Ueda H, Palkovits M (2003) Emerging functions for tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues. Trends Endocrinol Metab 14:14–19
Hunyady B, Krempels K, Harta G, Mezey E (1996) Immunohistochemical signal amplification by catalyzed reporter deposition and its application in double immunostaining. J Histochem Cytochem 44:1353–1362
Ben-Barak Y, Russell JT, Whitnall MH, Ozato K, Gainer H (1985) Neurophysin in the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. I. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci 5:81–97
Fremeau RT Jr, Troyer MD, Pahner I, Nygaard GO, Tran CH, Reimer RJ, Bellocchio EE, Fortin D, Storm-Mathisen J, Edwards RH (2001) The expression of vesicular glutamate transporters defines two classes of excitatory synapse. Neuron 31:247–260
Herkenham M (1987) Mismatches between neurotransmitter and receptor localizations in brain: observations and implications. Neuroscience 23:1–38
Lin W, McKinney K, Liu L, Lakhlani S, Jennes L (2003) Distribution of vesicular glutamate transporter−2 messenger ribonucleic acid and protein in the septum-hypothalamus of the rat. Endocrinology 144:662–670
Erlander MG, Tobin AJ (1991) The structural and functional heterogeneity of glutamic acid decarboxylase: a review. Neurochem Res 16:215–226
Vincent SR, Hokfelt T, Wu JY (1982) GABA neuron systems in hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. Immunohistochemical demonstration using antibodies against glutamate decarboxylase. Neuroendocrinology 34:117–125
Palkovits M (1984) Neuropeptides in the hypothalamo-hypophyseal system: lateral retrochiasmatic area as a common gate for neuronal fibers towards the median eminence. Peptides 5(Suppl 1):35–39
Kiss J, Kocsis K, Csaki A, Halasz B (2003) Evidence for vesicular glutamate transporter synapses onto gonadotropin-releasing hormone and other neurons in the rat medial preoptic area. Eur J Neurosci 18:3267–3278
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Carolyn Smith and the NINDS Light Imaging Facility for help with confocal microscopy. We thank Dr. H. Gainer, NINDS, NIH and Dr. R. Edwards, UCSF for generously providing the anti-arginine-vasopressin-neurophysin and the anti-vesicular glutamate transporter-2 antibodies, respectively. Support was provided by a NARSAD Young Investigator Award for Arpád Dobolyi and by the National Institute of Mental Health Intramural Research Program for Ted B. Usdin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue Dedicated to Miklós Palkovits.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobolyi, A., Irwin, S., Wang, J. et al. The Distribution and Neurochemistry of the Parathyroid Hormone 2 Receptor in the Rat Hypothalamus. Neurochem Res 31, 227–236 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-9011-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-9011-9
Keywords
- Parathyroid
- Hormone
- PTH2R
- Receptor
- Ligand
- Tuberoinfundibular
- Peptide
- TIP39
- Neuropeptide
- Hypothalamus
- Distribution
- Immunoreactivity
- Fluorescent
- Amplification
- Immunocytochemistry
- Immunolabeling
- Secretion
- Somatostatin
- Growth hormone releasing hormone
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone
- Corticotropin releasing hormone
- Arginine vasopressin
- Anatomical
- Double-labeling
- Release
- Fiber terminals
- Vesicular glutamate transporter
- Excitatory
- Median eminence
- Paraventricular
- Periventricular
- Arcuate
- Nucleus
- Preoptic
- Pituitary