Abstract
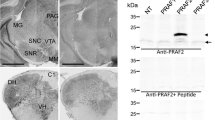
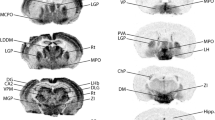
Protein kinase C interactive protein (PKCI; also known as histidine triad protein, HINT1) is a small intracellular protein widely expressed in tissues from both the peripheral and CNS. Although the structure of this protein is well characterized, the functional aspect and cellular distribution of the protein remain unknown, especially in CNS. To analyze the expression pattern of PKCI/HINT1 we used antibodies against either the whole recombinant protein or a peptide epitope of PKCI/HINT1. We find widespread of PKCI/HINT1 expression in the mouse CNS by Western blot and immunostaining. Our data indicates that PKCI/HINT1 is present broadly throughout the regions of CNS with relatively high abundance in olfactory system, cerebral cortex, hippocampus and part of thalamus, hypothalamus, midbrain, pons and medulla. On the cellular level, PKCI/HINT1 immunoreactivity is primarily located in neurons and neuronal processes. This study provides the anatomical evidence for the potential roles of PKCI/HINT1 in neuronal function.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3V:
-
3rd ventricle
- 4V:
-
4th ventricle
- 7n:
-
Facial nerve
- 7N:
-
Facial nucleus
- aca:
-
Anterior commissure, anterior part
- Acb:
-
Accumbens nucleus
- AHP:
-
Anterior hypothalamic area, posterior part
- AM:
-
Anteromedial nucleus
- AO:
-
Accessory olfactory bulb
- cc:
-
Corpus callosum
- Cc:
-
Central canal
- CGPn:
-
Central gray of pons
- Cor:
-
Cortex
- CPu:
-
Caudate putamen (striatum)
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DG:
-
Dentate gyrus
- EPL:
-
External plexiform layer (of olfactory blub)
- FrA:
-
Frontal association cortex
- Gi:
-
Gigantocellular reticular nucleus
- GL:
-
Glomerular layer (of olfactory bulb)
- Gr:
-
Gray matter
- GCL:
-
Granular layer (of olfactory bulb)
- hc:
-
Hippocampal commissure
- Inf coll:
-
Inferior colliculus
- IPL:
-
Internal plexiform layer
- LH:
-
Lateral hypothalamic area
- LMol:
-
Lacunosum molecular layer (of the hippocampus)
- lo:
-
Lateral olfactory tract
- LS:
-
Lateral septal nucleus
- LV:
-
Lateral ventricle
- M1:
-
Primary motor cortex
- M2:
-
Secondary motor cortex
- Med:
-
Medullary
- MCL:
-
Mitral cell layer (of olfactory bulb)
- ML:
-
Medial mammillary nucleus, lateral part
- MM:
-
Medial mammillary nucleus, medial part
- Mol:
-
Molecular layer
- MS:
-
Medial septal nucleus
- Or:
-
Oriens layer (of the hippocampus)
- Pir:
-
Piriform cortex
- PPy:
-
Parapyramidal nucleus
- Py:
-
Pyramidal cell layer (of the hippocampus)
- Rad:
-
Stratum radiatum (of the hippocampus)
- RSA:
-
Retrosplenial granular cortex
- S:
-
Subiculum
- S1:
-
Primary somatosensory cortex
- S2:
-
Secondary somatosensory cortex
- SCh:
-
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
- Sup coll:
-
Superior colliculus
- Tu:
-
Olfactory tubercle
- V2M:
-
Secondary visual cortex
- VMH:
-
Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus
- Wh:
-
White matter
References
Su T, Suzui M, Wang L, Lin CS, Xing WQ, Weinstein IB (2003) Deletion of histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1/PKC-interacting protein in mice enhances cell growth and carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:7824–7829
Klein MG, Yao Y, Slosberg ED, Lima CD, Doki Y, Weinstein IB (1998) Characterization of PKCI and comparative studies with FHIT, related members of the HIT protein family. Exp Cell Res 244:26–32
Lima CD, Klein MG, Weinstein IB, Hendrickson WA (1996) Three-dimensional structure of human protein kinase C interacting protein 1, a member of the HIT family of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5357–5362
Pearson JD, DeWald DB, Mathews WR, Mozier NM, Zurcher-Neely HA, Heinrikson RL, Morris MA, McCubbin WD, McDonald JR, Fraser ED (1990) Amino acid sequence and characterization of a protein inhibitor of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 265:4583–4591
McDonald JR, Walsh MP (1985) Ca2+-binding proteins from bovine brain including a potent inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem J 232:559–567
Fraser ED, Walsh MP (1991) The major endogenous bovine brain protein kinase C inhibitor is a heat-labile protein. FEBS Lett 294:285–289
Lima CD, Klein MG, Hendrickson WA (1997) Structure-based analysis of catalysis and substrate definition in the HIT protein family. Science 278:286–290
Lee JH, Cho ES, Kim MY, Seo YW, Kho DH, Chung IJ, Kook H, Kim NS, Ahn KY, Kim KK (2005) Suppression of progression and metastasis of established colon tumors in mice by intravenous delivery of short interfering RNA targeting KITENIN, a metastasis-enhancing protein. Cancer Res 65:8993–9003
Weiske J, Huber O (2005) The histidine triad protein Hint1 interacts with Pontin and Reptin and inhibits TCF-beta-catenin-mediated transcription. J Cell Sci 118:3117–3129
Razin E, Zhang ZC, Nechushtan H, Frenkel S, Lee YN, Arudchandran R, Rivera J (1999) Suppression of microphthalmia transcriptional activity by its association with protein kinase C-interacting protein 1 in mast cells. J Biol Chem 274:34272–34276
Korsisaari N, Makela TP (2000) Interactions of Cdk7 and Kin28 with Hint/PKCI-1 and Hnt1 histidine triad proteins. J Biol Chem 275:34837–34840
Choi EK, Rhee YH, Park HJ, Ahn SD, Shin KH, Park KK (2001) Effect of protein kinase C inhibitor (PKCI) on radiation sensitivity and c-fos transcription. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 49:397–405
Vawter MP, Crook JM, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR, Becker KG, Freed WJ (2002) Microarray analysis of gene expression in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: a preliminary study. Schizophr Res 58:11–20
Vawter MP, Shannon WC, Ferran E, Matsumoto M, Overman K, Hyde TM, Weinberger DR, Bunney WE, Kleinman JE (2004) Gene expression of metabolic enzymes and a protease inhibitor in the prefrontal cortex are decreased in schizophrenia. Neurochem Res 29:1245–1255
Guang W, Wang H, Su T, Weinstein IB, Wang JB (2004) Role of mPKCI, a novel mu-opioid receptor interactive protein, in receptor desensitization, phosphorylation, and morphine-induced analgesia. Mol Pharmacol 66:1285–1292
Puche AC, Heyward P, Shipley MT (2004) Transmembrane dye labeling and immunohistochemical staining of electrophysiologically characterized single neurons. J Neurosci Methods 137:235–240
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) The use of antiavidin antibody and avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex in immunoperoxidase technics. Am J Clin Pathol 75:816–821
Paxions G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Shipley MT, Ennis M, Puche AC (2004) Olfactory system. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system, 3ed edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 923–942
Parrish-Aungst S, Shipley MT, Erdelyi F, Szabo G, Puche AC (2007) Quantitative analysis of neuronal diversity in the mouse olfactory blub. J Comp Neurol 501:825–836
FitzGerald MJT, Folan-Curran J (2002) Hypothalamus, thalamus, epithalamus. In: Clinical neuroanatomy and related neuroscince. WB Saunders, London, pp 217–229
Martin JH (2003) Basal ganglia. In: Neuroanatomy text and atlas. McGraw-Hill, pp 327–329
Alheid GF, de Olmos JS, Beltramino CA (1995) Amygdala and extended amygdale. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 495–560
McDonald JR, Groschel-Stewart U, Walsh MP (1987) Properties and distribution of the protein inhibitor (Mr 17,000) of protein kinase C. Biochem J 242:695–705
Tanaka C, Saito N (1992) Localization of subspecies of protein kinase C in the mammalian central nervous system. Neurochem Int 21:499–512
Merchenthaler I, Liposits Z, Reid JJ, Wetsel WC (1993) Light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical localization of PKC delta immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 336:378–399
Saito N, Itouji A, Totani Y, Osawa I, Koide H, Fujisawa N, Ogita K, Tanaka C (1993) Cellular and intracellular localization of epsilon-subspecies of protein kinase C in the rat brain; presynaptic localization of the epsilon-subspecies. Brain Res 607:241–248
Saito N, Tsujino T, Fukuda K, Tanaka C (1994) Alpha-, beta II- and gamma-subspecies of protein kinase C localized in the monkey hippocampus: pre- and post-synaptic localization of gamma-subspecies. Brain Res 656:245–256
Wang H, Friedman E (2001) Increased association of brain protein kinase C with the receptor for activated C kinase-1 (RACK1) in bipolar affective disorder. Biol Psychiatry 50:364–370
Ajit SK, Ramineni S, Edris W, Hunt RA, Hum WT, Hepler JR, Young KH (2007) RGSZ1 interacts with protein kinase C interacting protein PKCI-1 and modulates mu opioid receptor signaling. Cell Signal 19:723–730
Tempel A, Zukin RS (1987) Neuroanatomical patterns of the mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors of rat brain as determined by quantitative in vitro autoradiography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4308–4312
Mansour A, Fox CA, Akil H, Watson SJ (1995) Opioid-receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: anatomical and functional implications. Trends Neurosci 18:22–29
Moriwaki A, Wang JB, Svingos A, van Bockstaele E, Cheng P, Pickel V, Uhl GR (1996) mu Opiate receptor immunoreactivity in rat central nervous system. Neurochem Res 21:1315–1331
Lewis DA, Lieberman JA (2000) Catching up on schizophrenia: natural history and neurobiology. Neuron 28:325–334
Seeman P (1987) Dopamine receptors and the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Synapse 1:133–152
Ongali B, Ase AR, Hebert C, Amdiss F, Reader TA (2000) Dopamine D(1) and D(2) receptors in the forebrain of dystonia musculorum mutant mice: an autoradiographic survey in relation to dopamine contents. Synapse 37:1–15
Reader TA, Ase AR, Hebert C, Amdiss F (1999) Distribution of dopamine, its metabolites, and D1 and D2 receptors in heterozygous and homozygous weaver mutant mice. Neurochem Res 24:1455–1470
Barbier E, Zapata A, Oh E, Liu Q, Zhu F, Undie A, Shippenberg T, Wang JB (2007) Supersensitivity to amphetamine in protein kinase-C interacting protein/HINT1 knockout mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(8):1774–1782
Kawaguchi Y, Kondo S (2002) Parvalbumin, somatostatin and cholecystokinin as chemical markers for specific GABAergic interneuron types in the rat frontal cortex. J Neurocytol 31:277–287
Alreja M, Shanabrough M, Liu W, Leranth C (2000) Opioids suppress IPSCs in neurons of the rat medial septum/diagonal band of Broca: involvement of mu-opioid receptors and septohippocampal GABAergic neurons. J Neurosci 20:1179–1189
McQuiston AR (2007) Effects of mu-opioid receptor modulation on GABAB receptor synaptic function in hippocampal CA1. J Neurophysiol 97:2301–2311
Steffensen SC, Stobbs SH, Colago EE, Lee RS, Koob GF, Gallegos RA, Henriksen SJ (2006) Contingent and non-contingent effects of heroin on mu-opioid receptor-containing ventral tegmental area GABA neurons. Exp Neurol 202:139–151
Svingos AL, Moriwaki A, Wang JB, Uhl GR, Pickel VM (1997) mu-Opioid receptors are localized to extrasynaptic plasma membranes of GABAergic neurons and their targets in the rat nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 17:2585–2594
Kalyuzhny AE, Wessendorf MW (1997) CNS GABA neurons express the mu-opioid receptor: immunocytochemical studies. Neuroreport 8:3367–3372
Kalyuzhny AE, Wessendorf MW (1998) Relationship of mu- and delta-opioid receptors to GABAergic neurons in the central nervous system, including antinociceptive brainstem circuits. J Comp Neurol 392:528–547
Stumm RK, Zhou C, Schulz S, Hollt V (2004) Neuronal types expressing mu- and delta-opioid receptor mRNA in the rat hippocampal formation. J Comp Neurol 469:107–118
Berghuis P, Dobszay MB, Ibanez RM, Ernfors P, Harkany T (2004) Turning the heterogeneous into homogeneous: studies on selectively isolated GABAergic interneuron subsets. Int J Dev Neurosci 22:533–543
Gupta A, Wang Y, Markram H (2000) Organizing principles for a diversity of GABAergic interneurons and synapses in the neocortex. Science 287:273–278
Weiske J, Huber O (2006) The histidine triad protein Hint1 triggers apoptosis independent of its enzymatic activity. J Biol Chem 281:27356–27366
Acknowledgments
Support for this work was provided by grants from NIDA/NIH to J.B. Wang (DA11925; DA018722). We thank Dr. I.B. Weinstein from Columbia University for providing PKCI/HINT1 KO mice and anti-hPKCI/HINT1 antibody.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Puche, A.C. & Wang, J.B. Distribution and Expression of Protein Kinase C Interactive Protein (PKCI/HINT1) in Mouse Central Nervous System (CNS). Neurochem Res 33, 1263–1276 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9578-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9578-4