Abstract
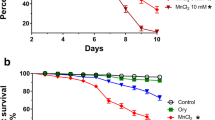
In this paper, we have demonstrated for the first time, the antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of Decalepis hamiltonii (Dh) root extract against paraquat (PQ)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Exposure of adult D. melanogaster (Oregon K) to PQ induced oxidative stress as evidenced by glutathione depletion, lipid peroxidation and enhanced activities of antioxidant enzymes such as catalase, superoxide dismutase as well as elevated levels of acetylcholine esterase. Pretreatment of flies by feeding with Dh extract (0.1, 0.5 %) for 14 days boosted the activities of antioxidant enzymes and prevented the PQ-induced oxidative stress. Dietary feeding of Dh extract prior to PQ exposure showed a lower incidence of mortality and enhanced motor activities of flies in a negative geotaxis assay; both suggesting the neuroprotective potential of Dh. Based on the results, we contemplate that the roots of Dh might prevent and ameliorate the human diseases caused by oxidative stress. The neuroprotective action of Dh can be attributed to the antioxidant constituents while the precise mechanism of its action needs further investigations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames BN (1989) Endogenous oxidative DNA damage, aging, and cancer. Free Radic Res 7:121–128
Jenner P (2003) Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53:S26–S38
Sau D, De Biasi S, Vitellaro-Zuccarello L, Riso P, Guarnieri S et al (2007) Mutation of SOD1 in ALS: a gain of a loss of function. Hum Mol Genet 16:1604–1618
Trushina E, McMurray C (2007) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Neuroscience 145:1233–1248
Chaudhuri A, Bowling K, Funderburk C, Lawal H, Inamdar A et al (2007) Interaction of genetic and environmental factors in a Drosophila parkinsonism model. J Neurosci 27:2457–2467
Kuter K, Śmiałowska M, Wierońska J, Zięba B, Wardas J et al (2007) Toxic influence of subchronic paraquat administration on dopaminergic neurons in rats. Brain Res 1155:196–207
Prasad K, Tarasewicz E, Mathew J, Strickland PAO, Buckley B et al (2009) Toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics of paraquat accumulation in mouse brain. Exp Neurol 215:358–367
Suntres ZE (2002) Role of antioxidants in paraquat toxicity. Toxicology 180:65–77
Halliwell B (2006) Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: where are we now? J Neurochem 97:1634–1658
Shimizu K, Matsubara K, Ohtaki K, Fujimaru S, Saito O et al (2003) Paraquat induces long-lasting dopamine overflow through the excitotoxic pathway in the striatum of freely moving rats. Brain Res 976:243–252
Yumino K, Kawakami I, Tamura M, Hayashi T, Nakamura M (2002) Paraquat-and diquat-induced oxygen radical generation and lipid peroxidation in rat brain microsomes. J Biochem 131:565–570
Bilen J, Bonini NM (2005) Drosophila as a model for human neurodegenerative disease. Annu Rev Genet 39:153–171
Dinis-Oliveira R, Remiao F, Carmo H, Duarte J, Navarro AS et al (2006) Paraquat exposure as an etiological factor of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 27:1110–1122
Hosamani R, Ramesh SR (2010) Attenuation of rotenone-induced mitochondrial oxidative damage and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster supplemented with creatine. Neurochem Res 35:1402–1412
Inamdar AA, Chaudhuri A, O’Donnell J (2012) The protective effect of minocycline in a paraquat-induced Parkinson’s disease model in Drosophila is modified in altered genetic backgrounds. Parkinson’s Dis 2012:938528
Halliwell B, Rafter J, Jenner A (2005) Health promotion by flavonoids, tocopherols, tocotrienols, and other phenols: direct or indirect effects? Antioxidant or not? Am J Clin Nutr 81:268S–276S
Havsteen BH (2002) The biochemistry and medical significance of the flavonoids. Pharmacol Ther 96:67–202
Nayar R, Shetty JKP, Mary Z, Yoganarasimhan S (1978) Pharmacognostical studies on the root of Decalepis hamiltonii Wt. and Arn., and comparison with Hemidesmus indicus (L.) R. Br Proc Plant Sci 87:37–48
Harish R, Divakar S, Srivastava A, Shivanandappa T (2005) Isolation of antioxidant compounds from the methanolic extract of the roots of Decalepis hamiltonii (Wight and Arn.). J Agric Food Chem 53:7709–7714
Srivastava A, Harish R, Shivanandappa T (2006) Novel antioxidant compounds from the aqueous extract of the roots of Decalepis hamiltonii (Wight and Arn.) and their inhibitory effect on low-density lipoprotein oxidation. J Agric Food Chem 54:790–795
Srivastava A, Shivanandappa T (2011) Antioxidant and cytoprotective properties of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-3-methoxybenzaldehyde. Food Chem 128:458–464
Srivastava A, Harish SR, Shivanandappa T (2006) Antioxidant activity of the roots of Decalepis hamiltonii (Wight & Arn.). LWT-Food Sci Technol 39:1059–1065
Srivastava A, Shivanandappa T (2010) Neuroprotective effect of Decalepis hamiltonii roots against ethanol-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem 119:626–629
Srivastava A, Shivanandappa T (2006) Hepatoprotective effect of the aqueous extract of the roots of Decalepis hamiltonii against ethanol-induced oxidative stress in rats. Hepatol Res 35:267–275
Tanimura T, Isono K, Takamura T, Shimada I (1982) Genetic dimorphism in the taste sensitivity to trehalose in Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Physiol 147:433–437
Feany MB, Bender WW (2000) A Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 404:394–398
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Meth Enzymol 105:121–126
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Hissin PJ (1976) A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Biochem 74:214–226
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Wilson DM, Sofinowski TM, McNeill DR (2003) Repair mechanisms for oxidative DNA damage. Front Biosci 8:d963–d981
Ballard PA, Tetrud JW, Langston JW (1985) Permanent human parkinsonism due to 1-methy 1-4-phenyl-1, 2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) Seven cases. Neurology 35:949–956
Arking R, Buck S, Berrios A, Dwyer S, Baker GT III (1991) Elevated paraquat resistance can be used as a bioassay for longevity in a genetically based long-lived strain of Drosophila. Dev Genet 12:362–370
Mohammadi-Bardbori A, Ghazi-Khansari M (2008) Alternative electron acceptors: proposed mechanism of paraquat mitochondrial toxicity. Environ Toxicol Pharm 26:1–5
Berry C, La Vecchia C, Nicotera P (2010) Paraquat and Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Differ 17:1115–1125
Pienaar IS, Götz J, Feany MB (2010) Parkinson’s disease: insights from non-traditional model organisms. Prog Neurobiol 92:558–571
Park JH, Jung JW, Ahn YJ, Kwon HW (2012) Neuroprotective properties of phytochemicals against paraquat-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Pestic Biochem Phys 104:118–125
Hosamani R (2009) Neuroprotective efficacy of Bacopa monnieri against rotenone induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Neurotoxicology 30:977–985
Li YM, Chan HYE, Huang Y, Chen ZY (2007) Green tea catechins upregulate superoxide dismutase and catalase in fruit flies. Mol Nutr Food Res 51:546–554
Peng C, Zuo Y, Kwan KM, Liang Y, Ma KY, et al. (2011) Blueberry extract prolongs lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster. Exp Gerontol 47:170–178
Schmatz R, Mazzanti CM, Spanevello R, Stefanello N, Gutierres J, Corrêa M et al (2009) Resveratrol prevents memory deficits and the increase in acetylcholinesterase activity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 610:42–48
Bernhardi R, Alarcon R, Mezzano D, Fuentes P, Inestrosa NC (2005) Blood cells cholinesterase activity in early stage Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 19:204–212
Jin Q, He H, Shi Y, Lu H, Zhang X (2004) Overexpression of acetylcholinesterase inhibited cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis in NRK cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25:1013–1021
Elufioye TO, Obuotor EM, Sennuga AT, Agbedahunsi JM, Adesanya SA (2010) Acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of some selected Nigerian medicinal plants. Rev Bras Farm 20:472–477
Pillay R, Maharaj DS, Daniel S, Daya S (2003) Acetylcholine reduces cyanide-induced superoxide anion generation and lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenates. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psych 27:61–64
Melo JB, Agostinho P, Oliveira CR (2003) Involvement of oxidative stress in the enhancement of acetylcholinesterase activity induced by amyloid beta-peptide. Neurosci Res 45:117–127
Girish C, Muralidhara (2012) Propensity of Selaginella delicatula aqueous extract to offset rotenone-induced oxidative dysfunctions and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 33:444–456
Prasad SN, Muralidhara (2012) Evidence of acrylamide induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster: Its amelioration with spice active enrichment: relevance to neuropathy. Neurotoxicology 33:1254–1264
Haddadi M, Jahromi SR, Shivanandappa T, Ramesh S (2013) Decalepis hamiltonii root extract attenuates the age-related decline in the cognitive function in Drosophila melanogaster. Behav Brain Res 249:8–14
Srivastava A, Jagan Mohan Rao L, Shivanandappa T (2012) 2, 4, 8-trihydroxybicyclo [3.2. 1] octan-3-one scavenges free radicals and protects against xenobiotic-induced cytotoxicity. Free Radic Res 46:320–328
Acknowledgments
We thank the Chairman, Department of Studies in Zoology, University of Mysore, for the facilities.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahromi, S.R., Haddadi, M., Shivanandappa, T. et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Decalepis hamiltonii in Paraquat-Induced Neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster: Biochemical and Behavioral Evidences. Neurochem Res 38, 2616–2624 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1179-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1179-9