Abstract
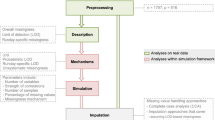
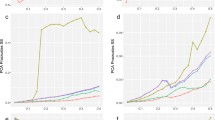
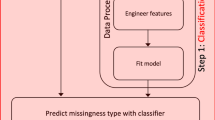
Missing values in mass spectrometry metabolomic datasets occur widely and can originate from a number of sources, including for both technical and biological reasons. Currently, little is known about these data, i.e. about their distributions across datasets, the need (or not) to consider them in the data processing pipeline, and most importantly, the optimal way of assigning them values prior to univariate or multivariate data analysis. Here, we address all of these issues using direct infusion Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry data. We have shown that missing data are widespread, accounting for ca. 20% of data and affecting up to 80% of all variables, and that they do not occur randomly but rather as a function of signal intensity and mass-to-charge ratio. We have demonstrated that missing data estimation algorithms have a major effect on the outcome of data analysis when comparing the differences between biological sample groups, including by t test, ANOVA and principal component analysis. Furthermore, results varied significantly across the eight algorithms that we assessed for their ability to impute known, but labelled as missing, entries. Based on all of our findings we identified the k-nearest neighbour imputation method (KNN) as the optimal missing value estimation approach for our direct infusion mass spectrometry datasets. However, we believe the wider significance of this study is that it highlights the importance of missing metabolite levels in the data processing pipeline and offers an approach to identify optimal ways of treating missing data in metabolomics experiments.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, D., Kniemeyer, O., Brakhage, A. A., & Guthke, R. (2010). Missing values in gell based proteomics. Proteomics, 10(6), 1202–1211.
Andersson, C. A., & Bro, R. (1998). Improving the speed of multi-way algorithms. Part I. Tucker 3. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 42, 93–103.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B, 57, 289–300.
Blanchet, L., Smolinska, A., Attali, A., Stoop, M. P., Ampt, K. A. M., van Aken, H., et al. (2011). Fusion of metabolomics and proteomics data for biomarkers discovery: Case study on the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. BMC Bioinformatics, 12, 254.
Broadhurst, D. I., & Kell, D. B. (2006). Statistical strategies for avoiding false discoveries in metabolomics and related experiments. Metabolomics, 2, 171–196.
de Brevern, A. G., Hazout, S., & Malpertuy, A. (2004). Influence of microarrays experiments missing values on the stability of gene groups by hierarchical clustering. BMC Bioinformatics, 5, 114.
Defamie, V. (2008). Gene expression profiling of human liver transplants identifies an early transcriptional signature associated with initial poor graft function. American Journal of Transplantation, 8, 1221–1236.
Dieterle, F., Ross, A., Scholtterbeck, G., & Senn, H. (2006). Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabolomics. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 4281–4290.
Goodacre, R., Vaidyanathan, S., Dunn, W. B., Harrigan, G., & Kell, D. B. (2004). Metabolomics by numbers: Acquiring and understanding global metabolite data. Trends in Biotechnology, 22, 245–252.
Hrydziuszko, O., Silva, M. A., Perera, T. P. R., Richards, D. A., Murphy, N., Mirza, D., et al. (2010). Application of metabolomics to investigate the process of human orthotopic liver transplantation: A proof-of-principle study. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 14, 143–150.
Jornsten, R., Wang, H., Welsh, W., & Ouyang, M. (2005). DNA microarray data imputation and significance analysis of differential expression. Bioinformatics, 21, 4155–4161.
Kanehisa, M., Araki, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., Hirakawa, M., & Itoh, M. (2008). KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Research, 36, D480–D484.
Kenny, L. C., Broadhurst, D. I., Dunn, W., Brown, M., North, R. A., McCowan, L., et al. (2010). Robust early pregnancy prediction of later preeclampsia using metabolomics biomarkers. Hypertension, 56, 741–749.
Kim, K. Y., Kim, B. J., & Yi, G. S. (2004). Reuse of imputed data in microarray analysis increases imputation efficiency. BMC Bioinformatics, 5, 160.
Kim, D. W., Lee, K. Y., Lee, K. H., & Lee, D. (2007). Towards clustering of incomplete microarray data without the use imputation. Bioinformatics, 23, 107–113.
Kincius, M., Liang, A., Nickkholgh, K., Hoffmann, C., Flechtenmacher, C., Ryschich, E., et al. (2007). Taurine protects from liver injury after warm ischemia in rats: The role of Kupffer cells. European Surgical Research, 39, 275–283.
Little, R. J. A. (1998). A test of missing completely at random for multivariate data with missing values. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 83, 1198–1202.
Little, R. J. A., & Rubin, D. B. (2002). Statistical analysis with missing data. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
Oba, S., Sato, M., Takemasa, I., Monden, M., et al. (2003). A Bayesian missing values estimation method for gene expression profile data. Bioinformatics, 19, 2088–2096.
Parsons, H. M., Ekman, D. R., Collette, T. W., & Viant, M. R. (2009). Spectral relative standard deviation: A practical benchmark in metabolomics. Analyst, 134, 478–484.
Parsons, H. M., Ludwig, C., Günther, U. L., & Viant, M. R. (2007). Improved classification accuracy in 1- and 2- dimensional NMR metabolomics data using the variance stabilizing generalised logarithm transformation. BMC Bioinformatics, 8, 234.
Payne, T. G., Southam, A. D., Arvanitis, T. N., & Viant, M. R. (2009). A signal filtering method for improved quantification and noise discrimination in Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry-based metabolomics data. Journal of American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 20, 1087–1095.
Pedreschi, R., Hertog, M. A. T. M., Carpentier, S., Lammertyn, J., Robben, J., et al. (2008). Treatment of missing values for multivariate statistical analysis of gel-based proteomics data. Proteomics, 8, 1371–1383.
Rubin, D. R. (1976). Inference and missing data. Biometrica, 63, 581–592.
Sangster, T. P., Wingate, J. E., Burton, L., Teichert, F., & Wilson, I. D. (2007). Investigation of analytical variation in metabonomics analysis using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrometry, 21, 2965–2970.
Schafer, J. L. (1999). Multiple imputation: A primer. Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 8, 3.
Scheel, I., Aldrin, M., Glad, I., Sorum, R., Lyng, H., & Frigessi, A. (2005). The influence of missing values imputation on detection of differentially expressed genes from microarray data. Bioinformatics, 21, 4272–4279.
Silva, M. A. (2006). Arginine and urea metabolism in the liver graft: A study using microdialysis in human orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation, 82, 1304–1311.
Southam, A. D., Payne, T. G., Cooper, H., Arvanitis, T. N., & Viant, M. R. (2007). Dynamic range and mass accuracy of widescan direct infusion nanoelectrospray Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry-based metabolomics increased by the spectral stitching method. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 4595–4602.
Steuer, R., Morgenthal, K., Weckwerth, W., & Selbig, J. (2007) A gentle guide to the analysis of metabolomic data. In: Metabolomics: Methods and protocols (pp. 105–129). New Jersey: Humana Press.
Sumner, L. W., Amberg, A., Barret, D., Beale, M. H., Berger, R., et al. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis chemical analysis working group (CAWG) metabolomics standards initiative (MSI). Metabolomics, 3, 211–221.
Taylor, N. S., Weber, R. J. M., Southam, A. D., Payne, T. G., Hrydziuszko, O., Arvanitis, T. N., et al. (2009). A new approach to toxicity testing in Daphnia magna: An application of high throughput FT-ICR mass spectrometry metabolomics. Metabolomics, 5, 44–58.
Taylor, N. S., Weber, R. J. M., White, T. A., & Viant, M. R. (2010). Discriminating between different acute chemical toxicities via changes in the daphnid metabolome. Toxicological Sciences, 118, 307–317.
Troyanskaya, O., Cantor, M., Sherlock, G., Brown, P., Hastie, T., et al. (2001). Missing value estimation methods for DNA microarrays. Bioinformatics, 17, 520–525.
Tuikkala, J., Elo, L. L., Nevalainen, O. S., & Aittokallio, T. (2008). Missing value imputation improves clustering and interpretation of gene expression microarray data. BMC Bioinformatics, 9, 202.
van Buuren, S., & Groothuis-Oudsshoorn, K. (2010). MICE: Multivariate imputation by chained equations in R. Journal of Statistical Software, 1, 68–74.
Walczak, B., & Massart, D. L. (2001). Dealing with missing data part I. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 58, 15–27.
Westerhuis, J. A., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Smit, S., Vis, D. J., Smilde, A. K., van Velzen, E. J. J., et al. (2008). Assessment of PLSDA cross validation. Metabolomics, 4, 81–89.
Wu, H., Southam, A. D., Hines, A., & Viant, M. R. (2008). High throughput tissue extraction protocol for NMR- and MS-based metabolomics. Analytical Biochemistry, 372, 204–212.
Xia, J., Psychogios, N., Young, N., & Wishart, D. S. (2009). MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomics data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, W652–W660.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Alessia Lodi, Stefano Tiziani and Chris Bunce for provision of the FT-ICR MS datasets of the cancer cell extracts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hrydziuszko, O., Viant, M.R. Missing values in mass spectrometry based metabolomics: an undervalued step in the data processing pipeline. Metabolomics 8 (Suppl 1), 161–174 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-011-0366-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-011-0366-4