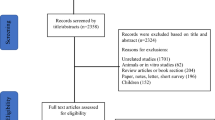
Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to accurately determine the prevalence of obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) in patients with epilepsy (PWE) and to evaluate the efficacy of seizure control after treating OSA.
Methods
Articles were identified through a search of both MEDLINE and Embase. The articles were collected and data were extracted independently by two authors. OSA was described using the following terms: Apnoea/hypopnoea index (AHI) and respiratory disturbance index (RDI). The variables were calculated using DerSimonian and Laird’s random-effects model and odds ratio (OR).
Results
The prevalence of mild-to-severe OSA in PWE was determined to be 33.4 % (95 % CI 20.8–46.1 %), and PWE are more susceptible to OSA as compared to healthy controls (OR 2.36; 95 % CI 1.33–4.18). Males were shown to be more susceptible to OSA than females (OR 3.00; 95 % CI 2.25–3.99). The results also indicated that the prevalence of OSA in patients with refractory epilepsy is not higher than the prevalence of OSA in PWE overall (17.5 vs 33.4 %). The prevalence of OSA was not found to be significantly different for different seizure types or in the number of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Patients that had been treated with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) were shown to have better seizure control than those untreated (OR 5.26; 95 % CI 2.04–13.5).
Conclusions
The prevalence of OSA in PWE is higher than in the general population. Additionally, the results of our study suggest that CPAP treatment results in a reduction of seizures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ngugi AK, Kariuki SM, Bottomley C, Kleinschmidt I, Sander JW, Newton CR (2011) Incidence of epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 77:1005–1012
Shorvon S, Tomson T (2011) Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. Lancet 378:2028–2038
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S (1993) The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med 328:1230–1235
Malow BA, Levy K, Maturen K, Bowes R (2000) Obstructive sleep apnea is common in medically refractory epilepsy patients. Neurology 55:1002–1007
Malow BA, Fromes GA, Aldrich MS (1997) Usefulness of polysomnography in epilepsy patients. Neurology 48:1389–1394
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283:2008–2012
Rostom A, Dube C, Cranney A, Saloojee N, Sy R, Garritty C, et al. (2004) Rockville: AHRQ Publication. Evidence report/technology assessment (Summary):1–6.
Nigro CA, Dibur E, Aimaretti S, Gonzalez S, Rhodius E (2011) Comparison of the automatic analysis versus the manual scoring from ApneaLink device for the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Sleep & breathing = Schlaf & Atmung 15:679–686
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Manni R, Terzaghi M, Arbasino C, Sartori I, Galimberti CA, Tartara A (2003) Obstructive sleep apnea in a clinical series of adult epilepsy patients: frequency and features of the comorbidity. Epilepsia 44:836–840
Marzec M, Edwards J, Sagher O, Fromes G, Malow BA (2003) Effects of vagus nerve stimulation on sleep-related breathing in epilepsy patients. Epilepsia 44:930–935
Weatherwax KJ, Lin X, Marzec ML, Malow BA (2003) Obstructive sleep apnea in epilepsy patients: the sleep apnea scale of the sleep disorders questionnaire (SA-SDQ) is a useful screening instrument for obstructive sleep apnea in a disease-specific population. Sleep Med 4:517–521
Becker DA, Fennell EB, Carney PR (2004) Daytime behavior and sleep disturbance in childhood epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 5:708–715
Khurana DS, Reumann M, Hobdell EF, Neff S, Valencia I, Legido A, et al. (2007) Vagus nerve stimulation in children with refractory epilepsy: unusual complications and relationship to sleep-disordered breathing. Childs Nerv Syst 23:1309–1312
Kaleyias J, Cruz M, Goraya JS, Valencia I, Khurana DS, Legido A, et al. (2008) Spectrum of polysomnographic abnormalities in children with epilepsy. Pediatr Neurol 39:170–176
Abd El Kader AA, Shaheen HA, El Gohary AM, El-Fayoumy NM, Afifi LM (2010) Clinical relevance of obstructive sleep apnea in epilepsy. Egyptian Journal of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery 47:461–469
Foldvary-Schaefer N, Andrews ND, Pornsriniyom D, Moul DE, Sun Z, Bena J (2012) Sleep apnea and epilepsy: who’s at risk? Epilepsy Behav 25:363–367
Li P, Ghadersohi S, Jafari B, Teter B, Sazgar M (2012) Characteristics of refractory vs. medically controlled epilepsy patients with obstructive sleep apnea and their response to CPAP treatment. Seizure 21:717–721
Zanzmera P, Shukla G, Gupta A, Singh H, Goyal V, Srivastava A, et al. (2012) Markedly disturbed sleep in medically refractory compared to controlled epilepsy—a clinical and polysomnography study. Seizure 21:487–490
Hashim SN, Abdullah B, Abdullah JM, Tharakan J, Musa Y (2013) Quality of life of epilepsy patients with obstructive sleep apnea in Malaysia. Biomedical Research (India) 24:230–234
Jain SV, Simakajornboon N, Glauser TA (2013) Provider practices impact adequate diagnosis of sleep disorders in children with epilepsy. J Child Neurol 28:589–595
Phillips MC, Costello CA, White EJ, Smit M, Carino J, Strawhorn A, et al. (2013) Routine polysomnography in an epilepsy monitoring unit. Epilepsy Res 105:401–404
Economou NT, Dikeos D, Andrews N, Foldvary-Schaefer N (2014) Use of the sleep apnea scale of the sleep disorders questionnaire (SA-SDQ) in adults with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 31:123–126
Ng MC, Bianchi MT (2014) Sleep misperception in persons with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 36:9–11
Pornsriniyom D, Kim H, Bena J, Andrews ND, Moul D, Foldvary-Schaefer N (2014) Effect of positive airway pressure therapy on seizure control in patients with epilepsy and obstructive sleep apnea. Epilepsy Behav 37:270–275
Vendrame M, Jackson S, Syed S, Kothare SV, Auerbach SH (2014) Central sleep apnea and complex sleep apnea in patients with epilepsy. Sleep and Breathing 18:119–124
Zambrelli E, Saibene AM, Furia F, Chiesa V, Vignoli A, Pipolo C, et al. (2016) Laryngeal motility alteration: a missing link between sleep apnea and vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy. Epilepsia 57:e24–ee7
Khatami R, Zutter D, Siegel A, Mathis J, Donati F, Bassetti CL (2006) Sleep-wake habits and disorders in a series of 100 adult epilepsy patients—a prospective study. Seizure 15:299–306
Pizzatto R, Lin K, Watanabe N, Campiolo G, Bicalho MAH, Guarnieri R, et al. (2013) Excessive sleepiness and sleep patterns in patients with epilepsy: a case-control study. Epilepsy Behav 29:63–66
Yazdi Z, Sadeghniiat-Haghighi K, Naimian S, Zohal MA, Ghaniri M (2013) Prevalence of sleep disorders and their effects on sleep quality in epileptic patients. Basic and Clinical Neuroscience 4:36–41
Ismayilova V, Demir AU, Tezer FI (2015) Subjective sleep disturbance in epilepsy patients at an outpatient clinic: a questionnaire-based study on prevalence. Epilepsy Res 115:119–125
Malow BA, Foldvary-Schaefer N, Vaughn BV, Selwa LM, Chervin RD, Weatherwax KJ, et al. (2008) Treating obstructive sleep apnea in adults with epilepsy: a randomized pilot trial. Neurology 71:572–577
Vendrame M, Auerbach S, Loddenkemper T, Kothare S, Montouris G (2011) Effect of continuous positive airway pressure treatment on seizure control in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and epilepsy. Epilepsia 52:e168–ee71
Arnardottir ES, Bjornsdottir E, Olafsdottir KA, Benediktsdottir B, Gislason T (2016) Obstructive sleep apnoea in the general population: highly prevalent but minimal symptoms. The European respiratory journal 47:194–202
Jelic S, Padeletti M, Kawut SM, Higgins C, Canfield SM, Onat D, et al. (2008) Inflammation, oxidative stress, and repair capacity of the vascular endothelium in obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 117:2270–2278
Rowley S, Patel M (2013) Mitochondrial involvement and oxidative stress in temporal lobe epilepsy. Free Radic Biol Med 62:121–131
Li G, Bauer S, Nowak M, Norwood B, Tackenberg B, Rosenow F, et al. (2011) Cytokines and epilepsy. Seizure 20:249–256
Dancey DR, Hanly PJ, Christine S, Bert L, John S, Victor H (2003) Gender differences in sleep apnea: the role of neck circumference. Chest 123:1544–1550
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This is a meta-analysis; thus, the requirement for an ethics and consent statement is not needed.
Funding
This study is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 3970046) and the Science & Technology Department of Sichuan Province, China (grant no. 2013SZ0003). The sponsor had no role in the design or conduct of this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Informed consent
This is a meta-analysis which does not involve human subjects; thus, the requirement for informed consent is not needed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Z., Si, Q. & Xiaoyi, Z. Obstructive sleep apnoea in patients with epilepsy: a meta-analysis. Sleep Breath 21, 263–270 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-016-1391-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-016-1391-3