ABSTRACT
Purpose
Site specific vascular gene delivery is a promising tool for treatment of cardiovascular diseases. By combining ultrasound mediated microbubble destruction with site specific magnetic targeting of lentiviruses, we aimed to develop a technique suitable for systemic application.
Methods
The magnetic nanoparticle coupling to lipid microbubbles was confirmed by absorbance measurements. Association of fluorescent lentivirus to magnetic microbubbles (MMB) was determined by microscopy and flow cytometry. Functionality and efficiency of GFP-encoding lentiviral MMB transduction was evaluated by endothelial (HMEC) GFP expression and cytotoxicity was measured by MTT reduction.
Results
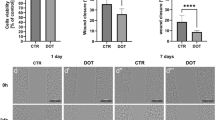
Microbubbles with a mean diameter of 4.3 ± 0.04 μm were stable for 2 days, readily magnetizable and magnetically steerable in vitro and efficiently associated with lentivirus. Exposure of eGFP-encoding lentiviral MMB to human endothelial cells followed by application of an external static magnetic field (30 min) and ultrasonic destruction of the microbubbles did not markedly affect cellular viability. Finally, this combination led to a 30-fold increase in transduction efficiency compared to application of naked virus alone.
Conclusions
By associating microbubbles with magnetic iron nanoparticles, these function as carriers for lentiviruses achieving tissue specific deposition at the site of interest.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DC:
-
duty cycle
- LV:
-
lentivirus
- MF:
-
magnetic field
- MMB:
-
magnetic microbubbles
- MNP:
-
magnetic nanoparticles
- US:
-
ultrasound
REFERENCES
Barry MA, Hofherr SE, Chen CY, Senac JS, Hillestad ML, Shashkova EV. Systemic delivery of therapeutic viruses. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2009;11:411–20.
Pfeiferand A, Hofmann A. Lentiviral transgenesis. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;530:391–405.
Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, McEver RP, Pober JS, Wick TM, Konkle BA, Schwartz BS, Barnathan ES, McCrae KR, Hug BA, Schmidt AM, Stern DM. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood. 1998;91:3527–61.
Phillips L, Klibanov A, Wamhoff B, Hossack J. Targeted gene transfection from microbubbles into vascular smooth muscle cells using focused, ultrasound-mediated delivery. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010;36:1470–80.
Zhou J, Wang Y, Xiong Y, Wang H, Feng Y, Chen J. Delivery of TFPI-2 using ultrasound with a microbubble agent (SonoVue) inhibits intimal hyperplasia after balloon injury in a rabbit carotid artery model. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010;36:1876–83.
Tinkov S, Coester C, Serba S, Geis N, Katus H, Winter G, Bekeredjian R. New doxorubicin-loaded phospholipid microbubbles for targeted tumor therapy: in-vivo characterization. J Control Release. 2010;148:368–72.
Kondo I, Ohmori K, Oshita A, Takeuchi H, Fuke S, Shinomiya K, Noma T, Namba T, Kohno M. Treatment of acute myocardial infarction by hepatocyte growth factor gene transfer: the first demonstration of myocardial transfer of a “functional” gene using ultrasonic microbubble destruction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:644–53.
Bekeredjian R, Chen S, Frenkel PA, Grayburn PA, Shohet RV. Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction can repeatedly direct highly specific plasmid expression to the heart. Circulation. 2003;108:1022–6.
Stride E, Porter C, Prieto AG, Pankhurst Q. Enhancement of microbubble mediated gene delivery by simultaneous exposure to ultrasonic and magnetic fields. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009;35:861–8.
Vlaskou D, Pradhan P, Bergemann C, Klibanov AL, Hensel K, Schmitz G, Plank C, Mykhaylyk O. Magnetic microbubbles: magnetically targeted and ultrasound-triggered vectors for gene delivery in vitro. AIP Conf Proc. 2010;1311:485–94.
Liu Y, Miyoshi H, Nakamura M. Encapsulated ultrasound microbubbles: therapeutic application in drug/gene delivery. J Control Release. 2006;114:89–99.
Lampe M, Briggs J, Endress T, Glass B, Riegelsberger S, Krausslich H, Lamb D, Brauchle C, Muller B. Double-labelled HIV-1 particles for study of virus-cell interaction. Virology. 2007;360:92–104.
Hofmann A, Wenzel D, Becher UM, Freitag DF, Klein AM, Eberbeck D, Schulte M, Zimmermann K, Bergemann C, Gleich B, Roell W, Weyh T, Trahms L, Nickenig G, Fleischmann BK, Pfeifer A. Combined targeting of lentiviral vectors and positioning of transduced cells by magnetic nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:44–9.
Trueck C, Zimmermann K, Mykhaylyk O, Anton M, Vosen S, Wenzel D, Fleischmann B, Pfeifer A. Optimization of magnetic nanoparticles assisted lentiviral gene transfer. Pharmaceut Res. In revision; 2011.
Mannell H, Hellwig N, Gloe T, Plank C, Sohn HY, Groesser L, Walzog B, Pohl U, Krotz F. Inhibition of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 suppresses angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J Vasc Res. 2008;45:153–63.
Mykhaylyk O, Antequera Y, Vlaskou D, Plank C. Generation of magnetic nonviral gene transfer agents and magnetofection in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:2391–411.
Vlaskou D, Mykhaylyk O, Tresilwised N, Pithayanukul P, Möller W, Plank C. Magnetic nanoparticle formulations for DNA and siRNA delivery. J Magn Magn Mater. 2007;311:275–81.
Mykhaylyk O, Sanchez-Antequera Y, Vlaskou D, Hammerschmid E, Anton M, Zelphati O, Plank C. Liposomal magnetofection. Meth Mol Biol. 2010;605:487–525.
Mykhaylyk O, Zelphati O, Hammerschmid E, Anton M, Rosenecker J, Plank C. Recent advances in magnetofection and its potential to deliver siRNAs in vitro. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;487:111–46.
Räthel T, Mannell H, Gleich B, Pohl U, Krötz F. Magnetic stents retain nanoparticle-bound antirestenotic drugs transported by lipid microbubbles Pharmaceutical Research. Accepted, 2011.
Krotz F, de Wit C, Sohn HY, Zahler S, Gloe T, Pohl U, Plank C. Magnetofection–a highly efficient tool for antisense oligonucleotide delivery in vitro and in vivo. Mol Ther. 2003;7:700–10.
Krotz F, Sohn HY, Gloe T, Plank C, Pohl U. Magnetofection potentiates gene delivery to cultured endothelial cells. J Vasc Res. 2003;40:425–34.
Soetanto K. Development of magnetic microbubbles for Drug Delivery System (DDS). Jpn J Appl Phys. 2000;39:3230–2.
Shohet RV, Chen S, Zhou Y-T, Wang Z, Meidell RS, Unger RH, Grayburn PA. Echocardiographic destruction of albumin microbubbles directs gene delivery to the myocardium. Circulation. 2000;101:2554–6.
Beeri R, Guerrero JL, Supple G, Sullivan S, Levine RA, Hajjar RJ. New efficient catheter-based system for myocardial gene delivery. Circulation. 2002;106:1756–9.
Taylor S, Rahim A, Bush N, Bamber J, Porter C. Targeted retroviral gene delivery using ultrasound. J Gene Med. 2007;9:77–87.
Su C, Chang C, Wang H, Wu Y, Bettinger T, Tsai C, Yeh H. Ultrasonic microbubble-mediated gene delivery causes phenotypic changes of human aortic endothelial cells. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010;36:449–58.
Wang Y, Xu H, Lu M, Tang Q. Expression of thymidine kinase mediated by a novel non-viral delivery system under the control of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 promoter selectively kills human umbilical vein endothelial cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:224–30.
Meijering B, Henning R, Van Gilst W, Gavrilovic I, Van Wamel A, Deelman L. Optimization of ultrasound and microbubbles targeted gene delivery to cultured primary endothelial cells. J Drug Target. 2007;15:664–71.
Pislaru SV, Harbuzariu A, Gulati R, Witt T, Sandhu NP, Simari RD, Sandhu GS. Magnetically targeted endothelial cell localization in stented vessels. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:1839–45.
Chorny M, Fishbein I, Yellen BB, Alferiev IS, Bakay M, Ganta S, Adamo R, Amiji M, Friedman G, Levy RJ. Targeting stents with local delivery of paclitaxel-loaded magnetic nanoparticles using uniform fields. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:8346–51.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS & DISCLOSURES
This work was funded by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG) within the DFG Research Unit FOR917.
We thank Professor Kräusslich at the Department of Virology, University Clinic Heidelberg for kindly providing the pCHIV.eGFP lentiviral vector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mannell, H., Pircher, J., Räthel, T. et al. Targeted Endothelial Gene Delivery by Ultrasonic Destruction of Magnetic Microbubbles Carrying Lentiviral Vectors. Pharm Res 29, 1282–1294 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0678-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0678-8