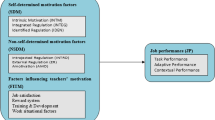
Abstract
The growing interest in public employee motivation and performance as a way to improve the quality of public service suggests the need to analyse different relationships. The overall goal of this work is to examine Public Service Motivation (PSM) and establish how it affects two positive outcomes, job satisfaction and individual performance, and two negative outcomes, resigned satisfaction and burnout. Firstly, this study aims to verify whether PSM positively influences employee job satisfaction and individual performance and, secondly, if PSM can reduce the risk of the two negative outcomes: burnout, which is a cause of people leaving their jobs, and resigned satisfaction, which in the long term leads to burnout. This analysis is based on a sample of 296 Italian teachers working in state primary and secondary schools. The collected data are analysed through structural equation modelling to establish the significant relationships among the mentioned variables. Moreover, partial least squares multi-group analysis was applied to investigate if there were significant differences between the two groups that belong to the variable relating to employee job tenure. Finally, suggestions for future research are offered based on the obtained results.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato, S., Esposito Vinzi, V., Tenenhaus, M.: A global Goodness-of-fit for PLS Structural Equation Modelling. Oral communication to PLS Club, HEC School of Management, Jouy-en-Josas (2004)
Andersen, L.B., Kjeldsen, A.M.: Public service motivation, user orientation, and job satisfaction: a question of employment sector? Int. Public Manag. J. 16(2), 252–274 (2013)
Bakker, A.B.: A Job demands-resources approach to public service motivation. Public Adm. Rev. 75(5), 723–732 (2015)
Bellé, N.: Experimental evidence on the relationship between public service motivation and job performance. Public Adm. Rev. 73(1), 143–153 (2013)
Bollen, K.A.: Structural Equations with Latent Variables. Wiley, New York (1989)
Brewer, G.A.: Does administrative reform improve bureacratic performance? A cross-country empirical analysis. Public Finan. Manag. 4, 399–428 (2004)
Bright, L.: Public employees with high levels of public service motivation: who are they, where are they and what do they want? Rev. Public Pers. Adm. 25(2), 138–155 (2008)
Bruggemann, A.: Zur empirischen Untersuchung verschiedener Formen der Arbeitszufriedenheit. Z. Abeitswissensch. 30, 71–74 (1976)
Bryant, F.B., Yarnold, P.R.: Principal-components analysis and exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. In: Grimm, L.G., Yarnold, P.R. (eds.) Reading and understanding multivariate statistics, pp. 99–136. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC (1995)
Bussing, A., Bissels, T.: Different forms of work satisfaction: concept and qualitative research. Eur. Psychol. 3(3), 209–218 (1998)
Camilleri, E.: Antecedents affecting public service motivation. Pers. Rev. 36(3), 356–377 (2007)
Chin, W.W.: The partial least squares approach for structural equation modeling. In: Marcoulides, G.A. (ed.) Modern Methods for Business Research, pp. 236–295. Lawrence Erlbaum, London (1998)
Chin, W.W., Newsted, P.R.: Structural equation modeling analysis with small samples using partial least squares. Stat. Strateg. Small Sample Res. 2, 307–342 (1999)
Choi, S.: Mediating effects of job satisfaction and organizational commitment on the relationship between public service motivation and performance: a meta-analysis. Available at SSRN 2605709 (2015)
Crisci, A., D’Ambra, A.: Permutation test for group comparison in PLS-Path. Electron. J. Appl. Stat. Anal. 5(3), 339–345 (2012)
Coursey, D.H., Perry, J.L., Brudney, J.L., Littlepage, L.: Psychometric verification of Perry’s public service motivation instrument: results for volunteer exemplars. Rev. Public Pers. Adm. 28, 79–90 (2008)
Demo, G., Neiva, E.R., Nunes, I., Rozzett, K.: Human resources management policies and practices scale (HRMPPS): exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. BAR Braz. Adm. Rev. 9(4), 395–420 (2012)
Edgingthon, E.: Randomization Test. Marcel Dekker, New York (1987)
Fornell, C., Bookstein, F.L.: Two Structural equation model: lISREL and PLS applied to consumer exit voice theory. J. Mark. Res. 19, 440–452 (1982)
Fornell, C., Larcker, D.: Evaluating structural equation models with unob-servable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 18(1), 39–50 (1981)
Giauque, D., Anderfuhren-Biget, S., Varone, F.: Stress perception in public organisations: expanding the job demands–job resources model by including public service motivation. Rev. Public Pers. Adm. 33(1), 53–83 (2012a)
Giauque, D., Ritz, A., Varone, F., Anderfhren-Biget, S.: Resigned but satisfied: the negative impact of public service motivation and red tape on work satisfaction. Public Adm. 90(1), 175–193 (2012b)
Grant, A.M., Campbell, E.M.: Doing good, doing harm, being well and burniong out: the interactions of perceived prosocial and antisocial impact in service work. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 80, 665–691 (2007)
Hair Jr., J.F., Hult, G.T.M., Ringle, C., Sarstedt, M.: A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). Sage, Thousands Oaks (2016)
Hair, J.F., Ringle, C.M., Sarstedt, M.: PLS-SEM: indeed a silver bullet. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 19(2), 139–152 (2011)
Hair Jr., J.F., Black, W.C., Barry, J.B., Rolph, E.A.: Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th edn. Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River (2010)
Henseler, J., Sarstedt, M.: Goodness-of-fit indices for partial least squares path modeling. Comput. Stat. 28(2), 565–580 (2013)
Homberg, F., McCarthy, D., Tabvuma, V.: A meta-analysis of the relationship between public service motivation and job satisfaction. Public Adm. Rev. 75(5), 711–722 (2015)
Horn, J.L., McArdle, J.J.: A practical and theoretical guide to measurement invariance in aging research. Exp. Aging Res. 18, 117–144 (1992)
Jennett, H.K., Harris, S.L., Mesibov, G.B.: Commitment to philosophy, teacher efficacy, and burnout among teachers of children with autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 33, 583–593 (2003)
Kaplan, D.: Structural Equation Modeling: Foundations and Extensions. Sage, Thousands Oaks (2000)
Kaiser, H.F.: The varimax criterion for analytic rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika 23, 187–200 (1958)
Kim, S.: Factors affecting state government information technology employee turnover intentions. Am. Rev. Public Adm. 35, 137–156 (2005)
Kim, J.-O., Muller, C.W.: Introduction to Factor Analysis: what it is and How to do it. Quantitative applications in the social sciences. Sage, Beverly Hills (1978)
Lawley, D.N., Maxwell, A.E.: Factor Analysis as a Statistical Method. Butterworth, London (1971)
Leisink, P., Steijn, B.: Public service motivation and job performance of public sector empoyees in the Netherlands. Int. Rev. Adm. Sci. 75(1), 35–52 (2009)
Lipsky, M.: Street-Level Bureaucracy, 30th Ann. Ed.: Dilemmas of the Individual in Public Service. Russell Sage Foundation, New York (1980)
Lord, F.M., Novick, M.R.: Statistical Theories of Mental Test Scores. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1968)
Maslach, C., Schaufeli, W.B., Leiter, M.P.: Job Burnout. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 52, 397–422 (2001)
Maydeu-Olivares, A., Garcia-Forero, C.: Goodness-of-fit testing. Int. Encycl. Educ. 7(1), 190–196 (2010)
Meredith, W.: Measurement invariance, factor analysis and factorial invariance. Psychometrika 56, 525–543 (1993)
Moyniham, D.P., Pandey, S.K.: Finding workable levers over work motivation comparing job satisfaction, job involvement, and organizational commitment. Adm. Soc. 39(7), 803–832 (2007)
Naff, K.C., Crum, J.: Working for America: does public service motivation make a difference? Rev. Public Pers. Adm. 19(4), 5–16 (1999)
Neuhaus, J.O., Wrigley, C.: The quartimax method. Br. J. Stat. Psychol. 7(2), 81–91 (1954)
Nielsen, V.L.: Are Street-level bureaucrats compelled or enticed to cope? Public Adm. 84(4), 861–889 (2006)
Nunnally, J.C.: Psychometric Theory, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York (1978)
Pandey, S.K., Wright, B.E., Moynihan, D.P.: Public service motivation and organizational citizenship behavior: testing a preliminary model. Int. Public Manag. J. 11(1), 89–108 (2008)
Perry, J.L.: Antecedents of public service motivation. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 7(2), 181–197 (1997)
Perry, J.L.: Measuring public service motivation: an assessment of construct reliability and validity. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 6(1), 5–22 (1996)
Perry, J.L., Wise, L.R.: The motivational bases of public service. Public Adm. Rev. 50, 367–373 (1990)
Perry, J.L., Brudney, J.L., Coursey, D., Littlepage, L.: What drives morally committed citizens? A study of the antecedents of public service motivation. Public Adm. Rev. 68(3), 445–458 (2008)
Petrovsky, N., Ritz, A.: Public service motivation and performance: A critical perspective. In: Homberg, F., Tabvuma, V., Heine, K. (eds.) Evidence-Based HRM: A Global Forum for Empirical Scholarship, vol. 2(1). Emerald Group Publishing Limited, Bingley (2014)
Quratulain, S., Khan, A.K.: Red tape, resigned satisfaction, public service motivation, and negative employee attitudes and behaviors testing a model of moderated mediation. Rev. Public Pers. Adm. 35(4), 307–332 (2015)
Report Education at a Glance: OECD Indicators Scheda Paese Italia, http://www.istruzione.it/allegati/2014/Italy-EAG2014-Country-Note-italian.pdf (2014)
Sanchez-Franco, M.J.: Exploring the influence of gender on the web usage via partial least squares. Behav. Inf. Technol. 25(1), 19–36 (2006)
Saunders, D.R.: An analytic method for rotation to orthogonal simple structure. ETS Res. Bull. Ser. 1, i-28 (1953)
Schaufeli, W.B., Salanova, M.: Efficacy or inefficacy, that’s the question: burnout and work engagement, and their relationships with efficacy beliefs. Anxiety Stress Coping 20, 177–196 (2007)
Steen, T.P.S., Rutgers, M.R.: The double-edged sword: public service motivation, the oath of office and the backlash of an instrumental approach. Public Manag. Rev. 13(3), 343–361 (2011)
Taylor, J., Westover, J.H.: Job satisfaction in the public service: the effects of public service motivation, workplace attributes and work relations. Public Manag. Rev. 13(5), 731–751 (2011)
Taylor, J.: Public service motivation, relational job design, and job satisfaction in local government. Public Adm. (2013). doi:10.1111/j.1467-9299.2012.02108.x
Tenenhaus, M., Amato, S., Esposito Vinzi, V.: A global goodness-of-fit index for PLS structural equation modelling. In: Proceedings of the XLII SIS Scientific Meeting, vol. 1, pp. 739–742. Contributed Papers, CLEUP, Padova (2004)
Tenenhaus, M., Esposito Vinzi, V., Chatelin, Y.M., Lauro, C.: PLS path modeling. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 48, 159–205 (2005)
van Loon, N.M., Vandenabeele, W., Leisink, P.: On the bright and dark side of public service motivation: the relationship between PSM and employee wellbeing. Public Money Manag. 35(5), 349–356 (2015)
Vandenabeele, W.: The mediating effect of job satisfaction and organizational commitment on self-reported performance: more robust evidence of the PSM-performance relationship. Int. Rev. Admin. Sci. 75(11), 11–34 (2009)
Vinzi, V.E., Trinchera, L., Amato, S.: PLS Path Modeling: From Foundations to Recent Developments and Open Issues for Model Assessment and Improvement. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Walker, R.M., Brewer, G.A., Boyne, G.A., Avellaneda, C.N.: Market orientation and public service performance: new public management gone mad? Public Admin. Rev. 71, 707–717 (2011)
Wold, H.: Estimation of principal component and related models by iterative least squares. In: Krishnaiah, P.R. (ed.) Multivariate Analysis, p. 391. Academic Press, New York (1966)
Wold, H.: PLS path models with latent variables: the nipals approach. In: Blalock, H.M., Aganbegian, A., Borodkin, F.M., Boudon, R., Cappecchi, V. (eds.) Quantitative Sociology: International Perspectives on Mathematical and Statistical Modeling. Academic Press, New York (1975a)
Wold, H.: Modelling in Complex Situations with Soft Infromation. Third World Congress of Econometric Society, Toronto (1975b)
Wold, H.: Soft modeling by latent variables: the nonlinear iterative partial least squares approach. In: Gani, J. (ed.) Perspectives in Probability and Statistics, Papers in Honor of M. S. Bartlett, pp. 117–142. Academic Press, London (1975c)
Wold, H.: Model construction and evaluation when theoretical knowledge is scarce. In: Kmenta, J., Ramsey, J.B. (eds.) Evaluation of Econometric Models, pp. 47–74. Academic Press, New York (1980)
Wold, H.: Soft modeling: the basic design and some extensions. In: Jöreskog, K.G., Wold, H. (eds.) Systems Under Indirect Observation: Causality, Structure, Prediction. Part II, pp. 1–54. North Holland, Amsterdam (1982)
Wold, H.: Partial least squares. In: Kotz, S., Johnson, N.L. (eds.) Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences, vol. 6, pp. 581–591. Wiley, New York (1985)
Wright, S.: Correlation and causation. J. Agric Res. 20(7), 557–585 (1921)
Wrigth, S.: The method of path coefficients. Ann. Math. Stat. 5, 161–215 (1934)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank reviewers for the suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palma, R., Sepe, E. Structural equation modelling: a silver bullet for evaluating public service motivation. Qual Quant 51, 729–744 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-016-0436-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-016-0436-9