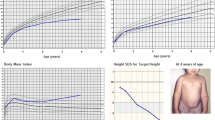
Abstract
Growth hormone (GH) is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in pediatric patients with disorders of growth failure or short stature and in adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD) and HIV/AIDS wasting and cachexia. For pediatric patients, guidelines for the use of GH have been developed by several organizations that have identified specific criteria for initiating GH therapy for each FDA-approved indication. Guidelines for adults have also been developed and include recommendations for transition (adolescent) patients with GHD. These patients are often treated with GH as children but may require continued treatment as young adults to attain full skeletal mineralization and improve cardiovascular risk factors. Adult and pediatric guidelines are supported by efficacy and safety studies, which show that, when started at an early age, GH treatment can increase growth velocity and that GH is safe and well-tolerated. We summarize the guidelines that are available for all FDA-approved indications among pediatric and transition patients. Adherence to these guidelines will help to ensure that patients with disorders of growth failure or short stature receive the necessary therapy to increase linear growth and transition smoothly to healthy adulthood.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilson TA, Rose SR, Cohen P, Rogol AD, Backeljauw P, Brown R, Hardin DS, Kemp SF, Lawson M, Radovick S, Rosenthal SM, Silverman L, Speiser P (2003) Update of guidelines for the use of growth hormone in children: the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrinology Society Drug and Therapeutics Committee. J Pediatr 143(4):415–421. doi:10.1067/s0022-3476(03)00246-4
Richmond E, Rogol AD (2010) Current indications for growth hormone therapy for children and adolescents. In: Hindmarsh PC (ed) Current indications for growth hormone therapy, vol 18. Endocrine development. S. Karger AG, Basel, pp 92–108
Lantos J, Siegler M, Cuttler L (1989) Ethical issues in growth hormone therapy. JAMA 261(7):1020–1024
Bullinger M, Koltowska-Haggstrom M, Sandberg D, Chaplin J, Wollmann H, Noeker M, Brutt AL (2009) Health-related quality of life of children and adolescents with growth hormone deficiency or idiopathic short stature—part 2: available results and future directions. Horm Res 72(2):74–81. doi:10.1159/000232159
Furlanetto RW, Allen DB, Gertner JM, et al (1995) Guidelines for the use of growth hormone in children with short stature: a report by the Drug and Therapeutics Committee of the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society. J Pediatr 127(6):857–867
Bondy CA (2007) Care of girls and women with Turner syndrome: a guideline of the Turner Syndrome Study Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(1):10–25. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-1374
Saenger P, Wikland KA, Conway GS, Davenport M, Gravholt CH, Hintz R, Hovatta O, Hultcrantz M, Landin-Wilhelmsen K, Lin A, Lippe B, Pasquino AM, Ranke MB, Rosenfeld R, Silberbach M (2001) Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Turner syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(7):3061–3069
Clayton PE, Cianfarani S, Czernichow P, Johannsson G, Rapaport R, Rogol A (2007) Management of the child born small for gestational age through to adulthood: a consensus statement of the international societies of pediatric endocrinology and the Growth Hormone Research Society. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(3):804–810. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-2017
Cohen P, Rogol AD, Deal CL, Saenger P, Reiter EO, Ross JL, Chernausek SD, Savage MO, Wit JM, on behalf of the ISS Consensus Workshop participants (2008) Consensus statement on the diagnosis and treatment of children with idiopathic short stature: a summary of the Growth Hormone Research Society, the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society, and the European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology Workshop. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(11):4210–4217. doi:10.1210/jc.2008-0509
Goldstone AP, Holland AJ, Hauffa BP, Hokken-Koelega AC, Tauber M (2008) Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Prader–Willi syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(11):4183–4197. doi:10.1210/jc.2008-0649
Romano AA, Allanson JE, Dahlgren J, Gelb BD, Hall B, Pierpont ME, Roberts AE, Robinson W, Takemoto CM, Noonan JA (2010) Noonan syndrome: clinical features, diagnosis, and management guidelines. Pediatrics 126(4):746–759. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-3207
Cook DM, Yuen KC, Biller BM, Kemp SF, Vance ML (2009) American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists medical guidelines for clinical practice for growth hormone use in growth hormone-deficient adults and transition patients—2009 update. Endocr Pract 15(Suppl 2):1–29
Molitch ME, Clemmons DR, Malozowski S, Merriam GR, Vance ML (2011) Evaluation and treatment of adult growth hormone deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(6):1587–1609. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0179
LaFranchi S, MacGillivray MH, Fullerton P (2000) Growth hormone use in transitioning patients—clinician and payer concerns. Am J Manag Care 6(15 Suppl):S828–S834
Clayton PE, Cuneo RC, Juul A, Monson JP, Shalet SM, Tauber M (2005) Consensus statement on the management of the GH-treated adolescent in the transition to adult care. Eur J Endocrinol 152(2):165–170. doi:10.1530/eje.1.01829
Fujieda K, Hanew K, Hirano T, Igarashi Y, Nishi Y, Tachibana K, Takano K, Tanaka T, Yokoya S (1996) Growth response to growth hormone therapy in patients with different degrees of growth hormone deficiency. Endocr J 43(Suppl):S19–S25
Mauras N, Attie KM, Reiter EO, Saenger P, Baptista J (2000) High dose recombinant human growth hormone (GH) treatment of GH-deficient patients in puberty increases near-final height: a randomized, multicenter trial. Genentech, Inc., Cooperative Study Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(10):3653–3660
Yokoya S, Araki K, Igarashi Y, Kohno H, Nishi Y, Hasegawa Y, Fujita K, Iwatani N, Tachibana K, Ohyama Y, Seino Y, Satoh M, Fujieda K, Tanaka T (1999) High-dose growth hormone (GH) treatment in prepubertal GH-deficient children. Acta Paediatr Suppl 88(428):76–79
Wit JM (2002) Growth hormone therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 16(3):483–503
Soriano-Guillen L, Coste J, Ecosse E, Leger J, Tauber M, Cabrol S, Nicolino M, Brauner R, Chaussain JL, Carel JC (2005) Adult height and pubertal growth in Turner syndrome after treatment with recombinant growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(9):5197–5204. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-0470
Kirk JM, Betts PR, Butler GE, Donaldson MD, Dunger DB, Johnston DI, Kelnar CJ, Price DA, Wilton P, Group U (2001) Short stature in Noonan syndrome: response to growth hormone therapy. Arch Dis Child 84(5):440–443
Wuhl E, Schaefer F (2002) Effects of growth hormone in patients with chronic renal failure: experience in children and adults. Horm Res 58(Suppl 3):35–38
Haffner D, Schaefer F, Nissel R, Wuhl E, Tonshoff B, Mehls O (2000) Effect of growth hormone treatment on the adult height of children with chronic renal failure. German Study Group for Growth Hormone Treatment in Chronic Renal Failure. N Engl J Med 343(13):923–930. doi:10.1056/NEJM200009283431304
de Zegher F, Hokken-Koelega A (2005) Growth hormone therapy for children born small for gestational age: height gain is less dose dependent over the long term than over the short term. Pediatrics 115(4):e458–e462. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-1934
Goldstone AP (2004) Prader–Willi syndrome: advances in genetics, pathophysiology and treatment. Trends Endocrinol Metab 15(1):12–20
Finkelstein BS, Imperiale TF, Speroff T, Marrero U, Radcliffe DJ, Cuttler L (2002) Effect of growth hormone therapy on height in children with idiopathic short stature: a meta-analysis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 156(3):230–240
Nutropin® (somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection) [package insert]. Genentech Inc., South San Francisco (2006)
Press Release. FDA Approves Genentech’s Drug to Treat Children’s Growth Disorder. October 18, 1985. http://www.gene.com/gene/news/press-releases/display.do?method=detail&id=4235
Molitch ME, Clemmons DR, Malozowski S, Merriam GR, Shalet SM, Vance ML, Stephens PA (2006) Evaluation and treatment of adult growth hormone deficiency: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(5):1621–1634. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2227
Growth Hormone Research Society (2000) Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of growth hormone (GH) deficiency in childhood and adolescence: summary statement of the GH Research Society. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(11):3990–3993. doi:10.1210/jc.85.11.3990
Backeljauw P, Bang P, Clayton PE, Geffner M, Woods KA (2010) Diagnosis and management of primary insulin-like growth factor-I deficiency: current perspectives and clinical update. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 7(Suppl 1):154–171
Carel JC, Butler G (2010) Safety of recombinant human growth hormone. Endocr Dev 18:40–54. doi:10.1159/000316126
Norditropin® (somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection) [package insert]. Novo Nordisk A/S, Bagsvaerd (2010)
Genotropin® (somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection) [package insert]. Vetter Pharma-Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG, Ravenswood (2009)
Allanson JE, Roberts AE (1993) Noonan syndrome. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Citation&list_uids=20301303
Allanson JE (2011) Noonan syndrome. GeneReviews [Internet]. Bookshelf, U.N.L.o.M., National Institutes of Health. Bookshelf ID NBK1124. University of Washington, Seattle. Initial posting 15 Nov 2001; last update 7 Oct 2008. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1124/. Accessed 26 May 2011
Conway GS, Szarras-Czapnik M, Racz K, Keller A, Chanson P, Tauber M, Zacharin M (2009) Treatment for 24 months with recombinant human GH has a beneficial effect on bone mineral density in young adults with childhood-onset GH deficiency. Eur J Endocrinol 160(6):899–907. doi:10.1530/EJE-08-0436
Baroncelli GI, Bertelloni S, Sodini F, Saggese G (2003) Acquisition of bone mass in normal individuals and in patients with growth hormone deficiency. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 16(Suppl 2):327–335
Bex M, Abs R, Maiter D, Beckers A, Lamberigts G, Bouillon R (2002) The effects of growth hormone replacement therapy on bone metabolism in adult-onset growth hormone deficiency: a 2-year open randomized controlled multicenter trial. J Bone Miner Res 17(6):1081–1094. doi:10.1359/jbmr.2002.17.6.1081
Underwood LE, Attie KM, Baptista J (2003) Growth hormone (GH) dose-response in young adults with childhood-onset GH deficiency: a two-year, multicenter, multiple-dose, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(11):5273–5280
Shalet SM, Shavrikova E, Cromer M, Child CJ, Keller E, Zapletalova J, Moshang T, Blum WF, Chipman JJ, Quigley CA, Attanasio AF (2003) Effect of growth hormone (GH) treatment on bone in postpubertal GH-deficient patients: a 2-year randomized, controlled, dose-ranging study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(9):4124–4129
Attanasio AF, Shavrikova E, Blum WF, Cromer M, Child CJ, Paskova M, Lebl J, Chipman JJ, Shalet SM (2004) Continued growth hormone (GH) treatment after final height is necessary to complete somatic development in childhood-onset GH-deficient patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(10):4857–4862. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0551
Johannsson G, Albertsson-Wikland K, Bengtsson BA (1999) Discontinuation of growth hormone (GH) treatment: metabolic effects in GH-deficient and GH-sufficient adolescent patients compared with control subjects. Swedish Study Group for Growth Hormone Treatment in Children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(12):4516–4524
Lanes R, Gunczler P, Lopez E, Esaa S, Villaroel O, Revel-Chion R (2001) Cardiac mass and function, carotid artery intima-media thickness, and lipoprotein levels in growth hormone-deficient adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(3):1061–1065
Colao A, Di Somma C, Salerno M, Spinelli L, Orio F, Lombardi G (2002) The cardiovascular risk of GH-deficient adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87(8):3650–3655
Stochholm K, Gravholt CH, Laursen T, Laurberg P, Andersen M, Kristensen LO, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Christiansen JS, Frydenberg M, Green A (2007) Mortality and GH deficiency: a nationwide study. Eur J Endocrinol 157(1):9–18. doi:10.1530/EJE-07-0013
Sherlock M, Ayuk J, Tomlinson JW, Toogood AA, Aragon-Alonso A, Sheppard MC, Bates AS, Stewart PM (2010) Mortality in patients with pituitary disease. Endocr Rev 31(3):301–342. doi:10.1210/er.2009-0033
Verhelst J, Abs R (2009) Cardiovascular risk factors in hypopituitary GH-deficient adults. Eur J Endocrinol 161(Suppl 1):S41–S49. doi:10.1530/EJE-09-0291
Humatrope® (somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection) [package insert]. Lilly France, Fegersheim (2010)
Willemsen RH, van Dijk M, de Rijke YB, van Toorenenbergen AW, Mulder PG, Hokken-Koelega AC (2007) Effect of growth hormone therapy on serum adiponectin and resistin levels in short, small-for-gestational-age children and associations with cardiovascular risk parameters. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(1):117–123. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-0852
Cohen P, Bright GM, Rogol AD, Kappelgaard AM, Rosenfeld RG (2002) Effects of dose and gender on the growth and growth factor response to GH in GH-deficient children: implications for efficacy and safety. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87(1):90–98
Lindgren AC, Ritzen EM (1999) Five years of growth hormone treatment in children with Prader–Willi syndrome. Swedish National Growth Hormone Advisory Group. Acta Paediatr Suppl 88(433):109–111
Bell J, Parker KL, Swinford RD, Hoffman AR, Maneatis T, Lippe B (2010) Long-term safety of recombinant human growth hormone in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(1):167–177. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-0178
Kemp SF, Kuntze J, Attie KM, Maneatis T, Butler S, Frane J, Lippe B (2005) Efficacy and safety results of long-term growth hormone treatment of idiopathic short stature. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(9):5247–5253. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-2513
van Dijk M, Bannink EM, van Pareren YK, Mulder PG, Hokken-Koelega AC (2007) Risk factors for diabetes mellitus type 2 and metabolic syndrome are comparable for previously growth hormone-treated young adults born small for gestational age (sga) and untreated short SGA controls. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(1):160–165. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-1073
Sode-Carlsen R, Farholt S, Rabben KF, Bollerslev J, Schreiner T, Jurik AG, Frystyk J, Christiansen JS, Hoybye C (2011) Growth hormone treatment for two years is safe and effective in adults with Prader–Willi syndrome. Growth Horm IGF Res 21(4):185–190. doi:10.1016/j.ghir.2011.05.002
Quigley CA, Gill AM, Crowe BJ, Robling K, Chipman JJ, Rose SR, Ross JL, Cassorla FG, Wolka AM, Wit JM, Rekers-Mombarg LT, Cutler GB Jr (2005) Safety of growth hormone treatment in pediatric patients with idiopathic short stature. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(9):5188–5196. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-2543
Omnitrope® (somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection) [package insert]. BD Medical-Pharmaceutical Systems, Franklin Lakes (2011)
Hartman ML (1998) The Growth Hormone Research Society consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of adult GH deficiency. Growth Horm IGF Res 8(Suppl A):25–29
Gharib H, Cook DM, Saenger PH, Bengtsson BA, Feld S, Nippoldt TB, Rodbard HW, Seibel JA, Vance ML, Zimmerman D (2003) American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists medical guidelines for clinical practice for growth hormone use in adults and children—2003 update. Endocr Pract 9(1):64–76
Ho KK (2007) Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of adults with GH deficiency II: a statement of the GH Research Society in association with the European Society for Pediatric Endocrinology, Lawson Wilkins Society, European Society of Endocrinology, Japan Endocrine Society, and Endocrine Society of Australia. Eur J Endocrinol 157(6):695–700. doi:10.1530/EJE-07-0631
Donaubauer J, Kiess W, Kratzsch J, Nowak T, Steinkamp H, Willgerodt H, Keller E (2003) Re-assessment of growth hormone secretion in young adult patients with childhood-onset growth hormone deficiency. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 58(4):456–463
Gasco V, Corneli G, Beccuti G, Prodam F, Rovere S, Bellone J, Grottoli S, Aimaretti G, Ghigo E (2008) Retesting the childhood-onset GH-deficient patient. Eur J Endocrinol 159(Suppl 1):S45–S52. doi:10.1530/EJE-08-0293
Acknowledgments
Editorial assistance was provided by Tamara Rahim Grow, PhD, ETHOS Health Communications, Newtown, Pennsylvania, with financial assistance from Novo Nordisk, Inc, Princeton, NJ, in compliance with international guidelines on Good Publication Practice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cook, D.M., Rose, S.R. A review of guidelines for use of growth hormone in pediatric and transition patients. Pituitary 15, 301–310 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-011-0372-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-011-0372-6