Abstract
Purpose
Several in vivo studies have found that the 5-HT1A PET radioligand 18F-MPPF is a substrate of rodent P-glycoprotein (P-gp). However, in vitro assays suggest that MPPF is not a substrate of human P-gp. We have now tested the influence of inhibiting P-gp on the brain kinetics of 18F-MPPF in mice and non-human primates.
Methods
We measured the peripheral kinetics (arterial input function, metabolism, free fraction in plasma (fP)) during 18F-MPPF brain PET scanning in baboons with or without cyclosporine A (CsA) infusion. We measured 3H-MPPF transport at the mouse BBB using in situ brain perfusion in P-gp/Bcrp deficient mice and after inhibiting P-gp with PSC833.
Results
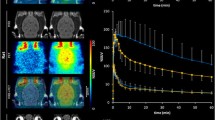
There was an unexpected 1.9-fold increase in brain area under the curve in CsA-treated baboons (n = 4), with no change in radiometabolite-corrected arterial input. However, total volume of distribution corrected for fP (VT/fP) remained unchanged. In situ brain perfusion showed that P-gp restricted the permeability of the mouse BBB to 3H-MPPF while Bcrp did not.
Conclusion
These and previous in vitro results suggest that P-gp may not influence the permeability of human BBB to 18F-MPPF. However, CsA treatment increased 18F-MPPF free fraction, which is responsible for a misleading, P-gp unrelated enhanced brain uptake.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABC:
-
ATP–binding cassette
- AUC:
-
area under the curve
- BBB:
-
blood–brain barrier
- BCRP:
-
breast cancer resistance protein
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- CsA:
-
cyclosporine A
- fP :
-
free fraction (unbound) in plasma
- HPLC:
-
high performance liquid chromatography
- MDCK:
-
Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
- MPPF:
-
4-fluoro-N-{2-[4-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-ethyl}-N-pyridin-2-yl-benzamide
- PET:
-
positron emission tomography
- PK:
-
pharmacokinetic
- P-gp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- VOI:
-
volume of interest
- VT :
-
total distribution volume
References
Scherrmann J-M. Transporters in absorption, distribution, and elimination. Chem Biodivers. 2009;6(11):1933–42.
Pike VW. PET radiotracers: crossing the blood–brain barrier and surviving metabolism. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009;30(8):431–40.
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AAK, Dolman DEM, Yusof SR, Begley DJ. Structure and function of the blood–brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;37(1):13–25.
Tournier N, Declèves X, Saubaméa B, Scherrmann J-M, Cisternino S. Opioid transport by ATP-binding cassette transporters at the blood–brain barrier: implications for neuropsychopharmacology. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(26):2829–42.
Bartels AL. Blood–brain barrier P-glycoprotein function in neurodegenerative disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(26):2771–7.
Aronica E, Sisodiya SM, Gorter JA. Cerebral expression of drug transporters in epilepsy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011 [Epub ahead of print].
van Assema DME, Lubberink M, Bauer M, van der Flier WM, Schuit RC, Windhorst AD, et al. Blood–brain barrier P-glycoprotein function in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2011; [Epub ahead of print].
Hall MD, Pike VW. Avoiding barriers to PET radioligand development: cellular assays of brain efflux transporters. J Nucl Med. 2011;52(3):338–40.
Giacomini KM, Huang S-M, Tweedie DJ, Benet LZ, Brouwer KLR, Chu X, et al. Membrane transporters in drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9(3):215–36.
Wooten DW, Moraino JD, Hillmer AT, Engle JW, Dejesus OJ, Murali D, et al. In vivo kinetics of [F-18]MEFWAY: a comparison with [C-11]WAY100635 and [F-18]MPPF in the nonhuman primate. Synapse. 2011;65(7):592–600.
Laćan G, Plenevaux A, Rubins DJ, Way BM, Defraiteur C, Lemaire C, et al. Cyclosporine, a P-glycoprotein modulator, increases [18F]MPPF uptake in rat brain and peripheral tissues: microPET and ex vivo studies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35(12):2256–66.
Passchier J, van Waarde A, Doze P, Elsinga PH, Vaalburg W. Influence of P-glycoprotein on brain uptake of [18F]MPPF in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;407(3):273–80.
la Fougère C, Böning G, Bartmann H, Wängler B, Nowak S, Just T, et al. Uptake and binding of the serotonin 5-HT1A antagonist [18F]-MPPF in brain of rats: effects of the novel P-glycoprotein inhibitor tariquidar. Neuroimage. 2010;49(2):1406–15.
Bartmann H, Fuest C, la Fougere C, Xiong G, Just T, Schlichtiger J, et al. Imaging of P-glycoprotein-mediated pharmacoresistance in the hippocampus: proof-of-concept in a chronic rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2010;51(9):1780–90.
Ishiwata K, Kawamura K, Yanai K, Hendrikse NH. In vivo evaluation of P-glycoprotein modulation of 8 PET radioligands used clinically. J Nucl Med. 2007;48(1):81–7.
Elsinga PH, Hendrikse NH, Bart J, van Waarde A, Vaalburg W. Positron emission tomography studies on binding of central nervous system drugs and P-glycoprotein function in the rodent brain. Mol Imaging Biol. 2005;7(1):37–44.
Hammers A, Bouvard S, Costes N, PereiradeSouza N, Keihaninejad S, Le Bars D, et al. Impact of P-glycoprotein on the distribution of [18F]-MPPF in pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsia [abstract]. Epilepsia. 2010;51(Suppl):48.
Tournier N, Valette H, Peyronneau M-A, Saba W, Goutal S, Kuhnast B, et al. Transport of selected PET radiotracers by human P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2): an in vitro screening. J Nucl Med. 2011;52(3):415–23.
Takeuchi T, Yoshitomi S, Higuchi T, Ikemoto K, Niwa S, Ebihara T, et al. Establishment and characterization of the transformants stably-expressing MDR1 derived from various animal species in LLC-PK1. Pharm Res. 2006;23(7):1460–72.
Zolnerciks JK, Booth-Genthe CL, Gupta A, Harris J, Unadkat JD. Substrate- and species-dependent inhibition of p-glycoprotein-mediated transport: Implications for predicting in vivo drug interactions. J Pharm Sci. 2011; [Epub ahead of print].
Le Bars D, Lemaire C, Ginovart N, Plenevaux A, Aerts J, Brihaye C, et al. High-yield radiosynthesis and preliminary in vivo evaluation of p-[18F]MPPF, a fluoro analog of WAY-100635. Nucl Med Biol. 1998;25(4):343–50.
Valette H, Xiao Y, Peyronneau M-A, Damont A, Kozikowski AP, Wei Z-L, et al. 18F-ZW-104: a new radioligand for imaging neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors–in vitro binding properties and PET studies in baboons. J Nucl Med. 2009;50(8):1349–55.
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wolf AP, Dewey SL, Schlyer DJ, et al. Graphical analysis of reversible radioligand binding from time-activity measurements applied to [N-11C-methyl]-(−)-cocaine PET studies in human subjects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1990;10(5):740–7.
Luna-Tortos C, Fedrowitz M, Loscher W. Several major antiepileptic drugs are substrates for human P-glycoprotein. Neuropharmacology. 2008;55(8):1364–75.
Cattelotte J, André P, Ouellet M, Bourasset F, Scherrmann J-M, Cisternino S. In situ mouse carotid perfusion model: glucose and cholesterol transport in the eye and brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2008;28(8):1449–59.
Aznavour N, Zimmer L. [18F]MPPF as a tool for the in vivo imaging of 5-HT1A receptors in animal and human brain. Neuropharmacology. 2007;52(3):695–707.
Eyal S, Chung FS, Muzi M, Link JM, Mankoff DA, Kaddoumi A, et al. Simultaneous PET imaging of P-glycoprotein inhibition in multiple tissues in the pregnant nonhuman primate. J Nucl Med. 2009;50(5):798–806.
Wacher VJ, Silverman JA, Zhang Y, Benet LZ. Role of P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 3A in limiting oral absorption of peptides and peptidomimetics. J Pharm Sci. 1998;87(11):1322–30.
Ma Y, Lang L, Kiesewetter DO, Eckelman WC. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry identification of metabolites of three phenylcarboxyl derivatives of the 5-HT(1A) antagonist, N-(2-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl)ethyl)-N-(2-pyridyl) trans-4-fluorocyclohexanecarboxamide (FCWAY), produced by human and rat hepatocytes. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002;780(1):99–110.
Thomas H, Coley HM. Overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer: an update on the clinical strategy of inhibiting p-glycoprotein. Cancer Control. 2003;10(2):159–65.
Carson RE, Wu Y, Lang L, Ma Y, Der MG, Herscovitch P, et al. Brain uptake of the acid metabolites of F-18-labeled WAY 100635 analogs. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23(2):249–60.
Plenevaux A, Weissmann D, Aerts J, Lemaire C, Brihaye C, Degueldre C, et al. Tissue distribution, autoradiography, and metabolism of 4-(2′-methoxyphenyl)-1-[2′ -[N-2″-pyridinyl)-p-[(18)F]fluorobenzamido]ethyl]piperazine (p-[(18)F]MPPF), a new serotonin 5-HT(1A) antagonist for positron emission tomography: an in vivo study in rats. J Neurochem. 2000;75(2):803–11.
Lang L, Jagoda E, Schmall B, Vuong BK, Adams HR, Nelson DL, et al. Development of fluorine-18-labeled 5-HT1A antagonists. J Med Chem. 1999;42(9):1576–86.
Costes N, Merlet I, Zimmer L, Lavenne F, Cinotti L, Delforge J, et al. Modeling [18-F]MPPF positron emission tomography kinetics for the determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine(1A) receptor concentration with multiinjection. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22(6):753–65.
Passchier J, van Waarde A, Vaalburg W, Willemsen AT. On the quantification of [18F]MPPF binding to 5-HT1A receptors in the human brain. J Nucl Med. 2001;42(7):1025–31.
Tournier N, Chevillard L, Megarbane B, Pirnay S, Scherrmann J-M, Declèves X. Interaction of drugs of abuse and maintenance treatments with human P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2). Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13(7):905–15.
Zhang C, Zuo Z, Kwan P, Baum L. In vitro transport profile of carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, eslicarbazepine acetate, and their active metabolites by human P-glycoprotein. Epilepsia. 2011;52(10):1894–904.
Mandula H, Parepally JM, Feng R, Smith QR. Role of site-specific binding to plasma albumin in drug availability to brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;317(2):667–75.
Passchier J, van Waarde A, Pieterman RM, Elsinga PH, Pruim J, Hendrikse HN, et al. In vivo delineation of 5-HT1A receptors in human brain with [18F]MPPF. J Nucl Med. 2000;41(11):1830–5.
Toffoli G, Aita P, Sorio R, Corona G, Bertola A, Colussi AM, et al. Effect of cyclosporin A on protein binding of teniposide in cancer patients. Anticancer Drugs. 1999;10(6):511–8.
Liow JS, Lu S, McCarron JA, Hong J, Musachio JL, Pike VW, et al. Effect of a P-glycoprotein inhibitor, Cyclosporin A, on the disposition in rodent brain and blood of the 5-HT1A receptor radioligand, [11C](R)-(−)-RWAY. Synapse. 2007;61(2):96–105.
Yasuno F, Zoghbi SS, McCarron JA, Hong J, Ichise M, Brown AK, et al. Quantification of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors in monkey brain with [11C](R)-(−)-RWAY. Synapse. 2006;60(7):510–20.
Syvänen S, Lindhe O, Palner M, Kornum BR, Rahman O, Langström B, et al. Species differences in blood–brain barrier transport of three positron emission tomography radioligands with emphasis on P-glycoprotein transport. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37(3):635–43.
Zoghbi SS, Liow JS, Yasuno F, Hong J, Tuan E, Lazarova N, et al. 11C-loperamide and its N-desmethyl radiometabolite are avid substrates for brain permeability-glycoprotein efflux. J Nucl Med. 2008;49(4):649–56.
Acknowledgments and disclosures
We thank Dr. Alfred H. Schinkel (The Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam) for providing the Mdr1a/1b;Bcrp(−/−;−/−) mice and the MDCKII transfected cells. Statistical analyses were kindly performed by Dr. Marcel Debray. The English text was edited by Dr. Owen Parkes. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tournier, N., Cisternino, S., Peyronneau, MA. et al. Discrepancies in the P-glycoprotein-Mediated Transport of 18F-MPPF: A Pharmacokinetic Study in Mice and Non-human Primates. Pharm Res 29, 2468–2476 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0776-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0776-7