Abstract
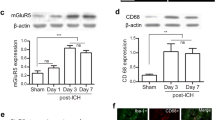
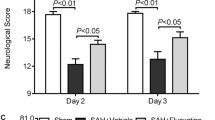
Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) provided neuroprotection in multiple central nervous system injury, but the roles of mGluR5 in subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) remain unclear. In present study, we aimed to evaluate whether activation of mGluR5 attenuates early brain injury (EBI) after experimental SAH in rats. We found that selective mGluR5 orthosteric agonist CHPG or positive allosteric modulator VU0360172 administration significantly improves neurological function and attenuates brain edema at 24 h after SAH. Furthermore, mGluR5 obviously expresses in activated microglia (ED-1 positive) after SAH. CHPG or VU0360172 administration significantly reduces the numbers of activated microglia and the protein and mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α at 24 h after SAH. Moreover, CHPG or VU0360172 administration obviously reduces the number of TUNEL-positive cells and active caspase-3/NeuN-positive neurons in cortex at 24 h after SAH. CHPG or VU0360172 administration significantly up-regulates the expression of Bcl-2, and down-regulates the expression of Bax and active caspase-3, which in turn increases the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax. Our results indicate that activation of mGluR5 attenuates microglial activation and neuronal apoptosis, and improves neurological function in EBI after SAH.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Macdonald RL (2014) Delayed neurological deterioration after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Nat Rev Neurol 10:44–58
Sehba FA, Hou J, Pluta RM, Zhang JH (2012) The importance of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Prog Neurobiol 97:14–37
Fujii M, Yan J, Rolland WB, Soejima Y, Caner B, Zhang JH (2013) Early brain injury, an evolving frontier in subarachnoid hemorrhage research. Transl Stroke Res 4:432–446
Chen S, Feng H, Sherchan P, Klebe D, Zhao G, Sun X, Zhang J, Tang J, Zhang JH (2014) Controversies and evolving new mechanisms in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Prog Neurobiol 115:64–91
Niswender CM, Conn PJ (2010) Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:295–322
Huang S, Cao J, Jiang M, Labesse G, Liu J, Pin JP, Rondard P (2011) Interdomain movements in metabotropic glutamate receptor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:15480–15485
Bao WL, Williams AJ, Faden AI, Tortella FC (2001) Selective mGluR5 receptor antagonist or agonist provides neuroprotection in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 922:173–179
Byrnes KR, Stoica B, Riccio A, Pajoohesh-Ganji A, Loane DJ, Faden AI (2009) Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 improves recovery after spinal cord injury in rodents. Ann Neurol 66:63–74
Byrnes KR, Loane DJ, Stoica BA, Zhang J, Faden AI (2012) Delayed mGluR5 activation limits neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration after traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation 9:43
Chen T, Zhang L, Qu Y, Huo K, Jiang X, Fei Z (2012) The selective mGluR5 agonist CHPG protects against traumatic brain injury in vitro and in vivo via ERK and Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med 29:630–636
Chen T, Cao L, Dong W, Luo P, Liu W, Qu Y, Fei Z (2012) Protective effects of mGluR5 positive modulators against traumatic neuronal injury through PKC-dependent activation of MEK/ERK pathway. Neurochem Res 37:983–990
Loane DJ, Stoica BA, Byrnes KR, Jeong W, Faden AI (2013) Activation of mGluR5 and inhibition of NADPH oxidase improves functional recovery after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 30:403–412
Wang JW, Wang HD, Cong ZX, Zhang XS, Zhou XM, Zhang DD (2013) Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 reduces the secondary brain injury after traumatic brain injury in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 430:1016–1021
Xu X, Zhang J, Chen X, Liu J, Lu H, Yang P, Xiao X, Zhao L, Jiao Q, Zhao B, Zheng P, Liu Y (2012) The increased expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in subventricular zone neural progenitor cells and enhanced neurogenesis in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Neuroscience 202:474–483
Loane DJ, Stoica BA, Tchantchou F, Kumar A, Barrett JP, Akintola T, Xue F, Conn PJ, Faden AI (2014) Novel mGluR5 positive allosteric modulator improves functional recovery, attenuates neurodegeneration, and alters microglial polarization after experimental traumatic brain injury. Neurother J Am Soc Exp NeuroTher 11:857–869
Movsesyan VA, Stoica BA, Faden AI (2004) MGLuR5 activation reduces beta-amyloid-induced cell death in primary neuronal cultures and attenuates translocation of cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor. J Neurochem 89:1528–1536
Zhu P, DeCoster MA, Bazan NG (2004) Interplay among platelet-activating factor, oxidative stress, and group I metabotropic glutamate receptors modulates neuronal survival. J Neurosci Res 77:525–531
Dai SH, Qin N, Chen T, Luo P, Zhang L, Rao W, Yang YF, Jiang XF, Fei Z (2014) Activation of mGluR5 attenuates NMDA-induced neurotoxicity through disruption of the NMDAR-PSD-95 complex and preservation of mitochondrial function in differentiated PC12 cells. Int J Mol Sci 15:10892–10907
Loane DJ, Stoica BA, Pajoohesh-Ganji A, Byrnes KR, Faden AI (2009) Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 modulates microglial reactivity and neurotoxicity by inhibiting NADPH oxidase. J Biol Chem 284:15629–15639
Byrnes KR, Stoica B, Loane DJ, Riccio A, Davis MI, Faden AI (2009) Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 activation inhibits microglial associated inflammation and neurotoxicity. Glia 57:550–560
Sugawara T, Ayer R, Jadhav V, Zhang JH (2008) A new grading system evaluating bleeding scale in filament perforation subarachnoid hemorrhage rat model. J Neurosci Methods 167:327–334
Chen S, Ma Q, Krafft PR, Chen Y, Tang J, Zhang J, Zhang JH (2013) P2X7 receptor antagonism inhibits p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and ameliorates neuronal apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Crit Care Med 41:e466–e474
Zhang Z, Yang M, Wang T, Li D, Liu Y, Zhang J, Sun B (2015) Cysteamine alleviates early brain injury via reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis in a rat experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage model. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35:543–553
Zhang ZY, Sun BL, Yang MF, Li DW, Fang J, Zhang S (2015) Carnosine attenuates early brain injury through its antioxidative and anti-apoptotic effects in a rat experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage model. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35:147–157
Hanafy KA (2013) The role of microglia and the TLR4 pathway in neuronal apoptosis and vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation 10:83
Plog BA, Moll KM, Kang H, Iliff JJ, Dashnaw ML, Nedergaard M, Vates GE (2014) A novel technique for morphometric quantification of subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced microglia activation. J Neurosci Methods 229:44–52
Rodriguez AL, Grier MD, Jones CK, Herman EJ, Kane AS, Smith RL, Williams R, Zhou Y, Marlo JE, Days EL, Blatt TN, Jadhav S, Menon UN, Vinson PN, Rook JM, Stauffer SR, Niswender CM, Lindsley CW, Weaver CD, Conn PJ (2010) Discovery of novel allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 reveals chemical and functional diversity and in vivo activity in rat behavioral models of anxiolytic and antipsychotic activity. Mol Pharmacol 78:1105–1123
Noetzel MJ, Rook JM, Vinson PN, Cho HP, Days E, Zhou Y, Rodriguez AL, Lavreysen H, Stauffer SR, Niswender CM, Xiang Z, Daniels JS, Jones CK, Lindsley CW, Weaver CD, Conn PJ (2012) Functional impact of allosteric agonist activity of selective positive allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 in regulating central nervous system function. Mol Pharmacol 81:120–133
Lea IV PM, Movsesyan VA, Faden AI (2005) Neuroprotective activity of the mGluR5 antagonists MPEP and MTEP against acute excitotoxicity differs and does not reflect actions at mGluR5 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 145:527–534
Caraci F, Battaglia G, Sortino MA, Spampinato S, Molinaro G, Copani A, Nicoletti F, Bruno V (2012) Metabotropic glutamate receptors in neurodegeneration/neuroprotection: still a hot topic? Neurochem Int 61:559–565
Drouin-Ouellet J, Brownell AL, Saint-Pierre M, Fasano C, Emond V, Trudeau LE, Levesque D, Cicchetti F (2011) Neuroinflammation is associated with changes in glial mGluR5 expression and the development of neonatal excitotoxic lesions. Glia 59:188–199
Byrnes KR, Loane DJ, Faden AI (2009) Metabotropic glutamate receptors as targets for multipotential treatment of neurological disorders. Neurother J Am Soc Exp NeuroTher 6:94–107
Allen JW, Knoblach SM, Faden AI (2000) Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors reduces neuronal apoptosis but increases necrotic cell death in vitro. Cell Death Differ 7:470–476
Willis S, Day CL, Hinds MG, Huang DC (2003) The Bcl-2-regulated apoptotic pathway. J Cell Sci 116:4053–4056
Chen J, Wang L, Wu C, Hu Q, Gu C, Yan F, Li J, Yan W, Chen G (2014) Melatonin-enhanced autophagy protects against neural apoptosis via a mitochondrial pathway in early brain injury following a subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Pineal Res 56:12–19
Hong Y, Shao A, Wang J, Chen S, Wu H, McBride DW, Wu Q, Sun X, Zhang J (2014) Neuroprotective effect of hydrogen-rich saline against neurologic damage and apoptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage: possible role of the Akt/GSK3beta signaling pathway. PLoS one 9:e96212
Acknowledgments
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 81301018, No. 81271275 and No. 31100548) supported this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zong-yong Zhang and Bao-liang Sun have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Zy., Sun, Bl., Liu, Jk. et al. Activation of mGluR5 Attenuates Microglial Activation and Neuronal Apoptosis in Early Brain Injury After Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats. Neurochem Res 40, 1121–1132 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1572-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1572-7