Objective
Our objectives were to develop the population pharmacokinetic (PK) for pertuzumab and examine the variability of steady-state trough serum concentrations (C SS,trough) and exposure after fixed, body-weight-based, or body-surface area (BSA)-based dosing methods in cancer patients.
Methods
Pertuzumab was administered by IV infusion (every 3 weeks) either as a weight-based dose (0.5–15 mg/kg) or a fixed dose (420 or 1050 mg). Data from three clinical studies, comprising 153 patients and 1458 concentration-time points, were pooled for this analysis using NONMEM.
Results
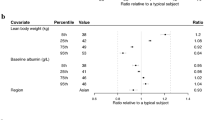
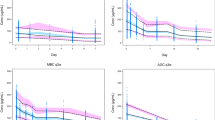
A linear two-compartment model best described the data. Body weight and BSA were significant covariates affecting clearance (CL) and distribution volume (Vc), respectively. However, weight and BSA only explained small percentage of interpatient variability for CL and Vc, respectively. Simulation results indicated that PK profiles were very similar after the three dosing methods. Compared to fixed dosing, weight- and BSA-based dosing only reduced the population variability of C SS,trough moderately.
Conclusion
A population PK model was developed for pertuzumab, the first monoclonal IgG1 antibody in a new class of agents known as HER dimerization inhibitors. In addition, our analyses demonstrate the feasibility of administering pertuzumab using a fixed dose in women with ovarian and breast cancers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Harari Y. Yarden (2000) ArticleTitleMolecular mechanisms underlying ErbB2/HER2 action in breast cancer Oncogene 19 6102–6114 Occurrence Handle11156523 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhsFyhtrg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.onc.1203973
Y. Yarden M. X. Sliwkowski (2001) ArticleTitleUntangling the ErbB signalling network Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2 127–137 Occurrence Handle11252954 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXivVWnt7k%3D Occurrence Handle10.1038/35052073
M. X. Sliwkowski (2003) ArticleTitleReady to partner Nat. Struct. Biol. 10 158–159 Occurrence Handle12605220 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhsVaksb8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1038/nsb0303-158
H. S. Cho K. Mason K. X. Ramyar A. M. Stanley S. B. Gabelli D. W. Denney SuffixJr. D. J. Leahy (2003) ArticleTitleStructure of the extracellular region of HER2 alone and in complex with the Herceptin Fab Nature 421 756–760 Occurrence Handle12610629 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhsV2rtrw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature01392
D. B. Agus R. W. Akita W. D. Fox G. D. Lewis B. Higgins P. I. Pisacane J. A. Lofgren C. Tindell D. P. Evans K. Maiese H. I. Scher M. X. Sliwkowski (2002) ArticleTitleTargeting ligand-activated ErbB2 signaling inhibits breast and prostate tumor growth Cancer Cell 2 127–137 Occurrence Handle12204533 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmslSksL4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1535-6108(02)00097-1
C. L. Arteaga (2003) ArticleTitleErbB-targeted therapeutic approaches in human cancer Exp. Cell Res. 284 122–130 Occurrence Handle12648471 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXitVylt7c%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-4827(02)00104-0
D. B. Agus M. S. Gordon C. Taylor R. B. Natale B. Karlan D. S. Mendelson M. F. Press D. E. Allison M. X. Sliwkowski G. Lieberman S. M. Kelsey G. Fyfe (2005) ArticleTitlePhase I clinical study of pertuzumab, a novel HER dimerization inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer J. Clin. Oncol. 23 2534–2543 Occurrence Handle15699478 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXjvVyktLk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1200/JCO.2005.03.184
D. E. Allison M. A. Malik F. Qureshi D. Baker S. Kelsey G. Fyfe M. Gordon C. Taylor D. B. Agus (2003) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetics of HER2-targeted rhuMAb 2C4 (pertuzumab) in patients with advanced solid malignancies: Phase Ia results Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 22 197
J. F. Lu S. Gourley R. Bruno (2003) ArticleTitleWhen should dose be adjusted to body size? A population pharmacokinetic (PPK) simulation Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 73 86 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-9236(03)90674-6
M. J. Egorin (2003) ArticleTitleHorseshoes, hand grenades, and body-surface area-based dosing: aiming for a target J. Clin. Oncol. 21 182–183 Occurrence Handle12525507 Occurrence Handle10.1200/JCO.2003.10.084
S. D. Baker J. Verweij E. K. Rowinsky R. C. Donehower J. H. Schellens L. B. Grochow A. Sparreboom (2002) ArticleTitleRole of body surface area in dosing of investigational anticancer agents in adults, 1991–2001 J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 94 1883–1888 Occurrence Handle12488482 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXlsFyisA%3D%3D
A. Felici J. Verweij A. Sparreboom (2002) ArticleTitleDosing strategies for anticancer drugs: the good, the bad and body-surface area Eur. J. Cancer 38 1677–1684 Occurrence Handle12175683 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmtVSmtb4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0959-8049(02)00151-X
A. J. Boeckmann S. L. Beal (1994) NONMEM User Guide, NONMEM Project Group University of California San Francisco
U. Wahlby E. N. Jonsson M. O. Karlsson (2001) ArticleTitleAssessment of actual significance levels for covariate effects in NONMEM J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 28 231–252 Occurrence Handle11468939 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FitlOktA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1011527125570
Y. Yano S. L. Beal L. B. Sheiner (2001) ArticleTitleEvaluating pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic models using the posterior predictive check J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 28 171–192 Occurrence Handle11381569 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FhtV2htg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1011555016423
A. Gelman X. L. Meng (1996) Model checking and model improvement W. R. Gilks S. Richardson D. J. Spiegelhalter (Eds) Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice Chapman & Hall/CRC Boca Raton 189–202
A. Gelman J. B. Carlin H. S. Stern D. B. Rubin (2004) Bayesian Data Analysis Chapman & Hall/CRC Boca Raton
K. A. Harris C. B. Washington G. Lieberman J. F. Lu R. Mass R. Bruno (2002) ArticleTitleA population pharmacokinetic (PK) model for trastuzumab (Herceptin) and implications for clinical dosing Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 21 488a
B. Leyland-Jones K. Gelmon J. P. Ayoub A. Arnold S. Verma R. Dias P. Ghahramani (2003) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of trastuzumab administered every three weeks in combination with paclitaxel J. Clin. Oncol. 21 3965–3971 Occurrence Handle14507946 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXpsVajsb0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1200/JCO.2003.12.109
J. F. Lu J. Gaudreault W. Novotny B. Lum R. Bruno (2004) ArticleTitleA population pharmacokinetic model for bevacizumab Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 75 91 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.clpt.2003.11.347
M. A. Malik K. Totpal I. Balter M. X. Sliwkowski N. Pelltier M. Reich T. Crocker S. Freiss S. Bauer N. H. Fiebig D. E. Allison (2003) ArticleTitleDose-response studies of recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody 2C4 in tumor xenograft models Proc. Am. Soc. Cancer Res. 44 176–177
W. J. Loos H. Gelderblom A. Sparreboom J. Verweij M. J. Jonge Particlede (2000) ArticleTitleInter- and intrapatient variability in oral topotecan pharmacokinetics: implications for body-surface area dosage regimens Clin. Cancer Res. 6 2685–2689 Occurrence Handle10914710 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlslent70%3D
F. E. Jongh Particlede J. Verweij W. J. Loos R. Wit Particlede M. J. Jonge Particlede A. S. Planting K. Nooter G. Stoter A. Sparreboom (2001) ArticleTitleBody-surface area-based dosing does not increase accuracy of predicting cisplatin exposure J. Clin. Oncol. 19 3733–3739 Occurrence Handle11533095
R. H. Mathijssen J. Verweij M. J. Jonge Particlede K. Nooter G. Stoter A. Sparreboom (2002) ArticleTitleImpact of body-size measures on irinotecan clearance: alternative dosing recommendations J. Clin. Oncol. 20 81–87 Occurrence Handle11773157 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnsFersg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1200/JCO.20.1.81
F. A. Jong Particlede R. H. Mathijssen R. Xie J. Verweij A. Sparreboom (2004) ArticleTitleFlat-fixed dosing of irinotecan: influence on pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic variability Clin. Cancer Res. 10 4068–4071 Occurrence Handle15217940 Occurrence Handle10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0591
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, C.M., Lum, B.L., Gimenez, V. et al. Rationale for Fixed Dosing of Pertuzumab in Cancer Patients Based on Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis. Pharm Res 23, 1275–1284 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-0205-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-0205-x