Abstract
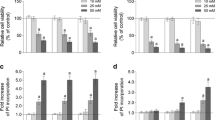
Glutamate uptake is a main function of astrocytes to keep extracellular glutamate levels low and protect neurons against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. On the other hand, astrocyte networks formed by gap junctions, which are consisted with connexins and connecting neighboring cells, are reported to play a critical role in maintaining the homeostasis in the brain. In the present study, we examined the effects of gap junction inhibitors on the glutamate uptake activity in cultured rat cortical astrocytes. At first, we confirmed the effects of gap junction inhibitors, 1-octanol and carbenoxolone, on cell–cell communication by the scrape-loading assay using a fluorescent dye Lucifer yellow. Both of 1-octanol and carbenoxolone treatments for 20 min in cultured astrocytes significantly suppressed the cell–cell communication assessed as the distance of dye-spreading. 1-octanol and carbenoxolone increased the glutamate uptake by astrocytes and glutamate aspartate transporter (GLAST) expression on the cell membrane. These results suggest that gap junction inhibitors increase the glutamate uptake activity through the increase of GLAST proteins located on the cell membrane. The regulation of gap junction in astrocytes might protect neurons against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- Cx:
-
Connexin
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- HHBSS:
-
HEPES-buffered Hank’s balanced salt solution
- HKR:
-
HEPES-buffered Krebs Ringer solution
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
References
Abbott NJ (2002) Astrocyte-endothelial interactions and blood-brain barrier permeability. J Anat 200:629–638
Anderson CM, Swanson RA (2000) Astrocyte glutamate transport: review of properties, regulation, and physiological functions. Glia 32:1–14
Correale J, Villa A (2009) Cellular elements of the blood-brain barrier. Neurochem Res 34:2067–2077
Koehler RC, Gebremedhin D, Harder DR (2006) Role of astrocytes in cerebrovascular regulation. J Appl Physiol 100:307–317
Weinberg RJ (1999) Glutamate: an excitatory neurotransmitter in the mammalian CNS. Brain Res Bull 55:12–18
Choi DW (1987) Ionic dependence of glutamate neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 7:369–379
Nedergaard M, Takano T, Hansen AJ (2002) Beyond the role of glutamate as a neurotransmitter. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:748–755
Sims KD, Robinson MB (1999) Expression patterns and regulation of glutamate transporters in the developing and adult nervous system. Crit Rev Neurobiol 13:169–197
Verkhratsky A (2010) Physiology of neuronal-glia networking. Neurochem Int 57:332–343
Newman EA (2003) New roles for astrocytes: regulation of synaptic transmission. Trends Neurosci 26:536–542
Takano T, Kang J, Jaiswal JK, Simon SM, Lin JH, Yu Y, Li Y, Yang J, Dienel G, Zielke HR, Nedergaard M (2005) Receptor-mediated glutamate release from volume sensitive channels in astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:16466–16471
Kielian T (2008) Glial connexins and gap junctions in CNS inflammation and disease. J Neurochem 106:1000–1016
Li H, Liu T-F, Lazrak A, Peracchia C, Goldberg GS, Lampe PD, Johnson RG (1996) Properties and regulation of gap junctional hemichannels in the plasma membranes of cultured cells. J Cell Biol 134:1019–1030
Robertson JD (1963) The occurrence of a subunit pattern in the unit membranes of club. J Cell Biol 19:201–221
Sáez JC, Berthoud VM, Brañes MC, Martínez AD, Beyer EC (2003) Plasma membrane channels formed by connexins: their regulation and functions. Physiol Rev 83:1359–1400
De Mello, WC. (1987) Cell-to-cell coupling assayed by means of electrical measurements. Experientia 43:1075–1079
Dermietzel R, Spray DC (1993) Gap junctions in the brain: where, what type, how many and why? Trends Neurosci 16:186–192
Tabernero A, Medina JM, Giaume C (2006) Glucose metabolism and proliferation in glia: role of astrocytic gap junctions. J Neurochem 99:1049–1061
Nagy JI, Dudek FE, Rash JE (2004) Update on connexins and gap junctions of neurons and glia in the mammalian nervous system. Brain Res Rev 47:191–215
Dermietzel R, Hertberg EL, KesslerJ A, Spray DC (1991) Gap junctions between cultured astrocytes: immunocytochemical, molecular, and electrophysiological analysis. J Neurosci 11:1421–1432
Scemes E, Giaume C (2006) Astrocyte calcium waves: what they are and what they do. Glia 54:716–725
Fonseca CG, Green CR, Nicholson LFB. (2002) Upregulation in astrocytic connexin 43 gap junction levels may exacerbate generalized seizures in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Res 929:105–116
Nemani VM, Binder DK (2005) Emerging role of gap junctions in epilepsy. Histol Histopathol 20:253–259
Yoon JJ, Green CR, O’Carroll SJ, Nicholson LFB. (2010) Dose-dependent protective effect of connexin43 mimetic peptide against neurodegeneration in an ex vivo model of epileptiform lesion. Epilepsy Res 92:153–162
Le HT, Sin WC, Lozinsky S, Bechberger J, Vega JL, Guo XQ, Sáez JC, Naus CC (2014) Gap junction intercellular communication mediated by connexin43 in astrocytes is essential for their resistance to oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 289:1345–1354
Nakase T, Fushiki S, Naus CCG. (2003) Astrocytic gap junctions composed of connexin 43 reduce apoptotic neuronal damage in cerebral ischemia. Stroke 34:1987–1993
Kawabe K, Takano K, Moriyama M, Nakamura Y (2017) Transglutaminases derived from astrocytes accelerate amyloid β aggregation. Neurochem Res 1–8
Figiel M, Allritz C, Lehmann C, Engele J (2007) Gap junctional control of glial glutamate transporter expression. Mol Cell Neurosci 35:1130–1137
Ishii M, Mueller I, Nakajima T, Pasquale EB, Ogawa K (2011) EphB signaling inhibits gap junctional intercellular communication and synchronized contraction in cultured cardiomyocytes. Basic Res Cardiol 106:1057–1068. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-011-0219-3
Ye Z-C, Wyeth MS, Baltan-Tekkok S, Ransom BR (2003) Functional hemichannels in astrocytes: a novel mechanism of glutamate release. J Neurosci 23:3588–3596
Jin MM, Chen Z (2011) Role of gap junctions in epilepsy. Neurosci Bull 27:389–406
Salameh A., Dhein S. (2005) Pharmacology of gap junctions. New pharmacological targets for treatment of arrhythmia, seizure and cancer? Biochim Biophys Acta 1719:36–58
Yamane Y, Shiga H, Asou H, Ito E (2002) Gap junctional channel inhibition alters actin organization and calcium propagation in rat cultured astrocytes. Neuroscience 112:593–603
Davidson JS, Baumgarten IM, Harley EH (1986) Reversible inhibition of intercellular junctional communication by glycyrrhetinic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 134:29–36
Duan S, Anderson CM, Stein BA, Swanson RA (1999) Glutamate induces rapid upregulation of astrocyte glutamate transport and cell-surface expression of GLAST. J Neurosci 19:10193–10200
Leite MC, Galland F, de Souza DF, Guerra MC, Bobermin L, Biasibetti R, Gottfried C, Gonçalves CA (2009) Gap junction inhibitors modulate S100B secretion in astrocyte cultures and acute hippocampal slices. J Neurosci Res 87:2439–2446
Chu B, Treistman SN (1997) Modulation of two cloned potassium channels by 1-alkanols demonstrates different cutoffs. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 21:1103–1107
Poyraz D, Bräu ME, Wotka F, Puhlmann B, Scholz AM, Hempelmann G, Kox WJ, Spies CD (2003) Lidocaine and octanol have different modes of action at tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ channels of peripheral nerves. Anesth Analg 97:1317–1324
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP26850209 to K.T., JP26450447 to M.M., JP24621008 to Y.N., and JP15K07768 to Y.N.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takano, K., Ogawa, M., Kawabe, K. et al. Inhibition of Gap Junction Elevates Glutamate Uptake in Cultured Astrocytes. Neurochem Res 43, 59–65 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2316-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2316-7