Abstract
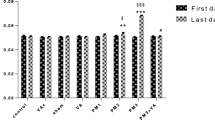
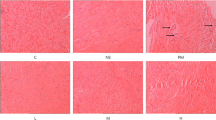
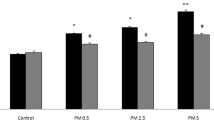
Myocardial infarction is the acute condition of myocardial necrosis that occurs as a result of imbalance between coronary blood supply and myocardial demand. Air pollution increases the risk of death from cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of particulate matter (PM) on oxidative stress, the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) messenger RNA (mRNA) level induced by ischemia–reperfusion injury, and the protective effects of vanillic acid (VA) in the isolated rat heart. Male Wistar rats were randomly divided into eight groups (n = 10), namely control, VAc, sham, VA, PMa (0.5 mg/kg), PMb (2.5 mg/kg), PMc (5 mg/kg), and PMc + VA groups. Particles with an aerodynamic diameter <10 μm (PM10) was instilled into the trachea through a fine intubation tube. Two days following the PM10 instillation, the animal’s hearts were isolated and transferred to a Langendorff apparatus. The hearts were subjected to 30 min of global ischemia followed by 60 min of reperfusion. The activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase (CAT), xanthine oxidase (XOX), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) were measured using special kits. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to determine levels of iNOS and eNOS mRNA. An increase in left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), S–T elevation, and oxidative stress in PM10 groups was observed. Ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) induction showed a significant augment in the expression of iNOS mRNA level and a significant decrease in the expression eNOS mRNA level. This effect was more pronounced in the PM groups than in the control and sham groups. Vanillic acid caused a significant decrease in LVEDP, S–T elevation, and also a significant difference in eNOS mRNA expression level, antioxidant enzymes, iNOS mRNA expression level, and oxidative stress occurred on myocardial dysfunction after I/R in isolated rat hearts. This study showed that PM10 exposure had devastating effects on the myocardial heart, oxidative stress, and eNOS and iNOS mRNA expression levels. Vanillic acid was able to improve these parameters. Vanillic acid as a potent antioxidant could also provide protection against particulate matter-induced toxicity.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MI:
-
Myocardial infarction
- I/R:
-
Ischemia–reperfusion
- PM:
-
Particulate matter
- PM10 :
-
Particles with an aerodynamic diameter <10 μm
- VA:
-
Vanillic acid
- LVDEP:
-
Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- XOX:
-
Xanthine oxidase
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- IHD:
-
Ischemic heart diseases
References
Aronow WS (2006) Epidemiology, pathophysiology, prognosis, and treatment of systolic and diastolic heart failure. Cardiol Rev 14:108–124
Atochin DN, Huang PL (2010) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase transgenic models of endothelial dysfunction. Pflugers Arch 460:965–74. doi:10.1007/s00424-010-0867-4
Bagate K, Meiring JJ, Gerlofs-Nijland ME, Cassee FR, Wiegand H, Osornio-Vargas A, Borm PJA (2006) “Ambient particulate matter affects cardiac recovery in a Langendorff ischemia model”. Inhal Toxicol 18(9):633–43. doi:10.1080/08958370600742706
Bai Y, Suzuki AK, Sagai M (2001) The cytotoxic effects of diesel exhaust particles on human pulmonary artery endothelial cells in vitro: role of active oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 30:555–562. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00499-8
Brook RD, Rajagopalan S, Pope CA III, Brook JR, Bhatnagar A, Diez-Roux AV, Holguin F, Hong Y, Luepker RV, Mittleman MA, Peters A, Siscovick D, Smith SC Jr, Whitsel L, Kaufman JD (2010) Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: an update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 121:2331–2378. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e3181dbece1
Chun TY, Bloem LJ, Pratt JH (2003) Aldosterone inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Endocrinology 144:1712–7. doi:10.1210/en.2002-220956
Comini L, Bachetti T, Agnoletti L, Gaia G, Curello S, Milanesi B et al (1999) Induction of functional inducible nitric oxide synthase in monocytes of patients with congestive heart failure. Link with tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Eur Heart J 20:1503–1513. doi:10.1053/euhj.1999.1580
Di Napoli P, Chierchia S, Taccardi AA, Grilli A, Felaco M, De Caterina R et al (2007) Trimetazidine improves post-ischemic recovery by preserving endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression in isolated working rat hearts. Nitric Oxide 16:228–36. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2006.09.001
Dianat M, Esmaeiliziadeh M, Badavi M, Samarbafzadeh A, Naghizadeh B (2014a) Cardiac protective effects of crocin on hemodynamic parameters and infarct size in compare vitamin E after ischemia reperfusion in isolated rat heart. Planta Med 80:393–398. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1360383
Dianat M, Hamzavi GH, Badavi M, Samarbafzadeh A (2014b) Effects of losartan and vanillic acid co-administration on ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in isolated rat heart. Iran Red Crescent Med J 16(7):e16664. doi:10.5812/ircmj.16664
Esmaeilizadeh M, Dianat M, Badavi M, Samarbaf-zadeh A, Naghizadeh B (2015) Effect of crocin on nitric oxide synthase expression in post-ischemic isolated rat heart. AJP 5(5):420–6
Garcıa-Villalon AL, Monge L, Fernandez N, Salcedo A (2009) Coronary response to diadenosinepentaphosphate after ischaemia– reperfusion in the isolated rat heart. Cardiovas Res 81:336–343
Gauthaman K, Banerjee SK, Dinda AK, Ghosh CC, Maulik SK (2005) Terminalia arjuna (Roxb.) protects rabbit heart against ischemic-reperfusion injury: role of antioxidant enzymes and heat shock protein. J Ethnopharmacol 96:403
Goldspink DF, Burniston JG, Ellison GM, Clark WA, Tan LB (2004) Catecholamine induced apoptosis and necrosis in cardiac and skeletal myocytes of the rat in vivo: the same or separate death pathways. ExpPhysiol 89:407–416. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2004.027482
Golomb E, Matza D, Cummings CA, Schwalb H, Kodavanti UP, Schneider A, Houminer E, Korach A, Nyska A, Shapira OM (2012) “Myocardial mitochondrial injury induced by pulmonary exposure to particulate matter in rats”. Toxicol Patho 40:779–88. doi:10.1177/0192623312441409
Goudarzi GH, Zallaghi E, Neissi A, AhmadiAnkali K, Sakid A, Babaeia A, Alavi N, Mohammadi M (2013) Cardiopulmonary mortalities and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease attributed to ozone air pollution. Arch HygSci 2(2):62–72, http://jhygiene.muq.ac.ir
Goudarzi GH, Shirmardi M, Khodarahmi F, Hashemi-Shahraki A, Alavi N, Ahmadi Ankali K, Babaei A, Soleimani Z, Bagherian Marzouni M (2014) Particulate matter and bacteria characteristics of the Middle East dust (MED) storms over Ahvaz, Iran. Aerobiologia 30:345–356. doi:10.1007/s10453-014-9333-7
Goudie AS (2014) Desert dust and human health disorders. Environ Int 63:101–13
Gurgueira SA, Lawrence J, Coull B, Murthy KGG, González-Flecha B (2002) Rapid increases in the steady-state concentration of reactive oxygen species in the lungs and heart after particulate air pollution inhalation. Environ Health Perspect 110(8):749–765
Heidari-Farsani M, Shirmardi M, Goudarzi GH, Alavi-Bakhtiarivand N, Ahmadi-Ankali K, Zallaghi E, Naeimabadi A, Hashemzadeh B (2014) The evaluation of heavy metals concentration related to PM10 in ambient air of Ahvaz City, Iran. J Adv Environ Health Res 1(2):120–8, http://jaehr.muk.ac.ir
Hoffmann C, Funk R, Wieland R, Li Y, Sommer M (2008) “Effects of grazing and topography on dust flux and deposition in the Xilingele grassland, Inner Mongolia”. J Arid Environ 72(5):792–807. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2007.09.004
Ikeda M, Watarai K, Suzuki M, Ito T, Yamasaki H, Sagai M, Tomita T (1998) Mechanism of pathophysiological effects of diesel exhaust particles on endothelial cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmaco 6(2):117–123. doi:10.1016/S1382-6689(98)00027-1
Jomova K, Valko M (2011) Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 283(2–3):65–87. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2011.03.001
Kodavanti UP, Schladweiler MC, Gilmour PS, Wallenborn JG, Mandavilli BS, Ledbetter AD et al (2008) The role of particulate matter-associated zinc in cardiac injury in rats. Environ Health 116(1):13–20
Kuhlencordt PJ, Gyurko R, Han F, Scherrer CM, Aretz TH et al (2001) Accelerated atherosclerosis aortic aneurysm formation, and ischemic heart disease in apolipoprotein E/endothelial nitric oxide synthase double knockout mice. Circulation 104:448–454. doi:10.1161/hc2901.091399
Manzano-Leon N, Quintana R, Sanchez B, Serrano J, Vega E, Vazquez-Lopez I et al (2013) “Variation in the composition and in vitro proinflammatory effect of urban particulate matter from different sites”. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 27(1):87–97. doi:10.1002/jbt.21471
Mard SA, Neisi N, Hassanpour M, Maleki M, Solgi G, Darbor M (2012) Gastroprotective effect of NaHS against mucosal lesions induced by ischemia–reperfusion injury in rat. Dig Dis Sci 57:1496–1503. doi:10.1007/s10620-012-2051-5
Mard SA, Maleki M, Askari H, Gharib Naseri MK (2014) Inhibition of histamine-stimulated gastric acid secretion by hydrogen sulfide in male rats. Adaptive Medicine 6(4):157–160. doi:10.4247/AM.2014.ABE089
Mohd TN, Poh SC, Suratman S, Ariffin MM, Shazali NA, Yunus K (2009) Determination of trace metals in airborne particulate matter of Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83(2):199–203. doi:10.1007/s00128-009-9751-3
Poljsak B, Suput D, Milisav I (2013) Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: when to use the synthetic antioxidants. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:956792. doi:10.1155/2013/956792
Pope CA III, Burnett RT, Thurston GD, Thun MJ, Calle EE, Krewski D et al (2004) Cardiovascular mortality and long-term exposure to particulate air pollution: epidemiological evidence of general pathophysiological pathways of disease. Circulation 109:71–7. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000108927.80044.7F
Raghuvanshi R, Kaul A, Bhakuni P, Mishra A, Misra MK (2007) Xanthine oxidase as a marker of myocardial infarction. Indian J Clin Biochem 22(2):90–92
Scherrer-Crosbie M, Ullrich R, Bloch KD, Nakajima H, Nasseri B, Aretz HT et al (2001) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase limits left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice. Circulation 104(11):1286–91. doi:10.1161/hc3601.094298
Schwartz J, Dockery DW, Neas LM (1996) Is daily mortality associated specifically with fine particles? J Air Waste Manag Assoc 46:927–39. doi:10.1080/10473289.10467528
Shahsavani A, Naddafi K, Jaafarzadeh HN, Mesdaghinia A, Yunesian M, Nabizadeh R et al (2012a) Characterization of ionic composition of TSP and PM10 during the Middle Eastern dust (MED) storms in Ahvaz, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 184(11):6683–92. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2451-6
Shahsavani A, Naddafi K, JafarzadeHaghighifard N, Mesdaghinia A, Yunesian M, Nabizadeh R et al (2012b) The evaluation of PM10, PM2.5, and PM1 concentrations during the Middle Eastern dust (MED) events in Ahvaz, Iran, from April through September 2010. J Arid Environ 77:72–83. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2011.09.007
Shaul PW (2002) Regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase location. Annu Rev Physiol 64:749–774. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.64.081501.155952
Soleimani Z, Goudarzi G, Alavi N, Babaei AA, Dehdari Rad H, Mohammadi MJ (2013) Determination of culturable indoor airborne fungi during normal and dust event days in Ahvaz, Iran. Aerobiologia 29:279–290. doi:10.1007/s10453-012-9279-6
Soleimani Z, Parhizgari N, Dehdari Rad H, Akhoond MR, Kermani M, Bagherian M, Arzouni M et al (2015) Normal and dusty days comparison of culturable indoor airborne bacteria in Ahvaz, Iran. Aerobiologia 31(2):127–41. doi:10.1007/s10453-014-9352-4
Sørensen M, Schins RPF, Hertel O, Loft S (2005) Transition metals in personal samples of PM2.5 and oxidative stress in human volunteers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14(5):1340–3
Tai A, Sawano T, Ito H (2012) Antioxidative properties of vanillic acid esters in multiple antioxidant assays. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76(2):314–18. doi:10.1271/bbb.110700
Valavanidis A, Vlahogianni T, Assenakis MD, Scoullos M (2006) Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64(2):178–189. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.03.013
Wilhelm Filho D, Júnior SA, Possamai FP et al (2010) Antioxidant therapy attenuates oxidative stress in the blood of subjects exposed to occupational airborne contamination from coal mining extraction and incineration of hospital residues. Ecotoxicology 19(7):1193–1200. doi:10.1007/s10646-010-0503-2
Zhang W, Zhuang G, Guo J, Xu D, Wang W, Baumgardner D et al (2010) Sources of aerosol as determined from elemental composition and size distributions in Beijing. Atmos Res 95(2–3):197–209. doi:10.1016/j.atmosres.2009.09.017
Acknowledgments
The source of data used in this paper was the Ph.D. thesis of Mrs. Esmat Radmanesh, a Ph.D. student of the Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran. The authors gratefully acknowledge the help and financial support (grant no. ajums APRC-9316) of the Physiology Research Center of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dianat, M., Radmanesh, E., Badavi, M. et al. Disturbance effects of PM10 on iNOS and eNOS mRNA expression levels and antioxidant activity induced by ischemia–reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart: protective role of vanillic acid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 5154–5165 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5759-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5759-x