Abstract
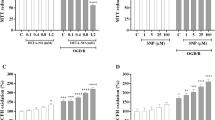
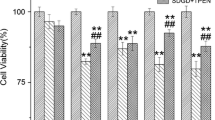
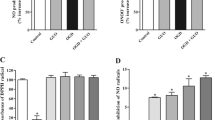
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is important for central nervous system function during pathological states such as ischemia. DHA reduces neuronal injury in experimental brain ischemia; however, the underlying mechanisms are not well understood. In the present study, we investigated the effects of DHA on acute hippocampal slices subjected to experimental ischemia by transient oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) and re-oxygenation and the possible involvement of purinergic receptors as the mechanism underlying DHA-mediated neuroprotection. We observed that cellular viability reduction induced by experimental ischemia as well as cell damage and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) production induced by glutamate (10 mM) were prevented by hippocampal slices pretreated with DHA (5 μM). However, glutamate uptake reduction induced by OGD and re-oxygenation was not prevented by DHA. The beneficial effect of DHA against cellular viability reduction induced by OGD and re-oxygenation was blocked with PPADS (3 μM), a nonselective P2X1–5 receptor antagonist as well as with a combination of TNP-APT (100 nM) plus brilliant blue (100 nM), which blocked P2X1, P2X3, P2X2/3, and P2X7 receptors, respectively. Moreover, adenosine receptors blockade with A1 receptor antagonist DPCPX (100 nM) or with A2B receptor antagonist alloxazine (100 nM) inhibited DHA-mediated neuroprotection. The addition of an A2A receptor antagonist ZM241385 (50 nM), or A3 receptor antagonist VUF5574 (1 μM) was ineffective. Taken together, our results indicated that neuroprotective actions of DHA may depend on P2X, A1, and A2B purinergic receptors activation. Our results reinforce the notion that dietary DHA may act as a local purinergic modulator in order to prevent neurodegenerative diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amadio S, D’Ambrosi N, Cavaliere F, Murra B, Sancesario G, Bernardi G, Burnstock G, Volonte C (2002) P2 receptor modulation and cytotoxic function in cultured CNS neurons. Neuropharmacology 42:489–501
Arias RL, Tasse JR, Bowlby MR (1999) Neuroprotective interaction effects of NMDA and AMPA receptor antagonists in an in vitro model of cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 816:299–308
Bazan NG, Molina MF, Gordon WC (2011) Docosahexaenoic acid signalolipidomics in nutrition: significance in aging, neuroinflammation, macular degeneration, Alzheimer’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Nutr 31:321–351
Bazan NG, Musto AE, Knott EJ (2011) Endogenous signaling by omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid-derived mediators sustains homeostatic synaptic and circuitry integrity. Mol Neurobiol 44:216–222
Begum G, Kintner D, Liu Y, Cramer SW, Sun D (2012) DHA inhibits ER Ca2+ release and ER stress in astrocytes following in vitro ischemia. J Neurochem 120:622–630
Belayev L, Khoutorova L, Atkins KD, Eady TN, Hong S, Lu Y, Obenaus A, Bazan NG (2011) Docosahexaenoic acid therapy of experimental ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res 2:33–41
Boison D (2009) Adenosine augmentation therapies (AATs) for epilepsy: prospect of cell and gene therapies. Epilepsy Res 85:131–141
Brenna JT, Salem N Jr, Sinclair AJ, Cunnane SC (2009) Alpha-Linolenic acid supplementation and conversion to n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in humans. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids 80:85–91
Brongholi K, Souza DG, Bainy AC, Dafre AL, Tasca CI (2006) Oxygen-glucose deprivation decreases glutathione levels and glutamate uptake in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res 1083:211–218
Brown P, Dale N (2000) Adenosine A1 receptors modulate high voltage-activated Ca2+ currents and motor pattern generation in the Xenopus embryo. J Physiol 525(Pt 3):655–667
Burnstock G (2007) Purine and pyrimidine receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1471–1483
Burnstock G, Krugel U, Abbracchio MP, Illes P (2011) Purinergic signalling: from normal behaviour to pathological brain function. Prog Neurobiol 95:229–274
Calon F, Cole G (2007) Neuroprotective action of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids against neurodegenerative diseases: evidence from animal studies. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids 77:287–293
Carmo MR, Simoes AP, Fonteles AA, Souza CM, Cunha RA, Andrade GM (2014) ATP P2Y1 receptors control cognitive deficits and neurotoxicity but not glial modifications induced by brain ischemia in mice. Eur J Neurosci 39:614–622
Cavaliere F, Florenzano F, Amadio S, Fusco FR, Viscomi MT, D’Ambrosi N, Vacca F, Sancesario G, Bernardi G, Molinari M, Volontà C (2003) Up-regulation of P2X2, P2X4 receptor and ischemic cell death: prevention by P2 antagonists. Neuroscience 120:85–98
Chen JF, Pedata F (2008) Modulation of ischemic brain injury and neuroinflammation by adenosine A2A receptors. Curr Pharm Des 14:1490–1499
Choi D (1998) Antagonizing excitotoxicity: a therapeutic strategy for stroke? Mt Sinai J Med 65:133–138
Chu S, Xiong W, Zhang D, Soylu H, Sun C, Albensi BC, Parkinson FE (2013) Regulation of adenosine levels during cerebral ischemia. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34:60–66
Cunha RA (2001) Adenosine as a neuromodulator and as a homeostatic regulator in the nervous system: different roles, different sources and different receptors. Neurochem Int 38:107–125
Cunha RA (2005) Neuroprotection by adenosine in the brain: from A(1) receptor activation to A (2A) receptor blockade. Purinergic Signal 1:111–134
Cunha RA, Almeida T, Ribeiro JA (2000) Modification by arachidonic acid of extracellular adenosine metabolism and neuromodulatory action in the rat hippocampus. J Biol Chem 275:37572–37581
Dale N, Frenguelli BG (2009) Release of adenosine and ATP during ischemia and epilepsy. Curr Neuropharmacol 7:160–179
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Denis I, Potier B, Vancassel S, Heberden C, Lavialle M (2013) Omega-3 fatty acids and brain resistance to ageing and stress: body of evidence and possible mechanisms. Ageing Res Rev 12:579–594
Di Virgilio F, Ceruti S, Bramanti P, Abbracchio MP (2009) Purinergic signalling in inflammation of the central nervous system. Trends Neurosci 32:79–87
Dunwiddie TV, Masino SA (2001) The role and regulation of adenosine in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:31–55
Eady TN, Khoutorova L, Anzola DV, Hong SH, Obenaus A, Mohd-Yusof A, Bazan NG, Belayev L (2013) Acute treatment with docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin reduces injury after a permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats. PLoS ONE 8:e77237
Eto K, Arimura Y, Mizuguchi H, Nishikawa M, Noda M, Ishibashi H (2006) Modulation of ATP-induced inward currents by docosahexaenoic acid and other fatty acids in rat nodose ganglion neurons. J Pharmacol Sci 102:343–346
Farooqui AA, Horrocks LA (2001) Plasmalogens, phospholipase A2, and docosahexaenoic acid turnover in brain tissue. J Mol Neurosci 16:263–272, discussion 279–84
Fedalto ML, Ludka FK, Tasca CI, Molz S (2013) Neuroprotection of Persea major extract against oxygen and glucose deprivation in hippocampal slices involves increased glutamate uptake and modulation of A1 and A2A adenosine receptors. Rev Bras Farmacognosia 23:789–795
Franke H, Krugel U, Illes P (2006) P2 receptors and neuronal injury. Pflugers Arch 452:622–644
Franke H, Verkhratsky A, Burnstock G, Illes P (2012) Pathophysiology of astroglial purinergic signalling. Purinergic Signal 8:629–657
Fredholm BB (2007) Adenosine, an endogenous distress signal, modulates tissue damage and repair. Cell Death Differ 14:1315–1323
Fredholm BB, Chen JF, Cunha RA, Svenningsson P, Vaugeois JM (2005) Adenosine and brain function. Int Rev Neurobiol 63:191–270
Fredholm BB, Irenius E, Kull B, Schulte G (2001) Comparison of the potency of adenosine as an agonist at human adenosine receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem Pharmacol 61:443–448
Grintal B, Champeil-Potokar G, Lavialle M, Vancassel S, Breton S, Denis I (2009) Inhibition of astroglial glutamate transport by polyunsaturated fatty acids: evidence for a signalling role of docosahexaenoic acid. Neurochem Int 54:535–543
Jiang LH, Mackenzie AB, North RA, Surprenant A (2000) Brilliant blue G selectively blocks ATP-gated rat P2X(7) receptors. Mol Pharmacol 58:82–88
Khakh BS (2001) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors and ATP signalling at synapses. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:165–174
Kim K, Lee SG, Kegelman TP, Su ZZ, Das SK, Dash R, Dasgupta S, Barral PM, Hedvat M, Diaz P, Reed JC, Stebbins JL, Pellecchia M, Sarkar D, Fisher PB (2011) Role of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 (EAAT2) and glutamate in neurodegeneration: opportunities for developing novel therapeutics. J Cell Physiol 226:2484–2493
Lopes LV, Sebastiao AM, Ribeiro JA (2011) Adenosine and related drugs in brain diseases: present and future in clinical trials. Curr Top Med Chem 11:1087–1101
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mahe G, Ronziere T, Laviolle B, Golfier V, Cochery T, De Bray JM, Paillard F (2010) An unfavorable dietary pattern is associated with symptomatic ischemic stroke and carotid atherosclerosis. J Vasc Surg 52:62–68
Mayurasakorn K, Williams JJ, Ten VS, Deckelbaum RJ (2011) Docosahexaenoic acid: brain accretion and roles in neuroprotection after brain hypoxia and ischemia. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 14:158–167
Menard C, Patenaude C, Gagne AM, Massicotte G (2009) AMPA receptor-mediated cell death is reduced by docosahexaenoic acid but not by eicosapentaenoic acid in area CA1 of hippocampal slice cultures. J Neurosci Res 87:876–886
Miyagawa N, Miura K, Okuda N, Kadowaki T, Takashima N, Nagasawa SY, Nakamura Y, Matsumura Y, Hozawa A, Fujiyoshi A, Hisamatsu T, Yoshita K, Sekikawa A, Ohkubo T, Abbott RD, Okamura T, Okayama A, Ueshima H (2014) Long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids intake and cardiovascular disease mortality risk in Japanese: a 24-year follow-up of NIPPON DATA80. Atherosclerosis 232:384–389
Moidunny S, Vinet J, Wesseling E, Bijzet J, Shieh CH, van Ijzendoorn SC, Bezzi P, Boddeke HW, Biber K (2012) Adenosine A2B receptor-mediated leukemia inhibitory factor release from astrocytes protects cortical neurons against excitotoxicity. J Neuroinflammation 9:198
Molz S, Dal-Cim T, Tasca CI (2009) Guanosine-5′-monophosphate induces cell death in rat hippocampal slices via ionotropic glutamate receptors activation and glutamate uptake inhibition. Neurochem Int 55:703–709
Molz S, Decker H, Dal-Cim T, Cremonez C, Cordova FM, Leal RB, Tasca CI (2008) Glutamate-induced toxicity in hippocampal slices involves apoptotic features and p38 MAPK signaling. Neurochem Res 33:27–36
Moreira JD, Knorr L, Thomazi AP, Simao F, Battu C, Oses JP, Gottfried C, Wofchuk S, Salbego C, Souza DO, Perry ML, Vinade L (2009) Dietary omega-3 fatty acids attenuate cellular damage after a hippocampal ischemic insult in adult rats. J Nutr Biochem 21:351–356
Mori TA (2014) Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: epidemiology and effects on cardiometabolic risk factors. Food Funct 5:2004–2019
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Nagan N, Zoeller RA (2001) Plasmalogens: biosynthesis and functions. Prog Lipid Res 40:199–229
Nishikawa M, Kimura S, Akaike N (1994) Facilitatory effect of docosahexaenoic acid on N-methyl-D-aspartate response in pyramidal neurones of rat cerebral cortex. J Physiol 475:83–93
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Oleskovicz SP, Martins WC, Leal RB, Tasca CI (2008) Mechanism of guanosine-induced neuroprotection in rat hippocampal slices submitted to oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neurochem Int 52:411–418
Oliveira IJ, Molz S, Souza DO, Tasca CI (2002) Neuroprotective effect of GMP in hippocampal slices submitted to an in vitro model of ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 22:335–344
Pedata F, Melani A, Pugliese AM, Coppi E, Cipriani S, Traini C (2007) The role of ATP and adenosine in the brain under normoxic and ischemic conditions. Purinergic Signal 3:299–310
Phillis JW, O’Regan MH (2004) A potentially critical role of phospholipases in central nervous system ischemic, traumatic, and neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 44:13–47
Pugliese AM, Coppi E, Spalluto G, Corradetti R, Pedata F (2006) A3 adenosine receptor antagonists delay irreversible synaptic failure caused by oxygen and glucose deprivation in the rat CA1 hippocampus in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 147:524–532
Rapoport SI, Rao JS, Igarashi M (2007) Brain metabolism of nutritionally essential polyunsaturated fatty acids depends on both the diet and the liver. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids 77:251–261
Rebola N, Pinheiro PC, Oliveira CR, Malva JO, Cunha RA (2003) Subcellular localization of adenosine A(1) receptors in nerve terminals and synapses of the rat hippocampus. Brain Res 987:49–58
Rodrigues RJ, Almeida T, Richardson PJ, Oliveira CR, Cunha RA (2005) Dual presynaptic control by ATP of glutamate release via facilitatory P2X1, P2X2/3, and P2X3 and inhibitory P2Y1, P2Y2, and/or P2Y4 receptors in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 25:6286–6295
Saremi A, Arora R (2009) The utility of omega-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular disease. Am J Ther 16:421–436
Sergeeva M, Strokin M, Reiser G (2005) Regulation of intracellular calcium levels by polyunsaturated fatty acids, arachidonic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, in astrocytes: possible involvement of phospholipase A2. Reprod Nutr Dev 45:633–646
Sheng H, Li P, Chen X, Liu B, Zhu Z, Cao W (2014) Omega-3 PUFAs induce apoptosis of gastric cancer cells via ADORA1. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 19:854–861
Sperlagh B, Vizi ES (2011) The role of extracellular adenosine in chemical neurotransmission in the hippocampus and Basal Ganglia: pharmacological and clinical aspects. Curr Top Med Chem 11:1034–1046
Stone TW, Ceruti S,Abbracchio MP (2009) Adenosine receptors and neurological disease: neuroprotection and neurodegeneration. Handb Exp Pharmacol 535–87
Strasser U, Fischer G (1995) Protection from neuronal damage induced by combined oxygen and glucose deprivation in organotypic hippocampal cultures by glutamate receptor antagonists. Brain Res 687:167–174
Strokin M, Chechneva O, Reymann KG, Reiser G (2006) Neuroprotection of rat hippocampal slices exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation by enrichment with docosahexaenoic acid and by inhibition of hydrolysis of docosahexaenoic acid-containing phospholipids by calcium independent phospholipase A2. Neuroscience 140:547–553
Strokin M, Sergeeva M, Reiser G (2003) Docosahexaenoic acid and arachidonic acid release in rat brain astrocytes is mediated by two separate isoforms of phospholipase A2 and is differently regulated by cyclic AMP and Ca2+. Br J Pharmacol 139:1014–1022
Taha AY, Jeffrey MA, Taha NM, Bala S, Burnham WM (2010) Acute administration of docosahexaenoic acid increases resistance to pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures in rats. Epilepsy Behav 17:336–343
Tetzlaff W, Schubert P, Kreutzberg GW (1987) Synaptic and extrasynaptic localization of adenosine binding sites in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 21:869–875
Thrift AG, Cadilhac DA, Thayabaranathan T, Howard G, Howard VJ, Rothwell PM, Donnan GA (2014) Global stroke statistics. Int J Stroke 9:6–18
Trotti D, Danbolt NC, Volterra A (1998) Glutamate transporters are oxidant-vulnerable: a molecular link between oxidative and excitotoxic neurodegeneration? Trends Pharmacol Sci 19:328–334
von Lubitz DK, Ye W, McClellan J, Lin RC (1999) Stimulation of adenosine A3 receptors in cerebral ischemia. Neuronal death, recovery, or both? Ann N Y Acad Sci 890:93–106
Wang X, Zhao X, Mao ZY, Wang XM, Liu ZL (2003) Neuroprotective effect of docosahexaenoic acid on glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in rat hippocampal cultures. Neuroreport 14:2457–2461
Wei JW, Wang JG, Huang Y, Liu M, Wu Y, Wong LK, Cheng Y, Xu E, Yang Q, Arima H, Heeley EL, Anderson CS (2010) Secondary prevention of ischemic stroke in urban China. Stroke 41:967–974
Wilding TJ, Chai YH, Huettner JE (1998) Inhibition of rat neuronal kainate receptors by cis-unsaturated fatty acids. J Physiol 513(Pt 2):331–339
Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Dans T, Avezum A, Lanas F, McQueen M, Budaj A, Pais P, Varigos J, Lisheng L (2004) Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case-control study. Lancet 364:937–952
Zhang M, Wang S, Mao L, Leak RK, Shi Y, Zhang W, Hu X, Sun B, Cao G, Gao Y, Xu Y, Chen J, Zhang F (2014) Omega-3 fatty acids protect the brain against ischemic injury by activating Nrf2 and upregulating heme oxygenase 1. J Neurosci 34:1903–1915
Zimmermann H (2000) Extracellular metabolism of ATP and other nucleotides. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 362:299–309
Acknowledgments
This study and FKL were supported by grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa e Inovação do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC). GO was supported by Fundo de Apoio à Manutenção e ao Desenvolvimento da Educação Superior (FUMDES). C.I.T. is recipient of CNPq productivity fellowship. The authors thank the Universidade do Contestado for the animal house facility.
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molz, S., Olescowicz, G., Kraus, J.R. et al. Purine receptors are required for DHA-mediated neuroprotection against oxygen and glucose deprivation in hippocampal slices. Purinergic Signalling 11, 117–126 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-014-9438-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-014-9438-z