Abstract
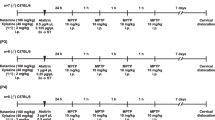
The etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease (PD) are complicated and have not been fully elucidated, but an important association has been identified between inflammation and PD. In this study, we investigated the role of the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine rich repeat and pyrin domain-containing (NLRP) 3 inflammasome, consisting of NLRP3, caspase-1 and cytokines of the IL-1 family, in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced and 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced PD rats. Microinjection of different doses of caspase-1 inhibitor (Ac-YVAD-CMK, 300 or 1200 ng/rat) was performed for seven consecutive days. Then, rotational behavior, the number of dopamine (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc), and the mRNA and protein expression levels of NLRP3 inflammasome components were measured 14 days after the microinjection setup was established. Results showed that high mRNA and protein expression levels of NLRP3 inflammasome components were observed in the injected side of the LPS- and 6-OHDA-induced PD rats; Ac-YVAD-CMK inhibited the mRNA and protein expression of NLRP3 inflammasome components in both LPS- and 6-OHDA-induced PD rats. Moreover, the number of rotations was significantly decreased, and the number of DA neurons in the SNc improved. Our data indicate that the NLRP3 inflammasome participates in the pathogenesis of PD and that inhibiting the downstream pathway of the NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β axis can alleviate the occurrence of PD symptoms, providing a new basis for the prevention and treatment of PD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- NLRP3:
-
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine rich repeat and pyrin domain-containing 3
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- 6-OHDA:
-
6-Hydroxydopamine
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- TH:
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase
- SNc:
-
Substantia nigra pars compacta
- ASC:
-
Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein
- MPTP:
-
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- SD:
-
Sprague–Dawley
- AP:
-
Anterior-posterior
- ML:
-
Medial–lateral
- DV:
-
Dorsal–ventral
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- mtDNA:
-
Mitochondrial DNA
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- ICV:
-
Intracerebroventricular
References
de Lau LM, Breteler MM (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5:525–535
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Bartels AL, Leenders KL (2007) Neuroinflammation in the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease: evidence from animal models to human in vivo studies with [11C]-PK11195 PET. Mov Disord 22:1852–1856
Monahan AJ, Warren M, Carvey PM (2008) Neuroinflammation and peripheral immune infiltration in Parkinson’s disease: an autoimmune hypothesis. Cell Transplant 17:363–372
Hirsch EC, Vyas S, Hunot S (2012) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18:70065–70067
Worlitzer MM, Bunk EC, Hemmer K, Schwamborn JC (2012) Anti-inflammatory treatment induced regenerative oligodendrogenesis in parkinsonian mice. Stem Cell Res Ther 3:33
Bauernfeind F, Ablasser A, Bartok E, Kim S, Schmid-Burgk J, Cavlar T, Hornung V (2011) Inflammasomes: current understanding and open questions. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:765–783
Tran TH, Pham JT, Shafeeq H, Manigault KR, Arya V (2013) Role of interleukin-1 inhibitors in the management of gout. Pharmacotherapy 33:744–753
Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I, Tschopp J (2010) Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol 11:136–140
Halle A, Hornung V, Petzold GC, Stewart CR, Monks BG, Reinheckel T, Fitzgerald KA, Latz E, Moore KJ, Golenbock DT (2008) The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate immune response to amyloid-beta. Nat Immunol 9:857–865
Li X, Zhang Y, Xia M, Gulbins E, Boini KM, Li PL (2014) Activation of Nlrp3 inflammasomes enhances macrophage lipid-deposition and migration: implication of a novel role of inflammasome in atherogenesis. PLoS One 9:e87552
Codolo G, Plotegher N, Pozzobon T, Brucale M, Tessari I, Bubacco L, de Bernard M (2013) Triggering of inflammasome by aggregated alpha-synuclein, an inflammatory response in synucleinopathies. PLoS One 8:31
Lu M, Sun XL, Qiao C, Liu Y, Ding JH, Hu G (2014) Uncoupling protein 2 deficiency aggravates astrocytic endoplasmic reticulum stress and nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome activation. Neurobiol Aging 35:421–430
Yan Y, Jiang W, Liu L, Wang X, Ding C, Tian Z, Zhou R (2015) Dopamine controls systemic inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell 160:62–73
Koprich JB, Reske-Nielsen C, Mithal P, Isacson O (2008) Neuroinflammation mediated by IL-1beta increases susceptibility of dopamine neurons to degeneration in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 5:1742–2094
Pott Godoy MC, Tarelli R, Ferrari CC, Sarchi MI, Pitossi FJ (2008) Central and systemic IL-1 exacerbates neurodegeneration and motor symptoms in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131:1880–1894
Griffin WS, Liu L, Li Y, Mrak RE, Barger SW (2006) Interleukin-1 mediates Alzheimer and Lewy body pathologies. J Neuroinflammation 3:5
Zhang F, Wang L, Wang JJ, Luo PF, Wang XT, Xia ZF (2016) The caspase-1 inhibitor AC-YVAD-CMK attenuates acute gastric injury in mice: involvement of silencing NLRP3 inflammasome activities. Sci Rep 6:24166
Watson C (2004) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates-the new coronal set. Academic Press, Boston
Hoban DB, Connaughton E, Connaughton C, Hogan G, Thornton C, Mulcahy P, Moloney TC, Dowd E (2013) Further characterisation of the LPS model of Parkinson’s disease: a comparison of intra-nigral and intra-striatal lipopolysaccharide administration on motor function, microgliosis and nigrostriatal neurodegeneration in the rat. Brain Behav Immun 27:91–100
Sarre S, Yuan H, Jonkers N, Van Hemelrijck A, Ebinger G, Michotte Y (2004) In vivo characterization of somatodendritic dopamine release in the substantia nigra of 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. J Neurochem 90:29–39
Liang C, Xu Y, Zheng D, Sun X, Xu Q, Duan D (2016) RNAi-mediated silencing of HLA A2 suppressed acute rejection against human fibroblast xenografts in the striatum of 6-OHDA lesioned rats. J Neuroimmunol 297:28–37
Lundblad M, Andersson M, Winkler C, Kirik D, Wierup N, Cenci MA (2002) Pharmacological validation of behavioural measures of akinesia and dyskinesia in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurosci 15:120–132
Chakraborty S, Kaushik DK, Gupta M, Basu A (2010) Inflammasome signaling at the heart of central nervous system pathology. J Neurosci Res 88:1615–1631
Macchi B, Di Paola R, Marino-Merlo F, Felice MR, Cuzzocrea S, Mastino A (2015) Inflammatory and cell death pathways in brain and peripheral blood in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 14:313–324
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J, Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, Jacobs AH, Wyss-Coray T, Vitorica J, Ransohoff RM, Herrup K, Frautschy SA, Finsen B, Brown GC, Verkhratsky A, Yamanaka K, Koistinaho J, Latz E, Halle A, Petzold GC, Town T, Morgan D, Shinohara ML, Perry VH, Holmes C, Bazan NG, Brooks DJ, Hunot S, Joseph B, Deigendesch N, Garaschuk O, Boddeke E, Dinarello CA, Breitner JC, Cole GM, Golenbock DT, Kummer MP (2015) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 14:388–405
Moon JS, Hisata S, Park MA, DeNicola GM, Ryter SW, Nakahira K, Choi AM (2015) mTORC1-induced HK1-dependent glycolysis regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Rep 12:102–115
Gao HM, Zhang F, Zhou H, Kam W, Wilson B, Hong JS (2011) Neuroinflammation and alpha-synuclein dysfunction potentiate each other, driving chronic progression of neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Environ Health Perspect 119:807–814
Hargus G, Cooper O, Deleidi M, Levy A, Lee K, Marlow E, Yow A, Soldner F, Hockemeyer D, Hallett PJ, Osborn T, Jaenisch R, Isacson O (2010) Differentiated Parkinson patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells grow in the adult rodent brain and reduce motor asymmetry in Parkinsonian rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:15921–15926
Kim WG, Mohney RP, Wilson B, Jeohn GH, Liu B, Hong JS (2000) Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: role of microglia. J Neurosci 20:6309–6316
Shimada K, Crother TR, Karlin J, Dagvadorj J, Chiba N, Chen S, Ramanujan VK, Wolf AJ, Vergnes L, Ojcius DM, Rentsendorj A, Vargas M, Guerrero C, Wang Y, Fitzgerald KA, Underhill DM, Town T, Arditi M (2012) Oxidized mitochondrial DNA activates the NLRP3 inflammasome during apoptosis. Immunity 36:401–414
Chen Y, Dorn GW 2nd (2013) PINK1-phosphorylated mitofusin 2 is a Parkin receptor for culling damaged mitochondria. Science 340:471–475
Dostert C, Petrilli V, Van Bruggen R, Steele C, Mossman BT, Tschopp J (2008) Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science 320:674–677
Mortiboys H, Johansen KK, Aasly JO, Bandmann O (2010) Mitochondrial impairment in patients with Parkinson disease with the G2019S mutation in LRRK2. Neurology 75:2017–2020
McCoy MK, Cookson MR (2011) DJ-1 regulation of mitochondrial function and autophagy through oxidative stress. Autophagy 7:531–532
Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Youle RJ (2008) Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol 183:795–803
Demento SL, Eisenbarth SC, Foellmer HG, Platt C, Caplan MJ, Mark Saltzman W, Mellman I, Ledizet M, Fikrig E, Flavell RA, Fahmy TM (2009) Inflammasome-activating nanoparticles as modular systems for optimizing vaccine efficacy. Vaccine 27:3013–3021
Irrcher I, Aleyasin H, Seifert EL, Hewitt SJ, Chhabra S, Phillips M, Lutz AK, Rousseaux MW, Bevilacqua L, Jahani-Asl A, Callaghan S, MacLaurin JG, Winklhofer KF, Rizzu P, Rippstein P, Kim RH, Chen CX, Fon EA, Slack RS, Harper ME, McBride HM, Mak TW, Park DS (2010) Loss of the Parkinson’s disease-linked gene DJ-1 perturbs mitochondrial dynamics. Hum Mol Genet 19:3734–3746
Shimura H, Hattori N, Kubo S, Mizuno Y, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Iwai K, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Suzuki T (2000) Familial Parkinson disease gene product, parkin, is a ubiquitin-protein ligase. Nat Genet 25:302–305
Mayor A, Martinon F, De Smedt T, Petrilli V, Tschopp J (2007) A crucial function of SGT1 and HSP90 in inflammasome activity links mammalian and plant innate immune responses. Nat Immunol 8:497–503
Bernardino L, Xapelli S, Silva AP, Jakobsen B, Poulsen FR, Oliveira CR, Vezzani A, Malva JO, Zimmer J (2005) Modulator effects of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on AMPA-induced excitotoxicity in mouse organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. J Neurosci 25:6734–6744
Tong L, Balazs R, Soiampornkul R, Thangnipon W, Cotman CW (2008) Interleukin-1 beta impairs brain derived neurotrophic factor-induced signal transduction. Neurobiol Aging 29:1380–1393
Coll RC, Robertson AA, Chae JJ, Higgins SC, Munoz-Planillo R, Inserra MC, Vetter I, Dungan LS, Monks BG, Stutz A, Croker DE, Butler MS, Haneklaus M, Sutton CE, Nunez G, Latz E, Kastner DL, Mills KH, Masters SL, Schroder K, Cooper MA, O’Neill LA (2015) A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat Med 21:248–255
Goldbach-Mansky R (2009) Blocking interleukin-1 in rheumatic diseases. Ann NY Acad Sci 1182:111–123
Rubbert-Roth A, Perniok A (2003) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist anakinra (Kineret) for treatment of rheumatic arthritis. Z Rheumatol 62:367–377
Akash MS, Shen Q, Rehman K, Chen S (2012) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: a new therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pharm Sci 101:1647–1658
Imeri L, Bianchi S, Opp MR (2006) Inhibition of caspase-1 in rat brain reduces spontaneous nonrapid eye movement sleep and nonrapid eye movement sleep enhancement induced by lipopolysaccharide. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 291:2
Schierle GS, Hansson O, Leist M, Nicotera P, Widner H, Brundin P (1999) Caspase inhibition reduces apoptosis and increases survival of nigral transplants. Nat Med 5:97–100
House SD, Mao X, Wu G, Espinelli D, Li WX, Chang SL (2001) Chronic morphine potentiates the inflammatory response by disrupting interleukin-1beta modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. J Neuroimmunol 118:277–285
Eda H, Shimada H, Beidler DR, Monahan JB (2011) Proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1beta and TNF-alpha, induce expression of interleukin-34 mRNA via JNK- and p44/42 MAPK-NF-kappaB pathway but not p38 pathway in osteoblasts. Rheumatol Int 31:1525–1530
Seki E, Tsutsui H, Nakano H, Tsuji N, Hoshino K, Adachi O, Adachi K, Futatsugi S, Kuida K, Takeuchi O, Okamura H, Fujimoto J, Akira S, Nakanishi K (2001) Lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-18 secretion from murine Kupffer cells independently of myeloid differentiation factor 88 that is critically involved in induction of production of IL-12 and IL-1beta. J Immunol 166:2651–2657
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number No. 30700244) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Grant Number 2012FFB02501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Z., Liu, C., Ji, S. et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease in Rats. Neurochem Res 42, 1104–1115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2185-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2185-0