Abstract
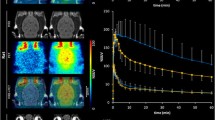
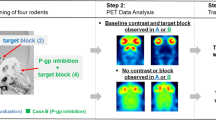
The permeability of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) is one of the factors determining the bioavailability of drugs in the brain. The BBB only allows passage of lipophilic drugs by passive diffusion. However, some lipophilic drugs hardly enter the brain. The transmembrane protein P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is one of the carrier systems that is responsible for transportation of drugs out of the brain. P-Glycoprotein affects the pharmacokinetics of many drugs and can be inhibited by administration of modulators or competitive substrates. Identification and classification of central nervous system (CNS) drugs as P-gp substrates or inhibitors are of crucial importance in drug development. Positron emission tomography (PET) studies can play an important role in the screening process as a follow-up of high-throughput in vitro assays. Several rodent studies have shown the potential value of PET to measure the effect of P-gp on the pharmacokinetics and brain uptake of radiolabeled compounds. P-Glycoprotein-mediated effects were observed for two 5-HT1a receptor ligands, [18F]MPPF vs. [carbonyl-11C]WAY100635. Under control conditions, the specific brain uptake of [18F]MPPF is five- to eightfold lower than that of [11C]WAY100635. After cyclosporin A (CsA) modulation, [18F]MPPF uptake in the rat brain increased five- to tenfold. Cerebral uptake of [carbonyl-11C]WAY100635 was also increased by modulation, but in general the increase was lower than that observed for [18F]MPPF (two- to threefold). Brain uptake of the β-adrenergic receptor ligands [11C]carazolol and [18F]fluorocarazolol was increased in P-gp knockout mice and CsA-treated rats. Both the specific and nonspecific binding of [18F]fluorocarazolol were doubled by CsA. Cerebral uptake of [11C]carazolol in rats was much lower than that of [18F]fluorocarazolol and no specific binding was measured. After CsA modulation, the uptake of [11C]carazolol increased five- to sixfold, but this uptake was not receptor-mediated. Quantitative PET studies in rodents on P-gp functionality demonstrated a dose-dependent increase of radioligands after administration of CsA. Studies with [11C]verapamil and [11C]carvedilol showed that complete modulation was achieved at 50 mg/kg CsA. The distribution volume of [11C]carvedilol increased from 0.25 in the control study to 1.0 after full modulation with CsA. By quantitative PET measurement of P-gp function, the dose of modulators required to increase the concentration of CNS drugs may be determined, which may result in improved drug therapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
MW Bradbury (1985) ArticleTitleThe blood–brain barrier. Transport across the cerebral endothelium Circ Res 57 213–222
B Alberts D Bray J Lewis (1989) Molecular biology of the cell EditionNumber2nd edn Garland Publishing, Inc New York
MW Bradbury (1993) ArticleTitleThe blood–brain barrier Exp Physiol 78 453–472
WM Pardridge (1995) ArticleTitleTransport of small molecules through the blood–brain barrier: Biology and methodology Adv Drug Deliv Rev 15 5–36 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0169-409X(95)00003-P
WM Pardridge (1995) ArticleTitleVector-mediated peptide drug delivery to the brain Adv Drug Deliv Rev 15 109–146 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0169-409X(95)00007-T
NJ Abbott IA Romero (1996) ArticleTitleTransporting therapeutics across the blood–brain barrier Mol Med Today 2 106–113 Occurrence Handle10.1016/1357-4310(96)88720-X
DJ Begley (1996) ArticleTitleThe blood–brain barrier: Principles for targeting peptides and drugs to the central nervous system J Pharm Pharmacol 48 136–146
BB Johansson (1990) ArticleTitleThe physiology of the blood–brain barrier Adv Exp Med Biol 274 25–39
LR Drewes (1999) ArticleTitleWhat is the blood–brain barrier? A molecular perspective. Cerebral vascular biology Adv Exp Med Biol 474 111–122
DJ Begley (1992) ArticleTitleThe interaction of some centrally active drugs with the blood–brain barrier and circumventricular organs Prog Brain Res 91 163–169
P Borst AH Schinkel (1996) ArticleTitleWhat have we learnt thus far from mice with disrupted P-glycoprotein genes? Eur J Cancer 32A 985–990 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0959-8049(96)00063-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XksVOnt7g%3D Occurrence Handle8763339
CS Hughes SL Vaden CA Manaugh (1998) ArticleTitleModulation of doxorubicin concentration by cyclosporin A in brain and testicular barrier tissues expressing P-glycoprotein in rats J Neurooncol 37 45–54 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005900908540
AH Schinkel E Wagenaar CA Mol (1996) ArticleTitleP-Glycoprotein in the blood–brain barrier of mice influences the brain penetration and pharmacological activity of many drugs J Clin Invest 97 2517–2524 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjsFKjs7Y%3D Occurrence Handle8647944
J Asperen ParticleVan AH Schinkel JH Beijnen (1996) ArticleTitleAltered pharmacokinetics of vinblastine in Mdr1a P-glycoprotein-deficient Mice J Natl Cancer Inst 88 994–999
J Asperen ParticleVan U Mayer O Tellingen Particlevan (1997) ArticleTitleThe functional role of P-glycoprotein in the blood–brain barrier J Pharm Sci 86 881–884 Occurrence Handle10.1021/js9701364 Occurrence Handle9269863
N Kartner JR Riordan V Ling (1983) ArticleTitleCell surface P-glycoprotein associated with multidrug resistance in mammalian cell lines Science 221 1285–1288
MM Gottesman I Pastan (1993) ArticleTitleBiochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter Ann Rev Biochem 62 385–427 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002125
AH Schinkel (1997) ArticleTitleThe physiological function of drug-transporting P-glycoproteins Semin Cancer Biol 8 161–170 Occurrence Handle10.1006/scbi.1997.0068
J Bart HJM Groen NH Hendrikse WTA Graaf Particlevan der W Vaalburg EGE Vries Particlede (2000) ArticleTitleThe blood–brain barrier and oncology: New insights into function and modulation Cancer Treat Rev 26 449–462 Occurrence Handle10.1053/ctrv.2000.0194
W Löscher H Potschka (2002) ArticleTitleRole of multidrug transporters in pharmacoresistance to antiepileptic drugs J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301 7–14 Occurrence Handle10.1124/jpet.301.1.7
E Hofsli J Nissen-Meyer (1990) ArticleTitleReversal of multidrug resistance by lipophilic drugs Cancer Res 50 3997–4002
HL Pearce MA Winter WT Beck (1990) ArticleTitleStructural characteristics of compounds that modulate P-glycoprotein-associated multidrug resistance Adv Enzyme Regul 30 357–373 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0065-2571(90)90026-X
L Jette GF Murphy JM Leclerc (1995) ArticleTitleInteraction of drugs with P-glycoprotein in brain capillaries Biochem Pharmacol 50 1701–1709 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-2952(95)02073-X
FJ Sharom (1997) ArticleTitleThe P-glycoprotein efflux pump: How does it transport drugs? J Membr Biol 160 161–175 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002329900305
K Ueda Y Taguchi M Morishima (1997) ArticleTitleHow does P-glycoprotein recognize its substrates? Semin Cancer Biol 8 151–159 Occurrence Handle10.1006/scbi.1997.0066
AB Pawagi J Wang M Silverman (1994) ArticleTitleTransmembrane aromatic amino acid distribution in P-glycoprotein. A functional role in broad substrate specificity J Mol Biol 235 554–564 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jmbi.1994.1013
S Ekins RB Kim BF Leake et al. (2002) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationships of inhibitors of P-glycoprotein Mol Pharmacol 61 964–973 Occurrence Handle10.1124/mol.61.5.964
IK Pajeva M Wiese (2002) ArticleTitlePharmacophore model of drugs involved in P-glycoprotein multidrug resistance: Explanation of structural variety (hypothesis) J Med Chem 45 5671–5686 Occurrence Handle10.1021/jm020941h
W Niederberger M Lemaire G Maurer (1983) ArticleTitleDistribution and binding of cyclosporine in blood and tissues Transplant Proc 15 2419–2421
J Greenwood (1992) ArticleTitleCharacterization of a rat retinal endothelial cell culture and the expression of P-glycoprotein in brain and retinal endothelium in vitro J Neuroimmunol 39 123–132 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0165-5728(92)90181-J
C Cordon-Cardo JP O’Brien D Casals (1989) ArticleTitleMultidrug-resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at blood–brain barrier sites Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86 695–698
I Sugawara H Hamada T Tsuruo (1990) ArticleTitleSpecialized localization of P-glycoprotein recognized by MRK 16 monoclonal antibody in endothelial cells of the brain and the spinal cord Jpn J Cancer Res 81 727–730
E Beaulieu M Demeule L Ghitescu (1997) ArticleTitleP-Glycoprotein is strongly expressed in the luminal membranes of the endothelium of blood vessels in the brain Biochem J 326 IssueIDPt 2 539–544
PL Golden WM Pardridge (1999) ArticleTitleP-Glycoprotein on astrocyte foot processes of unfixed isolated human brain capillaries Brain Res 819 143–146 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-8993(98)01305-5
T Tatsuta M Naito T Oh-hara (1992) ArticleTitleFunctional involvement of P-glycoprotein in blood–brain barrier J Biol Chem 267 20383–20391
F Thiebaut T Tsuruo H Hamada MM Gottesman I Pastan MC Willingham (1987) ArticleTitleCellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84 7735–7738 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXmtlels7k%3D Occurrence Handle2444983
BM Metha A Levchenko E Rosa SW Kim S Winnick JJ Zhang H Kalaigian SM Larson (1996) ArticleTitleEvaluation of carbon-14-colchicine biodistribution with whole-body quantitative autoradiography in colchicine-sensitive and -resistant xenografts J Nucl Med 37 312–314
D Schwab H Fischer A Tabatabaei S Poli J Huwyler (2003) ArticleTitleComparison of in vitro P-glycoprotein screening assays: Recommendations for their use in drug discovery J Med Chem 46 1716–1725 Occurrence Handle10.1021/jm021012t
NH Hendrikse AH Schinkel EGE Vries Particlede (1998) ArticleTitleComplete in vivo reversal of P-glycoprotein pump function in the blood–brain barrier visualised with positron emission tomography Br J Pharmacol 124 1413–1418
A Levchenko BM Mehta JB Lee et al. (2000) ArticleTitleEvaluation of [11C]colchicine for PET imaging of multiple drug resistance J Nucl Med 41 493–501
PH Elsinga EJ Franssen NH Hendrikse et al. (1996) ArticleTitleCarbon-11-labeled daunorubicin and verapamil for probing P-glycoprotein in tumors with PET J Nucl Med 37 1571–1575
JS Lewis JL Dearling JK Sosabowsli et al. (2000) ArticleTitleCopper bis(diphosphine) complexes: Radiopharmaceuticals for the detection of multidrug resistance in tumours by PET Eur J Nucl Med 27 638–646 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002590050557
AB Packard JF Kronauge E Barbarics S Kiani ST Treves (2002) ArticleTitleSynthesis and biodistribution of a lipophilic 64Cu-labeled monocationic copper (II) complex Nucl Med Biol 29 289–292 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0969-8051(02)00285-8
J Passchier KWM Lawrie D Bender I Fellows AD Gee (2003) ArticleTitle[11C]Loperamide as highly sensitive PET probe for measuring changes in P-glycoprotein functionality J Lab Comp Radiopharm 46 S94
KA Kurdziel DO Kiesewetter RE Carson WC Eckelman P Herscowitch (2003) ArticleTitleBiodistribution, radiation dose estimates, and in vivo Pgp modulation studies of 18F-paclitaxel in nonhuman primates J Nucl Med 44 1330–1339
J Passchier A Waarde ParticleVan P Doze PH Elsinga W Vaalburg (2000) ArticleTitleInfluence of P-glycoprotein on brain uptake of [18F]MPPF in rats Eur J Pharmacol 407 273–280 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-2999(00)00752-4
MS Berridge EH Cassidy AH Terris JM Vesselle (1992) ArticleTitlePreparation and in vivo binding of [11C]carazolol, a radiotracer for the β-adrenergic receptor Nucl Med Biol 19 563–569
P Doze A Waarde ParticleVan PH Elsinga AM Loenen-Weemaes Particlevan ATM Willemsen W Vaalburg (1998) ArticleTitleValidation of S-1′-[18F]fluorocarazolol for in vivo imaging and quantification of cerebral β-adrenoceptors Eur J Pharmacol 353 215–226 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-2999(98)00418-X
PH Elsinga MG Vos A Waarde ParticleVan et al. (1996) ArticleTitle(S,S)- and (S,R)-1′-[18F]fluorocarazolol, ligands for the visualization of pulmonary β-adrenergic receptors with PET Nucl Med Biol 23 159–167 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0969-8051(95)02049-7
LB Zheng MS Berridge P Ernsberger (1994) ArticleTitleSynthesis, binding properties, and 18F labeling of fluorocarazolol, a high-affinity β-adrenergic receptor antagonist J Med Chem 37 3219–3230
A Waarde ParticleVan TJ Visser PH Elsinga et al. (1997) ArticleTitleImaging β-adrenoceptors in the human brain with (S)-1′-[18F]fluorocarazolol J Nucl Med 38 934–939
P Doze A Waarde ParticleVan PH Elsinga NH Hendrikse W Vaalburg (2000) ArticleTitleEnhanced cerebral uptake of receptor ligands by modulation of P-glycoprotein function in the blood–brain barrier Synapse 36 66–74 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(200004)36:1<66::AID-SYN7>3.0.CO;2-J
LJ Grimm JA Blendy KJ Kellar DC Perry (1992) ArticleTitleChronic reserpine administration selectively up-regulates β1- and α1b-adrenergic receptors in rat brain: An autoradiographic study Neuroscience 47 77–86 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0306-4522(92)90122-I
RB Innis FMA Correa SH Snyder (1979) ArticleTitleCarazolol, an extremely potent β-adrenergic blocker: Binding to β-receptors in brain membranes Life Sci 24 2255–2264 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0024-3205(79)90102-4
PL Golden WM Pardridge (2000) ArticleTitleBrain microvascular P-glycoprotein and a revised model of multidrug resistance in brain Cell Mol Neurobiol 20 165–181 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1007093521681
WD Klohs RW Steinkampf MJ Havlick RC Jackson (1986) ArticleTitleResistance to anthrapyrazoles and anthracyclines in multidrug-resistant P388 murine leukemia cells: Reversal by calcium blockers and calmodulin antagonists Cancer Res 46 4352–4356
NH Hendrikse EGE Vries Particlede E Eriks-Fluks et al. (1999) ArticleTitleA new in vivo method to study P-glycoprotein transport in tumors and the blood–brain barrier Cancer Res 59 2411–2416
Bart J, Willemsen ATM, Groen HJM, et al. (2003) Quantitative assessment of P-glycoprotein function in the rat blood–brain barrier by distribution volume of [11C]verapamil measured with PET. Neuroimage (in press)
SK Martin AM Oduola WK Milhous (1987) ArticleTitleReversal of chloroguine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum by verapamil Science 235 899–901
C Hansch A Leo D Hoekman (1995) Exploring QSAR: Hydrophobic, electronic, and steric constants American Chemistry Society Washington, DC
DD Dishino MJ Welch MR Kilbourn ME Raichle (1983) ArticleTitleRelationship between lipophilicity and brain extraction of 11C-labeled radiopharmaceuticals J Nucl Med 24 1030–1038
P Buchwald N Bodor (1998) ArticleTitleOctanol–water partition: Searching for predictive models Curr Med Chem 5 353–380
O Jonsson P Behnam-Motlagh M Persson R Henriksson K Grankvist (1999) ArticleTitleIncrease in doxorubicin cytotoxicity by carvedilol inhibition of P-glycoprotein activity Biochem Pharmacol 58 1801–1806 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-2952(99)00262-2
P Doze PH Elsinga B Maas A Waarde ParticleVan T Wegman W Vaalburg (2002) ArticleTitleSynthesis and evaluation of radiolabeled antagonists for imaging of beta-adrenoceptors in the brain with PET Neurochem Int 40 145–155 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0197-0186(01)00081-X
WH Schaefer J Politowski B Hwang (1998) ArticleTitleMetabolism of carvedilol in dogs, rats, and mice Drug Metab Dispos 26 958–969
G Neugebauer P Neubert (1991) ArticleTitleMetabolism of carvedilol in man Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 16 257–260
S Neuhoff P Langguth C Dressler TB Andersson CG Regardh H Spahn-Langguth (2000) ArticleTitleAffinities at the verapamil binding site of MDR1-encoded P-glycoprotein: Drugs and analogs, stereoisomers and metabolites Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 38 168–179
AF List KJ Kopecky CL Willman et al. (2001) ArticleTitleBenefit of cyclosporine modulation of drug resistance in patients with poor-risk acute myeloid leukemia: A Southwest Oncology Group study Blood 98 3212–3220 Occurrence Handle10.1182/blood.V98.12.3212
DJ Boote IF Dennis PR Twentyman et al. (1996) ArticleTitlePhase I study of etoposide with SDZ PSC 833 as a modulator of multidrug resistance in patients with cancer J Clin Oncol 14 610–618
EK Rowinsky L Smith YM Wang et al. (1998) ArticleTitlePhase I and pharmacokinetic study of paclitaxel in combination with biricodar, a novel agent that reverses multidrug resistance conferred by overexpression of both MDR1 and MRP J Clin Oncol 16 2964–2976 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmtFSls7g%3D Occurrence Handle9738565
D Damiani M Michieli A Ermacora et al. (1998) ArticleTitleAdjuvant treatment with cyclosporin a increases the toxicity of chemotherapy for remission induction in acute non-lymphocytic leukemia Leukemia 12 1236–1240 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.leu.2401092
MJ Newman JC Rodarte KD Benbatoul et al. (2000) ArticleTitleDiscovery and characterization of OC144-093, a novel inhibitor of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance Cancer Res 60 2964–2972 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjvFOlt74%3D Occurrence Handle10850444
A Sparreboom AS Planting RC Jewell et al. (1999) ArticleTitleClinical pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin in combination with GF120918, a potent inhibitor of MDR1 P-glycoprotein Anticancer Drugs 10 719–728 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXntlGhtrw%3D Occurrence Handle10573204
P Mistry AJ Stewart W Dangerfield et al. (2001) ArticleTitleIn vitro and in vivo reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by a novel potent modulator XR9576 Cancer Res 61 749–758
D Toppmeyer AD Seidman M Pollak et al. (2002) ArticleTitleSafety and efficacy of the multidrug resistance inhibitor Incel (biricodar; VX-710) in combination with paclitaxel for advanced breast cancer refractory to paclitaxel Clin Cancer Res 8 670–678
LA Mickley JS Lee Z Weng et al. (1998) ArticleTitleGenetic polymorphism in MDR-1: A tool for examining allelic expression in normal cells, unselected and drug-selected cell lines and human tumors Blood 1 1749–1756
A Siddiqui R Kerb ME Weale et al. (2003) ArticleTitleAssociation of multidrug resistance in epilepsy with a polymorphism in the drug-transporter gene ABCB1 N Engl J Med 348 1442–1448 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJMoa021986 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXivVCgs7g%3D Occurrence Handle12686700
U Brinkmann I Roots M Eichelbaum (2001) ArticleTitlePharmacogenetics of the human drug-transporter gene MDR1: Impact of polymorphisms on phamacotherapy DDT 6 835–839
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elsinga, P.H., Hendrikse, N.H., Bart, J. et al. Positron Emission Tomography Studies on Binding of Central Nervous System Drugs and P-Glycoprotein Function in the Rodent Brain. Mol Imaging Biol 7, 37–44 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-005-0951-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-005-0951-x